Learning Objectives
- Identify the degree, leading coefficient, and leading term of a polynomial
- Add and subtract polynomial expressions
- Multiply polynomials
The area of the front of the doghouse described in the introduction was [latex]4{x}^{2}+\frac{1}{2}x[/latex] ft2.
This is an example of a polynomial, which is a sum of or difference of terms, each consisting of a variable raised to a nonnegative integer power. A number multiplied by a variable raised to an exponent, such as [latex]384\pi[/latex], is known as a coefficient. Coefficients can be positive, negative, or zero, and can be whole numbers, decimals, or fractions. Each product [latex]{a}_{i}{x}^{i}[/latex], such as [latex]384\pi w[/latex], is a term of a polynomial. If a term does not contain a variable, it is called a constant.
A polynomial containing only one term, such as [latex]5{x}^{4}[/latex], is called a monomial. A polynomial containing two terms, such as [latex]2x - 9[/latex], is called a binomial. A polynomial containing three terms, such as [latex]-3{x}^{2}+8x - 7[/latex], is called a trinomial.
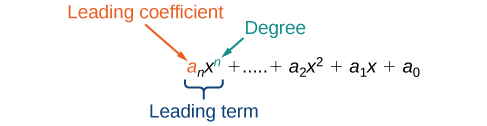
We can find the degree of a polynomial by identifying the highest power of the variable that occurs in the polynomial. The term with the highest degree is called the leading term because it is usually written first. The coefficient of the leading term is called the leading coefficient. When a polynomial is written so that the powers are descending, we say that it is in standard form.
A General Note: Polynomials
A polynomial is an expression that can be written in the form
Each real number aiis called a coefficient. The number [latex]{a}_{0}[/latex] that is not multiplied by a variable is called a constant. Each product [latex]{a}_{i}{x}^{i}[/latex] is a term of a polynomial. The highest power of the variable that occurs in the polynomial is called the degree of a polynomial. The leading term is the term with the highest power, and its coefficient is called the leading coefficient.
How To: Given a polynomial expression, identify the degree and leading coefficient.
- Find the highest power of x to determine the degree.
- Identify the term containing the highest power of x to find the leading term.
- Identify the coefficient of the leading term.
Example: Identifying the Degree and Leading Coefficient of a Polynomial
For the following polynomials, identify the degree, the leading term, and the leading coefficient.
- [latex]3+2{x}^{2}-4{x}^{3}[/latex]
- [latex]5{t}^{5}-2{t}^{3}+7t[/latex]
- [latex]6p-{p}^{3}-2[/latex]
Try It
Identify the degree, leading term, and leading coefficient of the polynomial [latex]4{x}^{2}-{x}^{6}+2x - 6[/latex].
In the following video example, we will identify the terms, leading coefficient, and degree of a polynomial.
Add and Subtract Polynomials
We can add and subtract polynomials by combining like terms, which are terms that contain the same variables raised to the same exponents. For example, [latex]5{x}^{2}[/latex] and [latex]-2{x}^{2}[/latex] are like terms, and can be added to get [latex]3{x}^{2}[/latex], but [latex]3x[/latex] and [latex]3{x}^{2}[/latex] are not like terms, and therefore cannot be added.
How To: Given multiple polynomials, add or subtract them to simplify the expressions.
- Combine like terms.
- Simplify and write in standard form. Standard form means you start with the leading term, and write the rest of the terms in descending order by degree.
Example: Adding Polynomials
Find the sum.
[latex]\left(12{x}^{2}+9x - 21\right)+\left(4{x}^{3}+8{x}^{2}-5x+20\right)[/latex]
Try It
Find the sum.
[latex]\left(2{x}^{3}+5{x}^{2}-x+1\right)+\left(2{x}^{2}-3x - 4\right)[/latex]
Example: Subtracting Polynomials
Find the difference.
[latex]\left(7{x}^{4}-{x}^{2}+6x+1\right)-\left(5{x}^{3}-2{x}^{2}+3x+2\right)[/latex]
Try It
Find the difference.
[latex]\left(-7{x}^{3}-7{x}^{2}+6x - 2\right)-\left(4{x}^{3}-6{x}^{2}-x+7\right)[/latex]
Watch this video to see more examples of adding and subtracting polynomials.
Multiply Polynomials
Multiplying polynomials is a bit more challenging than adding and subtracting polynomials. We must use the distributive property to multiply each term in the first polynomial by each term in the second polynomial. We then combine like terms. We can also use a shortcut called the FOIL method when multiplying binomials. Certain special products follow patterns that we can memorize and use instead of multiplying the polynomials by hand each time. We will look at a variety of ways to multiply polynomials.
Multiplying Polynomials Using the Distributive Property
To multiply a number by a polynomial, we use the distributive property. The number must be distributed to each term of the polynomial. We can distribute the [latex]2[/latex] in [latex]2\left(x+7\right)[/latex] to obtain the equivalent expression [latex]2x+14[/latex]. When multiplying polynomials, the distributive property allows us to multiply each term of the first polynomial by each term of the second. We then add the products together and combine like terms to simplify.
How To: Given the multiplication of two polynomials, use the distributive property to simplify the expression.
- Multiply each term of the first polynomial by each term of the second.
- Combine like terms.
- Simplify.
Example: Multiplying Polynomials Using the Distributive Property
Find the product.
[latex]\left(2x+1\right)\left(3{x}^{2}-x+4\right)[/latex]
Try It
Find the product.
[latex]\left(3x+2\right)\left({x}^{3}-4{x}^{2}+7\right)[/latex]
Watch this video to see more examples of how to use the distributive property to multiply polynomials.
Using FOIL to Multiply Binomials
A shortcut called FOIL is sometimes used to find the product of two binomials. It is called FOIL because we multiply the first terms, the outer terms, the inner terms, and then the last terms of each binomial.
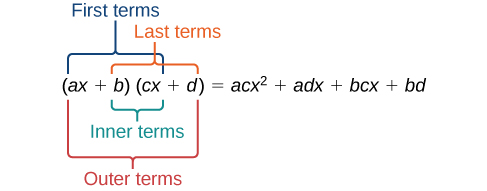
The FOIL method arises out of the distributive property. We are simply multiplying each term of the first binomial by each term of the second binomial, and then combining like terms.
How To: Given two binomials, use FOIL to simplify the expression.
- Multiply the first terms of each binomial.
- Multiply the outer terms of the binomials.
- Multiply the inner terms of the binomials.
- Multiply the last terms of each binomial.
- Add the products.
- Combine like terms and simplify.
Example: Using FOIL to Multiply Binomials
Use FOIL to find the product.
Try It
Use FOIL to find the product.
[latex]\left(x+7\right)\left(3x - 5\right)[/latex]
Candela Citations
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution
- College Algebra. Authored by: Abramson, Jay et al.. Provided by: OpenStax. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/9b08c294-057f-4201-9f48-5d6ad992740d@5.2. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/9b08c294-057f-4201-9f48-5d6ad992740d@5.2
- Examples: Intro to Polynomials. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com). Located at: https://youtu.be/3u16B2PN9zk. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Examples: Adding and Subtracting Polynomials. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com). Located at: https://youtu.be/jiq3toC7wGM. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Exmaples: Multiplying Polynomials. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com). Located at: https://youtu.be/bwTmApTV_8o. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Question ID 93531, 93536, 93537, 93539. Authored by: Michael Jenck. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: IMathAS Community License, CC-BY + GPL
- Question ID 3864. Authored by: Tyler Wallace. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: IMathAS Community License, CC-BY + GPL
- College Algebra. Authored by: OpenStax College Algebra. Provided by: OpenStax. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/9b08c294-057f-4201-9f48-5d6ad992740d@3.278:1/Preface. License: CC BY: Attribution



