Learning Outcomes
- Calculate formula masses for covalent and ionic compounds
- Define the amount unit mole and the related quantity Avogadro’s number
- Explain the relation between mass, moles, and numbers of atoms or molecules, and perform calculations deriving these quantities from one another
We can argue that modern chemical science began when scientists started exploring the quantitative as well as the qualitative aspects of chemistry. For example, Dalton’s atomic theory was an attempt to explain the results of measurements that allowed him to calculate the relative masses of elements combined in various compounds. Understanding the relationship between the masses of atoms and the chemical formulas of compounds allows us to quantitatively describe the composition of substances.
Formula Mass
Earlier, we described the development of the atomic mass unit, the concept of average atomic masses, and the use of chemical formulas to represent the elemental makeup of substances. These ideas can be extended to calculate the formula mass of a substance by summing the average atomic masses of all the atoms represented in the substance’s formula.
Formula Mass for Covalent Substances
For covalent substances, the formula represents the numbers and types of atoms composing a single molecule of the substance; therefore, the formula mass may be correctly referred to as a molecular mass. Consider chloroform (CHCl3), a covalent compound once used as a surgical anesthetic and now primarily used in the production of the “anti-stick” polymer, Teflon. The molecular formula of chloroform indicates that a single molecule contains one carbon atom, one hydrogen atom, and three chlorine atoms. The average molecular mass of a chloroform molecule is therefore equal to the sum of the average atomic masses of these atoms. Figure 1 outlines the calculations used to derive the molecular mass of chloroform, which is 119.37 amu.
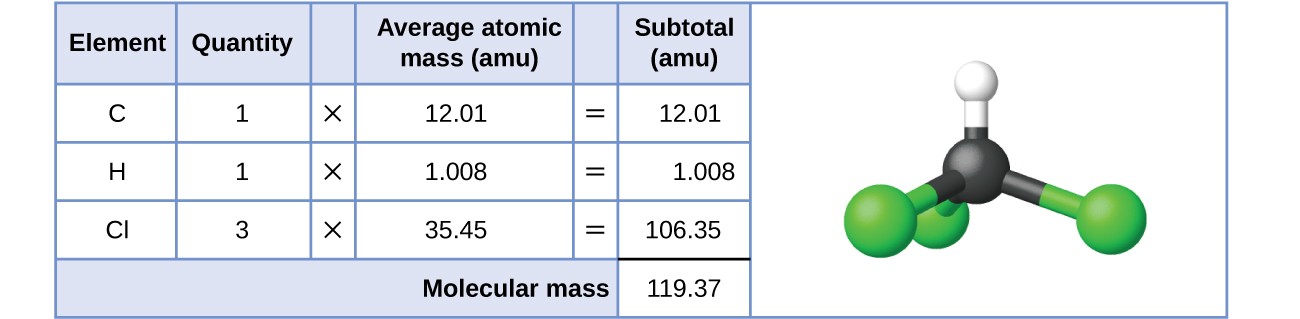
Figure 1. The average mass of a chloroform molecule, CHCl3, is 119.37 amu, which is the sum of the average atomic masses of each of its constituent atoms. The model shows the molecular structure of chloroform.
Likewise, the molecular mass of an aspirin molecule, C9H8O4, is the sum of the atomic masses of nine carbon atoms, eight hydrogen atoms, and four oxygen atoms, which amounts to 180.15 amu (Figure 2).
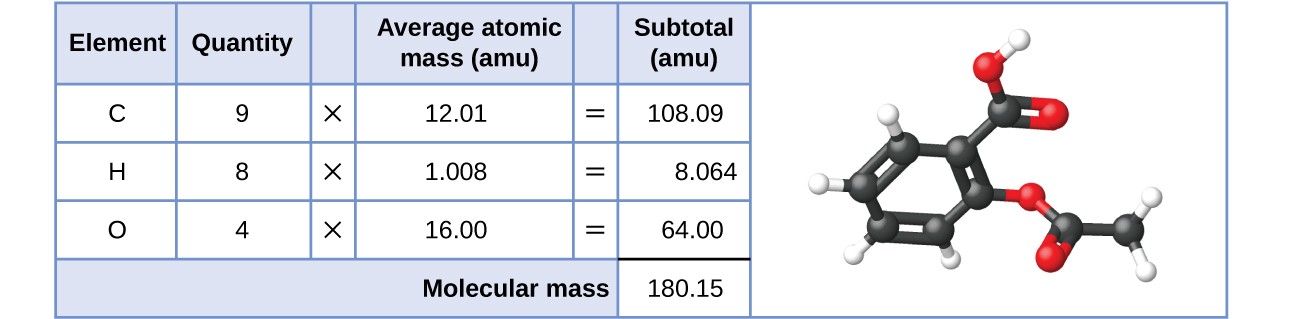
Figure 2. The average mass of an aspirin molecule is 180.15 amu. The model shows the molecular structure of aspirin, C9H8O4.
Example 1: Computing Molecular Mass for a Covalent Compound
Ibuprofen, C13H18O2, is a covalent compound and the active ingredient in several popular nonprescription pain medications, such as Advil and Motrin. What is the molecular mass (amu) for this compound?
Check Your Learning
Acetaminophen, C8H9NO2, is a covalent compound and the active ingredient in several popular nonprescription pain medications, such as Tylenol. What is the molecular mass (amu) for this compound?
Formula Mass for Ionic Compounds
Ionic compounds are composed of discrete cations and anions combined in ratios to yield electrically neutral bulk matter. The formula mass for an ionic compound is calculated in the same way as the formula mass for covalent compounds: by summing the average atomic masses of all the atoms in the compound’s formula. Keep in mind, however, that the formula for an ionic compound does not represent the composition of a discrete molecule, so it may not correctly be referred to as the “molecular mass.”
As an example, consider sodium chloride, NaCl, the chemical name for common table salt. Sodium chloride is an ionic compound composed of sodium cations, Na+, and chloride anions, Cl–, combined in a 1:1 ratio. The formula mass for this compound is computed as 58.44 amu (see Figure 3).
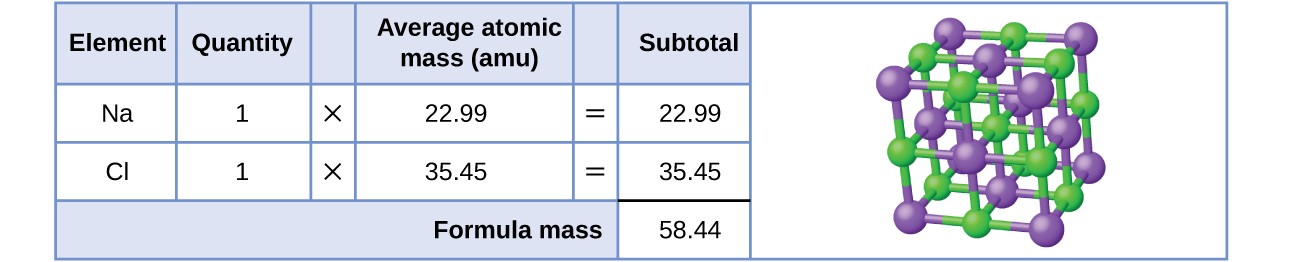
Figure 3. Table salt, NaCl, contains an array of sodium and chloride ions combined in a 1:1 ratio. Its formula mass is 58.44 amu.
Note that the average masses of neutral sodium and chlorine atoms were used in this computation, rather than the masses for sodium cations and chlorine anions. This approach is perfectly acceptable when computing the formula mass of an ionic compound. Even though a sodium cation has a slightly smaller mass than a sodium atom (since it is missing an electron), this difference will be offset by the fact that a chloride anion is slightly more massive than a chloride atom (due to the extra electron). Moreover, the mass of an electron is negligibly small with respect to the mass of a typical atom. Even when calculating the mass of an isolated ion, the missing or additional electrons can generally be ignored, since their contribution to the overall mass is negligible, reflected only in the nonsignificant digits that will be lost when the computed mass is properly rounded. The few exceptions to this guideline are very light ions derived from elements with precisely known atomic masses.
Example 2: Computing Formula Mass for an Ionic Compound
Aluminum sulfate, Al2(SO4)3, is an ionic compound that is used in the manufacture of paper and in various water purification processes. What is the formula mass (amu) of this compound?
Check Your Learning
Calcium phosphate, Ca3(PO4)2, is an ionic compound and a common anti-caking agent added to food products. What is the formula mass (amu) of calcium phosphate?
The Mole
The identity of a substance is defined not only by the types of atoms or ions it contains, but by the quantity of each type of atom or ion. For example, water, H2O, and hydrogen peroxide, H2O2, are alike in that their respective molecules are composed of hydrogen and oxygen atoms. However, because a hydrogen peroxide molecule contains two oxygen atoms, as opposed to the water molecule, which has only one, the two substances exhibit very different properties. Today, we possess sophisticated instruments that allow the direct measurement of these defining microscopic traits; however, the same traits were originally derived from the measurement of macroscopic properties (the masses and volumes of bulk quantities of matter) using relatively simple tools (balances and volumetric glassware). This experimental approach required the introduction of a new unit for amount of substances, the mole, which remains indispensable in modern chemical science.
The mole is an amount unit similar to familiar units like pair, dozen, gross, etc. It provides a specific measure of the number of atoms or molecules in a bulk sample of matter. One Latin connotation for the word “mole” is “large mass” or “bulk,” which is consistent with its use as the name for this unit. The mole provides a link between an easily measured macroscopic property, bulk mass, and an extremely important fundamental property, number of atoms, molecules, and so forth. A mole of a substance is that amount in which there are [latex]6.02214179\times {10}^{23}[/latex] discrete entities (atoms or molecules). This larger number is a fundamental constant known as Avogadro’s number (NA) or the Avogadro constant in honor of Italian scientist Amedeo Avogadro. This constant is properly reported with an explicit unit of “per mole,” a conveniently rounded version being [latex]6.022\times {10}^{23}\text{/mol}[/latex].
Consistent with its definition as an amount unit, 1 mole of any element contains the same number of atoms as 1 mole of any other element. The masses of 1 mole of different elements, however, are different, since the masses of the individual atoms are drastically different. The molar mass of an element (or compound) is the mass in grams of 1 mole of that substance, a property expressed in units of grams per mole (g/mol) (see Figure 4).
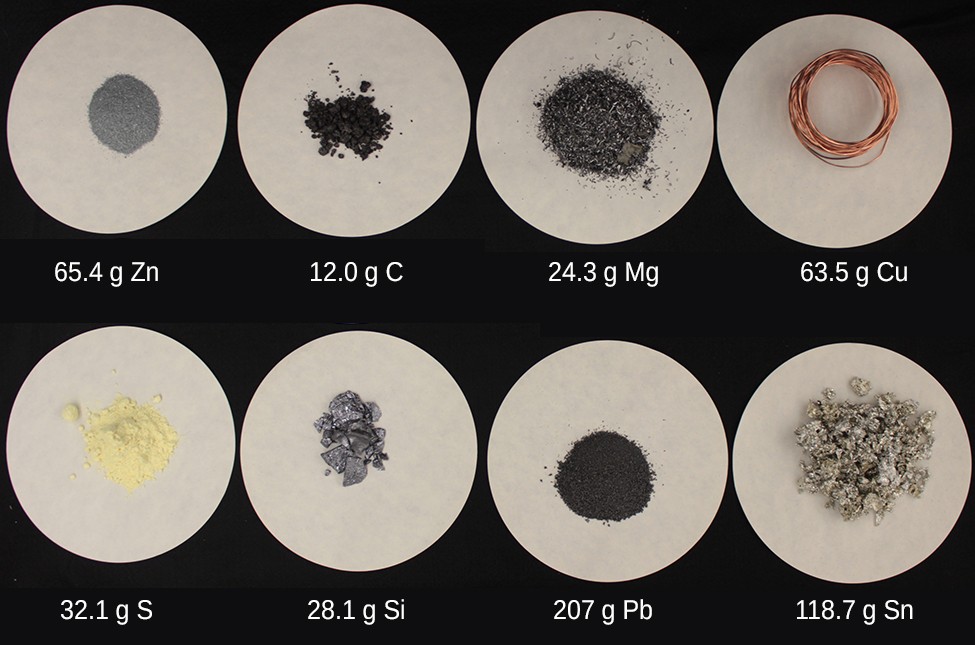

Figure 4. Each sample contains 6.022 × 1023 atoms—1.00 mol of atoms. From left to right (top row): 65.4g zinc, 12.0g carbon, 24.3g magnesium, and 63.5g copper. From left to right (bottom row): 32.1g sulfur, 28.1g silicon, 207g lead, and 118.7g tin. (credit: modification of work by Mark Ott)
The molar mass of any substance is numerically equivalent to its atomic or formula weight in amu. Per the amu definition, a single 12C atom weighs 12 amu (its atomic mass is 12 amu). A mole of 12C weighs 12 g (its molar mass is 12 g/mol). This relationship holds for all elements, since their atomic masses are measured relative to that of the amu-reference substance, 12C. Extending this principle, the molar mass of a compound in grams is likewise numerically equivalent to its formula mass in amu (Figure 5).
Figure 5. Each sample contains 6.02 × 1023 molecules or formula units—1.00 mol of the compound or element. Clock-wise from the upper left: 130.2g of C8H17OH (1-octanol, formula mass 130.2 amu), 454.9g of HgI2 (mercury(II) iodide, formula mass 459.9 amu), 32.0g of CH3OH (methanol, formula mass 32.0 amu) and 256.5g of S8 (sulfur, formula mass 256.6 amu). (credit: Sahar Atwa)
| Element | Average Atomic Mass (amu) | Molar Mass (g/mol) | Atoms/Mole |
|---|---|---|---|
| C | 12.01 | 12.01 | [latex]6.022\times {10}^{23}[/latex] |
| H | 1.008 | 1.008 | [latex]6.022\times {10}^{23}[/latex] |
| O | 16.00 | 16.00 | [latex]6.022\times {10}^{23}[/latex] |
| Na | 22.99 | 22.99 | [latex]6.022\times {10}^{23}[/latex] |
| Cl | 35.45 | 35.45 | [latex]6.022\times {10}^{23}[/latex] |
While atomic mass and molar mass are numerically equivalent, keep in mind that they are vastly different in terms of scale, as represented by the vast difference in the magnitudes of their respective units (amu versus g). To appreciate the enormity of the mole, consider a small drop of water weighing about 0.03 g (see Figure 6). Although this represents just a tiny fraction of 1 mole of water (~18 g), it contains more water molecules than can be clearly imagined. If the molecules were distributed equally among the roughly seven billion people on earth, each person would receive more than 100 billion molecules.

Figure 6. The number of molecules in a single droplet of water is roughly 100 billion times greater than the number of people on earth.
The mole is used in chemistry to represent [latex]6.022\times {10}^{23}[/latex] of something, but it can be difficult to conceptualize such a large number. Watch this video to learn more.
You can view the transcript for “How big is a mole? (Not the animal, the other one.) – Daniel Dulek” here (opens in new window).
The relationships between formula mass, the mole, and Avogadro’s number can be applied to compute various quantities that describe the composition of substances and compounds, as demonstrated in the next several example problems.
Example 3: Deriving Moles from Grams for an Element
According to nutritional guidelines from the US Department of Agriculture, the estimated average requirement for dietary potassium is 4.7 g. What is the estimated average requirement of potassium in moles?
Check Your Learning
Beryllium is a light metal used to fabricate transparent X-ray windows for medical imaging instruments. How many moles of Be are in a thin-foil window weighing 3.24 g?
Example 4: Deriving Grams from Moles for an Element
A liter of air contains [latex]9.2\times {10}^{-4}[/latex] mol argon. What is the mass of Ar in a liter of air?
Check Your Learning
What is the mass of 2.561 mol of gold?
Example 5: Deriving Number of Atoms from Mass for an Element
Copper is commonly used to fabricate electrical wire (Figure 7). How many copper atoms are in 5.00 g of copper wire?

Figure 7. Copper wire is composed of many, many atoms of Cu. (credit: Emilian Robert Vicol)
Check Your Learning
A prospector panning for gold in a river collects 15.00 g of pure gold. How many Au atoms are in this quantity of gold?
Example 6: Deriving Moles from Grams for a Compound
Our bodies synthesize protein from amino acids. One of these amino acids is glycine, which has the molecular formula C2H5O2N. How many moles of glycine molecules are contained in 28.35 g of glycine?
Check Your Learning
How many moles of sucrose, C12H22O11, are in a 25-g sample of sucrose?
Example 7: Deriving Grams from Moles for a Compound
Vitamin C is a covalent compound with the molecular formula C6H8O6. The recommended daily dietary allowance of vitamin C for children aged 4–8 years is [latex]1.42\times {10}^{-4}\text{mol.}[/latex] What is the mass of this allowance in grams?
Check Your Learning
What is the mass of 0.443 mol of hydrazine, N2H4?
Example 8: Deriving the Number of Atoms and Molecules from the Mass of a Compound
A packet of an artificial sweetener contains 40.0 mg of saccharin (C7H5NO3S), which has the structural formula:

Given that saccharin has a molar mass of 183.18 g/mol, how many saccharin molecules are in a 40.0-mg (0.0400-g) sample of saccharin? How many carbon atoms are in the same sample?
Check Your Learning
How many C4H10 molecules are contained in 9.213 g of this compound? How many hydrogen atoms?
Connection: Counting Neurotransmitter Molecules in the Brain
The brain is the control center of the central nervous system (Figure 8). It sends and receives signals to and from muscles and other internal organs to monitor and control their functions; it processes stimuli detected by sensory organs to guide interactions with the external world; and it houses the complex physiological processes that give rise to our intellect and emotions. The broad field of neuroscience spans all aspects of the structure and function of the central nervous system, including research on the anatomy and physiology of the brain. Great progress has been made in brain research over the past few decades, and the BRAIN Initiative, a federal initiative announced in 2013, aims to accelerate and capitalize on these advances through the concerted efforts of various industrial, academic, and government agencies (more details available at the NIH website).

Figure 8. (a) A typical human brain weighs about 1.5 kg and occupies a volume of roughly 1.1 L. (b) Information is transmitted in brain tissue and throughout the central nervous system by specialized cells called neurons (micrograph shows cells at 1600× magnification).
Specialized cells called neurons transmit information between different parts of the central nervous system by way of electrical and chemical signals. Chemical signaling occurs at the interface between different neurons when one of the cells releases molecules (called neurotransmitters) that diffuse across the small gap between the cells (called the synapse) and bind to the surface of the other cell. These neurotransmitter molecules are stored in small intracellular structures called vesicles that fuse to the cell wall and then break open to release their contents when the neuron is appropriately stimulated. This process is called exocytosis (see Figure 9). One neurotransmitter that has been very extensively studied is dopamine, C8H11NO2. Dopamine is involved in various neurological processes that impact a wide variety of human behaviors. Dysfunctions in the dopamine systems of the brain underlie serious neurological diseases such as Parkinson’s and schizophrenia.

Figure 9. (a) Chemical signals are transmitted from neurons to other cells by the release of neurotransmitter molecules into the small gaps (synapses) between the cells. (b) Dopamine, C8H11NO2, is a neurotransmitter involved in a number of neurological processes.
One important aspect of the complex processes related to dopamine signaling is the number of neurotransmitter molecules released during exocytosis. Since this number is a central factor in determining neurological response (and subsequent human thought and action), it is important to know how this number changes with certain controlled stimulations, such as the administration of drugs. It is also important to understand the mechanism responsible for any changes in the number of neurotransmitter molecules released—for example, some dysfunction in exocytosis, a change in the number of vesicles in the neuron, or a change in the number of neurotransmitter molecules in each vesicle.
Significant progress has been made recently in directly measuring the number of dopamine molecules stored in individual vesicles and the amount actually released when the vesicle undergoes exocytosis. Using miniaturized probes that can selectively detect dopamine molecules in very small amounts, scientists have determined that the vesicles of a certain type of mouse brain neuron contain an average of 30,000 dopamine molecules per vesicle (about [latex]5\times {10}^{-20}[/latex] mol or 50 zmol). Analysis of these neurons from mice subjected to various drug therapies shows significant changes in the average number of dopamine molecules contained in individual vesicles, increasing or decreasing by up to three-fold, depending on the specific drug used. These studies also indicate that not all of the dopamine in a given vesicle is released during exocytosis, suggesting that it may be possible to regulate the fraction released using pharmaceutical therapies.[1]
Key Concepts and Summary
The formula mass of a substance is the sum of the average atomic masses of each atom represented in the chemical formula and is expressed in atomic mass units. The formula mass of a covalent compound is also called the molecular mass. A convenient amount unit for expressing very large numbers of atoms or molecules is the mole. Experimental measurements have determined the number of entities composing 1 mole of substance to be [latex]6.022\times {10}^{23}[/latex], a quantity called Avogadro’s number. The mass in grams of 1 mole of substance is its molar mass. Due to the use of the same reference substance in defining the atomic mass unit and the mole, the formula mass (amu) and molar mass (g/mol) for any substance are numerically equivalent (for example, one H2O molecule weighs approximately18 amu and 1 mole of H2O molecules weighs approximately 18 g).
Try It
- What is the total mass (amu) of carbon in each of the following molecules?
- CH4
- CHCl3
- C12H10O6
- CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
- What is the total mass of hydrogen in each of the molecules?
- CH4
- CHCl3
- C12H10O6
- CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3
- Calculate the molecular or formula mass of each of the following:
- P4
- H2O
- Ca(NO3)2
- CH3CO2H (acetic acid)
- C12H22O11 (sucrose, cane sugar).
- Determine the molecular mass of the following compounds:
- Determine the molecular mass of the following compounds:
- Which molecule has a molecular mass of 28.05 amu?
- Write a sentence that describes how to determine the number of moles of a compound in a known mass of the compound if we know its molecular formula.
- Compare 1 mole of H2, 1 mole of O2, and 1 mole of F2.
- Which has the largest number of molecules? Explain why.
- Which has the greatest mass? Explain why.
- Which contains the greatest mass of oxygen: 0.75 mol of ethanol (C2H5OH), 0.60 mol of formic acid (HCO2H), or 1.0 mol of water (H2O)? Explain why.
- Which contains the greatest number of moles of oxygen atoms: 1 mol of ethanol (C2H5OH), 1 mol of formic acid (HCO2H), or 1 mol of water (H2O)? Explain why.
- How are the molecular mass and the molar mass of a compound similar and how are they different?
- Calculate the molar mass of each of the following compounds:
- hydrogen fluoride, HF
- ammonia, NH3
- nitric acid, HNO3
- silver sulfate, Ag2SO4
- boric acid, B(OH)3
- Calculate the molar mass of each of the following:
- S8
- C5H12
- Sc2(SO4)3
- CH3COCH3 (acetone)
- C6H12O6 (glucose)
- Calculate the empirical or molecular formula mass and the molar mass of each of the following minerals:
- limestone, CaCO3
- halite, NaCl
- beryl, Be3Al2Si6O18
- malachite, Cu2(OH)2CO3
- turquoise, CuAl6(PO4)4(OH)8(H2O)4
- Calculate the molar mass of each of the following:
- the anesthetic halothane, C2HBrClF3
- the herbicide paraquat, C12H14N2Cl2
- caffeine, C8H10N4O2
- urea, CO(NH2)2
- a typical soap, C17H35CO2Na
- Determine the number of moles of compound and the number of moles of each type of atom in each of the following:
- 25.0 g of propylene, C3H6
- [latex]3.06\times {10}^{-3}\text{g}[/latex] of the amino acid glycine, C2H5NO2
- 25 lb of the herbicide Treflan, C13H16N2O4F (1 lb = 454 g)
- 0.125 kg of the insecticide Paris Green, Cu4(AsO3)2(CH3CO2)2
- 325 mg of aspirin, C6H4(CO2H)(CO2CH3)
- Determine the mass of each of the following:
- 0.0146 mol KOH
- 10.2 mol ethane, C2H6
- [latex]1.6\times {10}^{-3}\text{ mol }{\text{Na}}_{2}{\text{SO}}_{4}[/latex]
- [latex]6.854\times {10}^{3}\text{ mol glucose},{\text{C}}_{6}{\text{H}}_{12}{\text{O}}_{6}[/latex]
- 2.86 mol Co(NH3)6Cl3
- Determine the number of moles of the compound and determine the number of moles of each type of atom in each of the following:
- 2.12 g of potassium bromide, KBr
- 0.1488 g of phosphoric acid, H3PO4
- 23 kg of calcium carbonate, CaCO3
- 78.452 g of aluminum sulfate, Al2(SO4)3
- 0.1250 mg of caffeine, C8H10N4O2
- Determine the mass of each of the following:
- 2.345 mol LiCl
- 0.0872 mol acetylene, C2H2
- [latex]3.3\times {10}^{-2}\text{ mol }{\text{Na}}_{2}{\text{CO}}_{3}[/latex]
- [latex]1.23\times {10}^{3}\text{ mol fructose, }{\text{C}}_{6}{\text{H}}_{12}{\text{O}}_{6}[/latex]
- 0.5758 mol FeSO4(H2O)7
- The approximate minimum daily dietary requirement of the amino acid leucine, C6H13NO2, is 1.1 g. What is this requirement in moles?
- Determine the mass in grams of each of the following:
- 0.600 mol of oxygen atoms
- 0.600 mol of oxygen molecules, O2
- 0.600 mol of ozone molecules, O3
- A 55-kg woman has [latex]7.5\times {10}^{-3}\text{mol}[/latex] of hemoglobin (molar mass = 64,456 g/mol) in her blood. How many hemoglobin molecules is this? What is this quantity in grams?
- Determine the number of atoms and the mass of zirconium, silicon, and oxygen found in 0.3384 mol of zircon, ZrSiO4, a semiprecious stone.
- Determine which of the following contains the greatest mass of hydrogen: 1 mol of CH4, 0.6 mol of C6H6, or 0.4 mol of C3H8.
- Determine which of the following contains the greatest mass of aluminum: 122 g of AlPO4, 266 g of A12C16, or 225 g of A12S3.
- Diamond is one form of elemental carbon. An engagement ring contains a diamond weighing 1.25 carats (1 carat = 200 mg). How many atoms are present in the diamond?
- The Cullinan diamond was the largest natural diamond ever found (January 25, 1905). It weighed 3104 carats (1 carat = 200 mg). How many carbon atoms were present in the stone
- One 55-gram serving of a particular cereal supplies 270 mg of sodium, 11% of the recommended daily allowance. How many moles and atoms of sodium are in the recommended daily allowance?
- A certain nut crunch cereal contains 11.0 grams of sugar (sucrose, C12H22O11) per serving size of 60.0 grams. How many servings of this cereal must be eaten to consume 0.0278 moles of sugar?
- A tube of toothpaste contains 0.76 g of sodium monofluorophosphate (Na2PO3F) in 100 mL
- What mass of fluorine atoms in mg was present?
- How many fluorine atoms were present?
- Which of the following represents the least number of molecules?
- 20.0 g of H2O (18.02 g/mol)
- 77.0 g of CH4 (16.06 g/mol)
- 68.0 g of CaH2 (42.09 g/mol)
- 100.0 g of N2O (44.02 g/mol)
- 84.0 g of HF (20.01 g/mol)
Glossary
Avogadro’s number (NA): experimentally determined value of the number of entities comprising 1 mole of substance, equal to [latex]6.022\times {10}^{23}{\text{mol}}^{-1}[/latex]
formula mass: sum of the average masses for all atoms represented in a chemical formula; for covalent compounds, this is also the molecular mass
molar mass: mass in grams of 1 mole of a substance
mole: amount of substance containing the same number of atoms, molecules, ions, or other entities as the number of atoms in exactly 12 grams of 12C
Candela Citations
- Chemistry 2e. Provided by: OpenStax. Located at: https://openstax.org/. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/chemistry-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Water drop on a leaf. Authored by: tanakawho. Located at: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Water_drop_on_a_leaf.jpg. License: CC BY: Attribution
- How big is a mole? (Not the animal, the other one.) - Daniel Dulek. Authored by: TED-Ed. Located at: https://youtu.be/TEl4jeETVmg. License: Other. License Terms: Standard YouTube License
- Omiatek, Donna M., Amanda J. Bressler, Ann-Sofie Cans, Anne M. Andrews, Michael L. Heien, and Andrew G. Ewing. “The Real Catecholamine Content of Secretory Vesicles in the CNS Revealed by Electrochemical Cytometry.” Scientific Report 3 (2013): 1447, accessed January 14, 2015, doi:10.1038/srep01447. ↵



















