Learning Outcomes
- Evaluate a composition of functions using a table.
- Evaluate a composition of functions using an equation.
Once we compose a new function from two existing functions, we need to be able to evaluate it for any input in its domain. We will do this with specific numerical inputs for functions expressed as tables, graphs, and formulas and with variables as inputs to functions expressed as formulas. In each case we evaluate the inner function using the starting input and then use the inner function’s output as the input for the outer function.
Evaluating Composite Functions Using Tables
When working with functions given as tables, we read input and output values from the table entries and always work from the inside to the outside. We evaluate the inside function first and then use the output of the inside function as the input to the outside function.
Example: Using a Table to Evaluate a Composite Function
Using the table below, evaluate [latex]f\left(g\left(3\right)\right)[/latex] and [latex]g\left(f\left(3\right)\right)[/latex].
| [latex]x[/latex] | [latex]f\left(x\right)[/latex] | [latex]g\left(x\right)[/latex] |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | 3 |
| 2 | 8 | 5 |
| 3 | 3 | 2 |
| 4 | 1 | 7 |
Try It
Using the table below, evaluate [latex]f\left(g\left(1\right)\right)[/latex] and [latex]g\left(f\left(4\right)\right)[/latex].
| [latex]x[/latex] | [latex]f\left(x\right)[/latex] | [latex]g\left(x\right)[/latex] |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 6 | 3 |
| 2 | 8 | 5 |
| 3 | 3 | 2 |
| 4 | 1 | 7 |
Evaluating Composite Functions Using Graphs
When we are given individual functions as graphs, the procedure for evaluating composite functions is similar to the process we use for evaluating tables. We read the input and output values, but this time, from the [latex]x\text{-}[/latex] and [latex]y\text{-}[/latex] axes of the graphs.
How To: Given a composite function and graphs of its individual functions, evaluate it using the information provided by the graphs.
- Locate the given input to the inner function on the [latex]x\text{-}[/latex] axis of its graph.
- Read off the output of the inner function from the [latex]y\text{-}[/latex] axis of its graph.
- Locate the inner function output on the [latex]x\text{-}[/latex] axis of the graph of the outer function.
- Read the output of the outer function from the [latex]y\text{-}[/latex] axis of its graph. This is the output of the composite function.
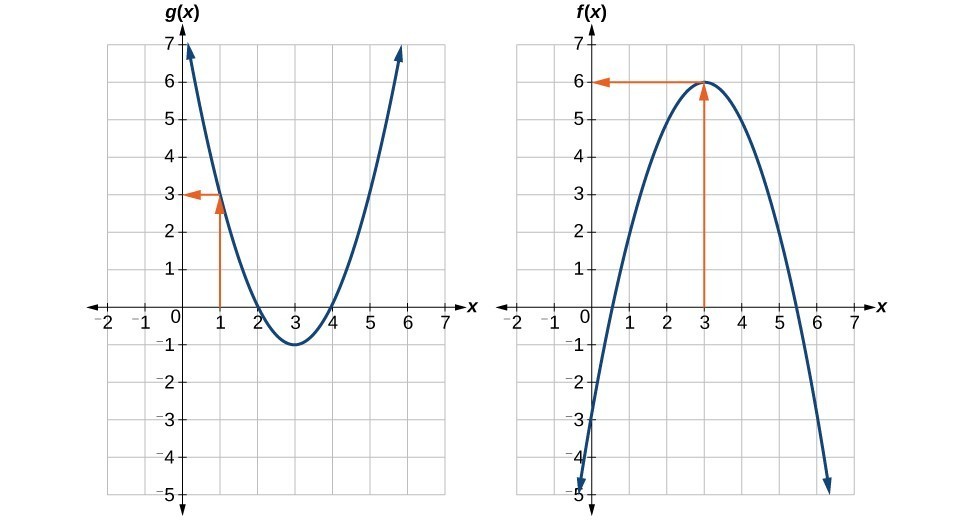
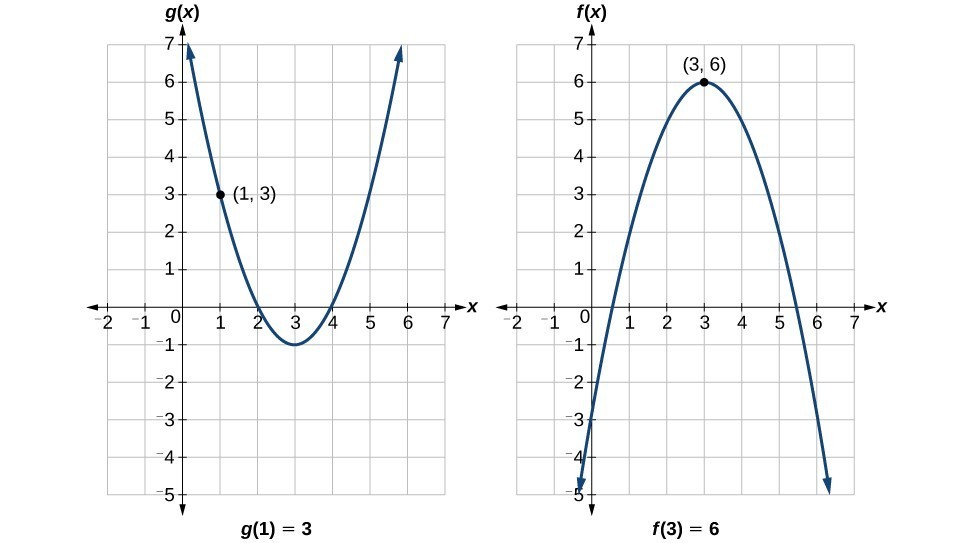
Example: Using a Graph to Evaluate a Composite Function
Using the graphs below, evaluate [latex]f\left(g\left(1\right)\right)[/latex].
Try It
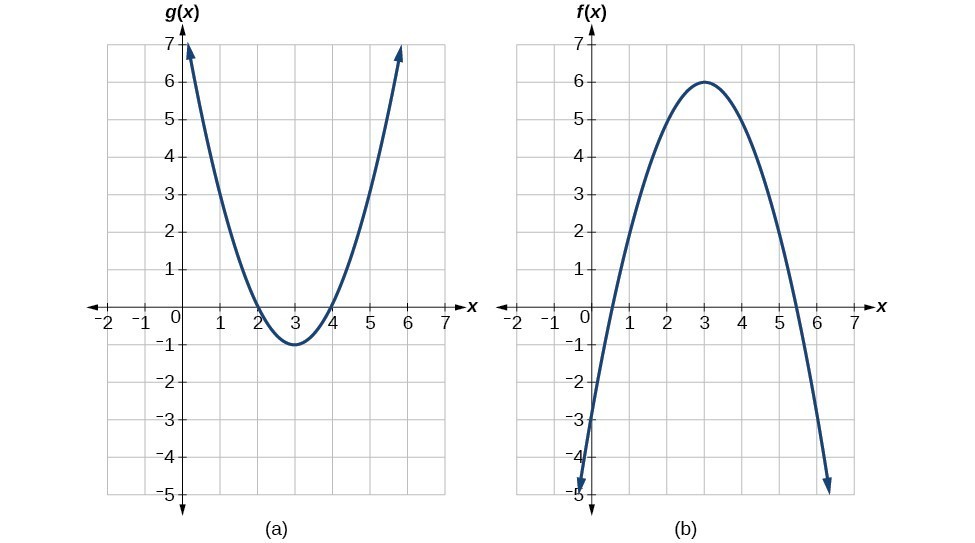
Using the graphs below, evaluate [latex]g\left(f\left(2\right)\right)[/latex].
Evaluating Composite Functions Using Formulas
When evaluating a composite function where we have either created or been given formulas, the rule of working from the inside out remains the same. The input value to the outer function will be the output of the inner function, which may be a numerical value, a variable name, or a more complicated expression.
While we can compose the functions for each individual input value, it is sometimes helpful to find a single formula that will calculate the result of a composition [latex]f\left(g\left(x\right)\right)[/latex]. To do this, we will extend our idea of function evaluation. Recall that, when we evaluate a function like [latex]f\left(t\right)={t}^{2}-t[/latex], we substitute the value inside the parentheses into the formula wherever we see the input variable.
How To: Given a formula for a composite function, evaluate the function.
- Evaluate the inside function using the input value or variable provided.
- Use the resulting output as the input to the outside function.
Example: Evaluating a Composition of Functions Expressed as Formulas with a Numerical Input
Given [latex]f\left(t\right)={t}^{2}-{t}[/latex] and [latex]h\left(x\right)=3x+2[/latex], evaluate [latex]f\left(h\left(1\right)\right)[/latex].
Try It
Given [latex]f\left(t\right)={t}^{2}-t[/latex] and [latex]h\left(x\right)=3x+2[/latex], evaluate
a. [latex]h\left(f\left(2\right)\right)[/latex]
b. [latex]h\left(f\left(-2\right)\right)[/latex]
Candela Citations
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution
- College Algebra. Authored by: Abramson, Jay et al.. Provided by: OpenStax. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/9b08c294-057f-4201-9f48-5d6ad992740d@5.2. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/9b08c294-057f-4201-9f48-5d6ad992740d@5.2
- Question ID 3585. Authored by: Reidel,Jessica. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: IMathAS Community License CC-BY + GPL
- Question ID 69936. Authored by: Smart, Jim. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: IMathAS Community License CC-BY + GPL
- Question ID 16852. Authored by: Pierpoint,William. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: IMathAS Community License CC-BY + GPL