Solutions to Try Its
1. [latex]|x - 2|\le 3[/latex]
2. using the variable [latex]p[/latex] for passing, [latex]|p - 80|\le 20[/latex]
3. [latex]f\left(x\right)=-|x+2|+3[/latex]
4. [latex]x=-1[/latex] or [latex]x=2[/latex]
5. [latex]f\left(0\right)=1[/latex], so the graph intersects the vertical axis at [latex]\left(0,1\right)[/latex]. [latex]f\left(x\right)=0[/latex] when [latex]x=-5[/latex] and [latex]x=1[/latex] so the graph intersects the horizontal axis at [latex]\left(-5,0\right)[/latex] and [latex]\left(1,0\right)[/latex].
6. [latex]4\le x\le 8[/latex]
7. [latex]k\le 1[/latex] or [latex]k\ge 7[/latex]; in interval notation, this would be [latex]\left(-\infty ,1\right]\cup \left[7,\infty \right)[/latex]
Solutions to Odd-Numbered Exercises
1. Isolate the absolute value term so that the equation is of the form [latex]|A|=B[/latex]. Form one equation by setting the expression inside the absolute value symbol, [latex]A[/latex], equal to the expression on the other side of the equation, [latex]B[/latex]. Form a second equation by setting [latex]A[/latex] equal to the opposite of the expression on the other side of the equation, -B. Solve each equation for the variable.
3. The graph of the absolute value function does not cross the [latex]x[/latex] -axis, so the graph is either completely above or completely below the [latex]x[/latex] -axis.
5. First determine the boundary points by finding the solution(s) of the equation. Use the boundary points to form possible solution intervals. Choose a test value in each interval to determine which values satisfy the inequality.
7. [latex]|x+4|=\frac{1}{2}[/latex]
9. [latex]|f\left(x\right)-8|<0.03[/latex]
11. [latex]\left\{1,11\right\}[/latex]
13. [latex]\left\{\frac{9}{4},\frac{13}{4}\right\}[/latex]
15. [latex]\left\{\frac{10}{3},\frac{20}{3}\right\}[/latex]
17. [latex]\left\{\frac{11}{5},\frac{29}{5}\right\}[/latex]
19. [latex]\left\{\frac{5}{2},\frac{7}{2}\right\}[/latex]
21. No solution
23. [latex]\left\{-57,27\right\}[/latex]
25. [latex]\left(0,-8\right);\left(-6,0\right),\left(4,0\right)[/latex]
27. [latex]\left(0,-7\right)[/latex]; no [latex]x[/latex] -intercepts
29. [latex]\left(-\infty ,-8\right)\cup \left(12,\infty \right)[/latex]
31. [latex]\frac{-4}{3}\le x\le 4[/latex]
33. [latex]\left(-\infty ,-\frac{8}{3}\right]\cup \left[6,\infty \right)[/latex]
35. [latex]\left(-\infty ,-\frac{8}{3}\right]\cup \left[16,\infty \right)[/latex]
37.
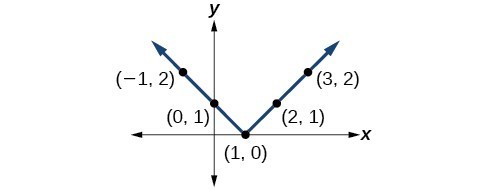
39.
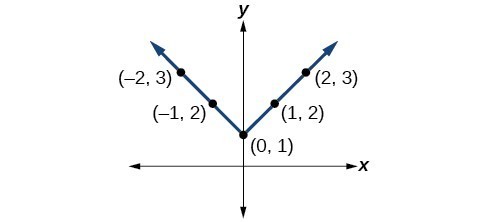
41.
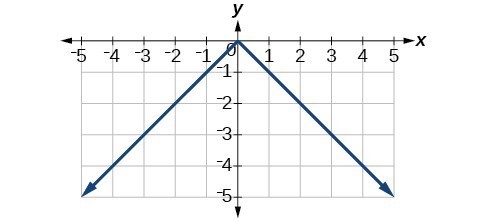
43.
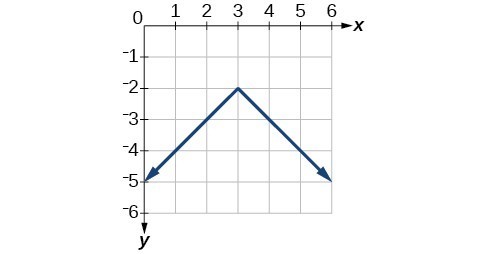
45.
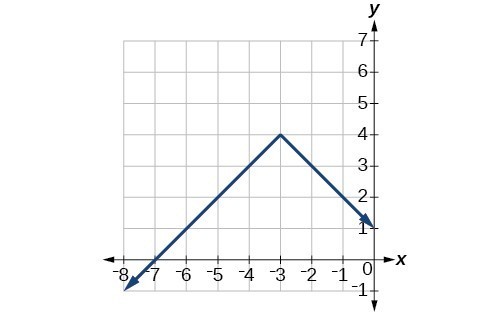
47.
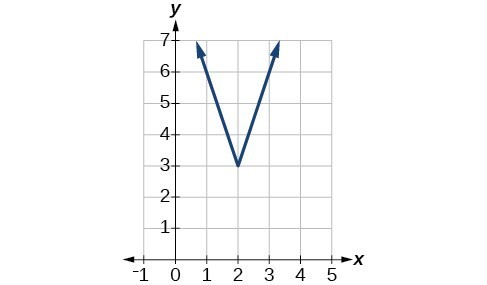
49.
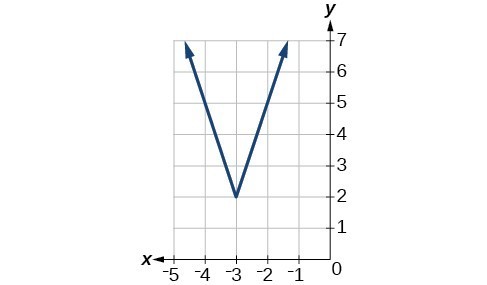
51.
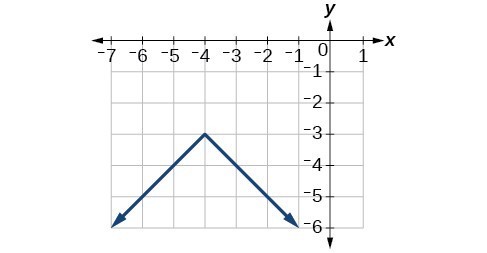
53. range: [latex]\left[0,20\right][/latex]
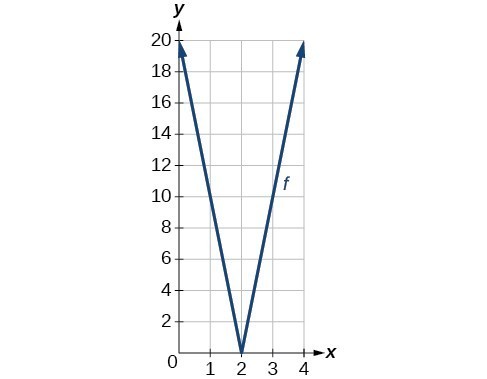
55. [latex]x\text{-}[/latex] intercepts:
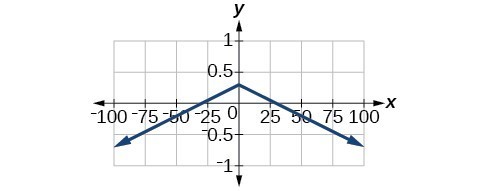
57. [latex]\left(-\infty ,\infty \right)[/latex]
59. There is no solution for [latex]a[/latex] that will keep the function from having a [latex]y[/latex] -intercept. The absolute value function always crosses the [latex]y[/latex] -intercept when [latex]x=0[/latex].
61. [latex]|p - 0.08|\le 0.015[/latex]
63. [latex]|x - 5.0|\le 0.01[/latex]
Candela Citations
- Precalculus. Authored by: Jay Abramson, et al.. Provided by: OpenStax. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/fd53eae1-fa23-47c7-bb1b-972349835c3c@5.175. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download For Free at : http://cnx.org/contents/fd53eae1-fa23-47c7-bb1b-972349835c3c@5.175.