Learning Objectives
- Define the components of the Cartesian coordinate system
- Plot points on the Cartesian coordinate plane
An old story describes how seventeenth-century philosopher/mathematician René Descartes invented the system that has become the foundation of algebra while sick in bed. According to the story, Descartes was staring at a fly crawling on the ceiling when he realized that he could describe the fly’s location in relation to the perpendicular lines formed by the adjacent walls of his room. He viewed the perpendicular lines as horizontal and vertical axes. Further, by dividing each axis into equal unit lengths, Descartes saw that it was possible to locate any object in a two-dimensional plane using just two numbers—the displacement from the horizontal axis and the displacement from the vertical axis.
While there is evidence that ideas similar to Descartes’ grid system existed centuries earlier, it was Descartes who introduced the components that comprise the Cartesian coordinate system, a grid system having perpendicular axes. Descartes named the horizontal axis the x-axis and the vertical axis the y-axis.
The Cartesian coordinate system, also called the rectangular coordinate system, is based on a two-dimensional plane consisting of the x-axis and the y-axis. Perpendicular to each other, the axes divide the plane into four sections. Each section is called a quadrant; the quadrants are numbered counterclockwise as shown in Figure 2.
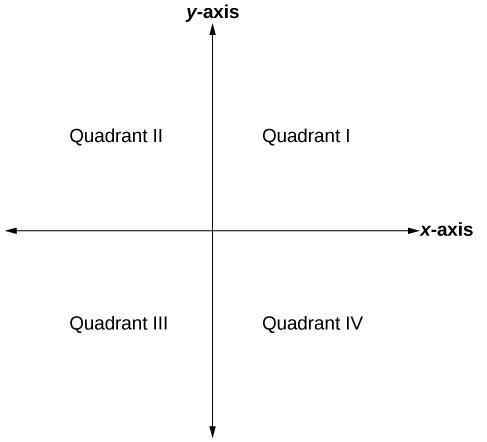
Figure 2
Try It
The center of the plane is the point at which the two axes cross. It is known as the origin, or point [latex]\left(0,0\right)[/latex]. From the origin, each axis is further divided into equal units: increasing, positive numbers to the right on the x-axis and up the y-axis; decreasing, negative numbers to the left on the x-axis and down the y-axis. The axes extend to positive and negative infinity as shown by the arrowheads in Figure 3.
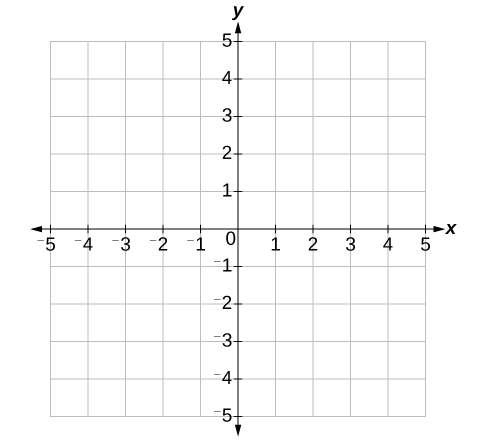
Figure 3
Each point in the plane is identified by its x-coordinate, or horizontal displacement from the origin, and its y-coordinate, or vertical displacement from the origin. Together, we write them as an ordered pair indicating the combined distance from the origin in the form [latex]\left(x,y\right)[/latex]. An ordered pair is also known as a coordinate pair because it consists of x- and y-coordinates. For example, we can represent the point [latex]\left(3,-1\right)[/latex] in the plane by moving three units to the right of the origin in the horizontal direction, and one unit down in the vertical direction.
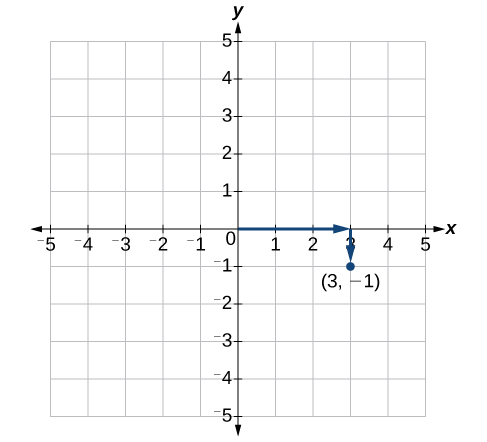
Figure 4
When dividing the axes into equally spaced increments, note that the x-axis may be considered separately from the y-axis. In other words, while the x-axis may be divided and labeled according to consecutive integers, the y-axis may be divided and labeled by increments of 2, or 10, or 100. In fact, the axes may represent other units, such as years against the balance in a savings account, or quantity against cost, and so on. Consider the rectangular coordinate system primarily as a method for showing the relationship between two quantities.
A General Note: Cartesian Coordinate System
A two-dimensional plane where the
- x-axis is the horizontal axis
- y-axis is the vertical axis
A point in the plane is defined as an ordered pair, [latex]\left(x,y\right)[/latex], such that x is determined by its horizontal distance from the origin and y is determined by its vertical distance from the origin.
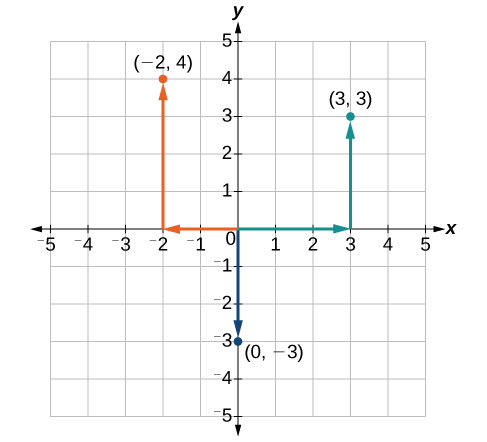
Example: Plotting Points in a Rectangular Coordinate System
Plot the points [latex]\left(-2,4\right)[/latex], [latex]\left(3,3\right)[/latex], and [latex]\left(0,-3\right)[/latex] in the plane.
Try It
Key Takeaways
You can use Desmos to practice plotting points on the Cartesian Coordinate plane. Watch the following short video to learn how!
Now try plotting the following points with Desmos.
[latex](4,0)[/latex]
[latex](-1,5)[/latex]
[latex](0,-10)[/latex]
[latex](2,7)[/latex]
[latex](3,-5)[/latex]
[latex](-4,-7)[/latex]
Candela Citations
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution
- College Algebra. Authored by: Abramson, Jay et al.. Provided by: OpenStax. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/9b08c294-057f-4201-9f48-5d6ad992740d@5.2. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/9b08c294-057f-4201-9f48-5d6ad992740d@5.2
- Question ID 92752, 92753. Authored by: Michael Jenck. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: IMathAS Community License, CC-BY + GPL
- College Algebra. Authored by: OpenStax College Algebra. Provided by: OpenStax. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/9b08c294-057f-4201-9f48-5d6ad992740d@3.278:1/Preface. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Learn Desmos: Points. Authored by: Desmos. Located at: https://youtu.be/eS6kabG2omI?list=PLfM6zMGnbgOGLZc-_Yj3QVK3Vz_L4Cw59. License: All Rights Reserved. License Terms: Standard YouTube License