Learning Outcomes
- Define, evaluate, and simplify single variable polynomials
In the example on the previous page, we saw how combining the formulas for different shapes provides a way to accurately predict the amount of paint needed for a construction project. The result was a polynomial.
A polynomial function is a function consisting of the sum or difference of terms in which each term is a real number, a variable, or the product of a real number and variable(s) with a non-negative integer exponents. Non negative integers are [latex]0, 1, 2, 3, 4[/latex], …
You may see a resemblance between expressions and polynomials which we have been studying in this course. Polynomials are a special sub-group of mathematical expressions and equations.
The following table is intended to help you tell the difference between what is a polynomial and what is not.
| IS a Polynomial | Is NOT a Polynomial | Reason |
| [latex]2x^2-\frac{1}{2}x -9[/latex] | [latex]\frac{2}{x^{2}}+x[/latex] | Polynomials only have variables in the numerator |
| [latex]\frac{y}{4}-y^3[/latex] | [latex]\frac{2}{y}+4[/latex] | Polynomials only have variables in the numerator |
| [latex]\sqrt{12}\left(a\right)+9[/latex] | [latex]\sqrt{a}+7[/latex] | Roots are equivalent to rational exponents, and polynomials only have integer exponents on variables |
The basic building block of a polynomial is a monomial. A monomial is one term and can be a number, a variable, or the product of a number and variable(s) with an exponent. The number part of the term is called the coefficient.
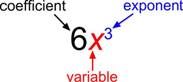
A polynomial containing two terms, such as [latex]2x - 9[/latex], is called a binomial. A polynomial containing three terms, such as [latex]-3{x}^{2}+8x - 7[/latex], is called a trinomial.
We can find the degree of a polynomial by identifying the highest power of the variable that occurs in the polynomial. The term with the highest degree is called the leading term because it is usually written first. The coefficient of the leading term is called the leading coefficient. When a polynomial is written so that the powers on a specified variable are descending, we say that it is in standard form. It is important to note that polynomials only have integer exponents.
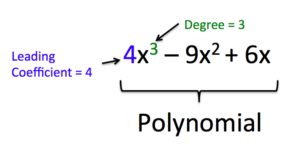
How to: Given a polynomial expression, identify the degree and leading coefficient
- Find the highest power of x to determine the degree.
- Identify the term containing the highest power of x to find the leading term.
- Identify the coefficient of the leading term.
Example
For the following polynomials, identify the degree, the leading term, and the leading coefficient.
- [latex]3+2{x}^{2}-4{x}^{3}[/latex]
- [latex]5{t}^{5}-2{t}^{3}+7t[/latex]
- [latex]6p-{p}^{3}-2[/latex]
In the following video, we will identify the terms, leading coefficient, and degree of a polynomial.
The table below illustrates some examples of monomials, binomials, trinomials, and other polynomials. They are all written in standard form.
| Monomials | Binomials | Trinomials | Other Polynomials |
| [latex]15[/latex] | [latex]3y+13[/latex] | [latex]x^{3}-x^{2}+1[/latex] | [latex]5x^{4}+3x^{3}-6x^{2}+2x[/latex] |
| [latex]\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}x[/latex] | [latex]4p-7[/latex] | [latex]3x^{2}+2x-9[/latex] | [latex]\frac{1}{3}x^{5}-2x^{4}+\frac{2}{9}x^{3}-x^{2}+4x-\frac{5}{6}[/latex] |
| [latex]-4y^{3}[/latex] | [latex]3x^{2}+\frac{5}{8}x[/latex] | [latex]3y^{3}+y^{2}-2[/latex] | [latex]3t^{3}-3t^{2}-3t-3[/latex] |
| [latex]16n^{4}[/latex] | [latex]14y^{3}+3y[/latex] | [latex]a^{7}+2a^{5}-3a^{3}[/latex] | [latex]q^{7}+2q^{5}-3q^{3}+q[/latex] |
When the coefficient of a polynomial term is [latex]0[/latex], you usually do not write the term at all (because [latex]0[/latex] times anything is [latex]0[/latex], and adding [latex]0[/latex] does not change the value). The last binomial above could be written as a trinomial, [latex]14y^{3}+0y^{2}+3y[/latex].
A term without a variable is called a constant term, and the degree of that term is [latex]0[/latex]. For example, [latex]13[/latex] is the constant term in [latex]3y+13[/latex]. You would usually say that [latex]14y^{3}+3y[/latex] has no constant term or that the constant term is [latex]0[/latex].
Evaluate a Polynomial
You can evaluate polynomials just as you have been evaluating expressions all along. To evaluate an expression for a value of the variable, you substitute the value for the variable every time it appears. Then use the order of operations to find the resulting value for the expression.
Example
Evaluate [latex]3x^{2}-2x+1[/latex] for [latex]x=-1[/latex].
Example
Evaluate [latex]\displaystyle -\frac{2}{3}p^{4}+2p^{3}-p[/latex] for [latex]p = 3[/latex].
In the following video, we show more examples of evaluating polynomials for given values of the variable.
Candela Citations
- Evaluate a Polynomial in One Variable. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) for Lumen Learning. Located at: https://youtu.be/2EeFrgQP1hM. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Unit 11: Exponents and Polynomials, from Developmental Math: An Open Program. Provided by: Monterey Institute of Technology. Located at: http://nrocnetwork.org/dm-opentext. License: CC BY: Attribution
- College Algebra. Authored by: Abramson, Jay, et al.. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/9b08c294-057f-4201-9f48-5d6ad992740d@3.278:1/Preface. License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright. License Terms: Download for free at :http://cnx.org/contents/9b08c294-057f-4201-9f48-5d6ad992740d@3.278:1/Preface
- Ex: Intro to Polynomials in One Variable. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) . Located at: https://youtu.be/3u16B2PN9zk. License: CC BY: Attribution
