Learning Objectives
- Identify the base of an exponential function, and restrictions for it’s value
- Evaluate an exponential growth function
- Use a compound interest Formula
- Evaluate exponential functions with base e
![]()
India is the second most populous country in the world with a population of about 1.25 billion people in 2013. The population is growing at a rate of about 1.2% each year.[1] If this rate continues, the population of India will exceed China’s population by the year 2031. When populations grow rapidly, we often say that the growth is “exponential,” meaning that something is growing very rapidly. To a mathematician, however, the term exponential growth has a very specific meaning. In this section, we will take a look at exponential functions, which model this kind of rapid growth.
Recall that the base of an exponential function must be a positive real number other than 1. Why do we limit the base b to positive values? To ensure that the outputs will be real numbers. Observe what happens if the base is not positive:
- Let b = –9 and [latex]x=\frac{1}{2}[/latex]. Then [latex]f\left(x\right)=f\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)={\left(-9\right)}^{\frac{1}{2}}=\sqrt{-9}[/latex], which is not a real number.
Why do we limit the base to positive values other than 1? Because base 1 results in the constant function. Observe what happens if the base is 1:
- Let b = 1. Then [latex]f\left(x\right)={1}^{x}=1[/latex] for any value of x.
To evaluate an exponential function with the form [latex]f\left(x\right)={b}^{x}[/latex], we simply substitute x with the given value, and calculate the resulting power. For example:
Let [latex]f\left(x\right)={2}^{x}[/latex]. What is [latex]f\left(3\right)[/latex]?
[latex]\begin{array}{c}f\left(x\right)\hfill & ={2}^{x}\hfill & \hfill \\ f\left(3\right)\hfill & ={2}^{3}\text{ }\hfill & \text{Substitute }x=3.\hfill \\ \hfill & =8\text{ }\hfill & \text{Evaluate the power}\text{.}\hfill \end{array}[/latex]
To evaluate an exponential function with a form other than the basic form, it is important to follow the order of operations. For example:
Let [latex]f\left(x\right)=30{\left(2\right)}^{x}[/latex]. What is [latex]f\left(3\right)[/latex]?
[latex]\begin{array}{c}f\left(x\right)\hfill & =30{\left(2\right)}^{x}\hfill & \hfill \\ f\left(3\right)\hfill & =30{\left(2\right)}^{3}\hfill & \text{Substitute }x=3.\hfill \\ \hfill & =30\left(8\right)\text{ }\hfill & \text{Simplify the power first}\text{.}\hfill \\ \hfill & =240\hfill & \text{Multiply}\text{.}\hfill \end{array}[/latex]
Note that if the order of operations were not followed, the result would be incorrect:
[latex]f\left(3\right)=30{\left(2\right)}^{3}\ne {60}^{3}=216,000[/latex]
Example: Evaluating Exponential Functions
Let [latex]f\left(x\right)=5{\left(3\right)}^{x+1}[/latex]. Evaluate [latex]f\left(2\right)[/latex] without using a calculator.
Try It
Let [latex]f\left(x\right)=8{\left(1.2\right)}^{x - 5}[/latex]. Evaluate [latex]f\left(3\right)[/latex] using a calculator. Round to four decimal places.
Because the output of exponential functions increases very rapidly, the term “exponential growth” is often used in everyday language to describe anything that grows or increases rapidly. However, exponential growth can be defined more precisely in a mathematical sense. If the growth rate is proportional to the amount present, the function models exponential growth.
A General Note: Exponential Growth
A function that models exponential growth grows by a rate proportional to the amount present. For any real number x and any positive real numbers a and b such that [latex]b\ne 1[/latex], an exponential growth function has the form
[latex]\text{ }f\left(x\right)=a{b}^{x}[/latex]
where
- a is the initial or starting value of the function.
- b is the growth factor or growth multiplier per unit x.
In more general terms, we have an exponential function, in which a constant base is raised to a variable exponent. To differentiate between linear and exponential functions, let’s consider two companies, A and B. Company A has 100 stores and expands by opening 50 new stores a year, so its growth can be represented by the function [latex]A\left(x\right)=100+50x[/latex]. Company B has 100 stores and expands by increasing the number of stores by 50% each year, so its growth can be represented by the function [latex]B\left(x\right)=100{\left(1+0.5\right)}^{x}[/latex].
A few years of growth for these companies are illustrated below.
| Year, x | Stores, Company A | Stores, Company B |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100 + 50(0) = 100 | 100(1 + 0.5)0 = 100 |
| 1 | 100 + 50(1) = 150 | 100(1 + 0.5)1 = 150 |
| 2 | 100 + 50(2) = 200 | 100(1 + 0.5)2 = 225 |
| 3 | 100 + 50(3) = 250 | 100(1 + 0.5)3 = 337.5 |
| x | A(x) = 100 + 50x | B(x) = 100(1 + 0.5)x |
The graphs comparing the number of stores for each company over a five-year period are shown in below. We can see that, with exponential growth, the number of stores increases much more rapidly than with linear growth.
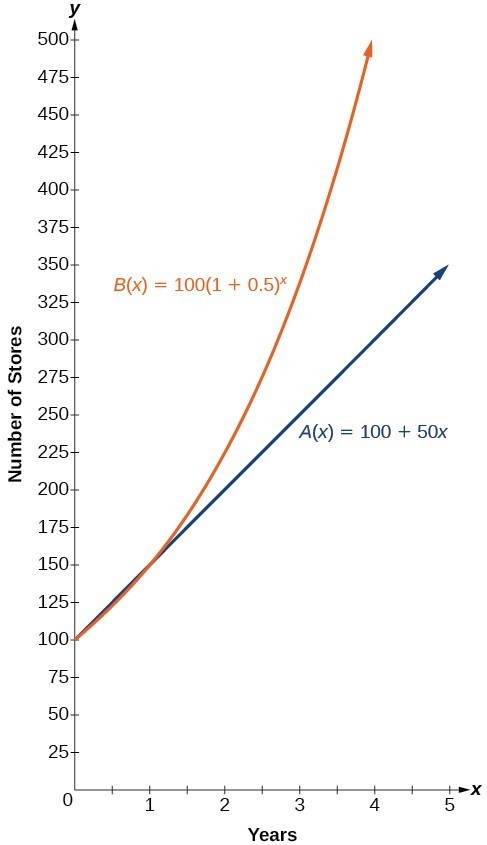
The graph shows the numbers of stores Companies A and B opened over a five-year period.
Notice that the domain for both functions is [latex]\left[0,\infty \right)[/latex], and the range for both functions is [latex]\left[100,\infty \right)[/latex]. After year 1, Company B always has more stores than Company A.
Now we will turn our attention to the function representing the number of stores for Company B, [latex]B\left(x\right)=100{\left(1+0.5\right)}^{x}[/latex]. In this exponential function, 100 represents the initial number of stores, 0.50 represents the growth rate, and [latex]1+0.5=1.5[/latex] represents the growth factor. Generalizing further, we can write this function as [latex]B\left(x\right)=100{\left(1.5\right)}^{x}[/latex], where 100 is the initial value, 1.5 is called the base, and x is called the exponent.
Example: Evaluating a Real-World Exponential Model
At the beginning of this section, we learned that the population of India was about 1.25 billion in the year 2013, with an annual growth rate of about 1.2%. This situation is represented by the growth function [latex]P\left(t\right)=1.25{\left(1.012\right)}^{t}[/latex], where t is the number of years since 2013. To the nearest thousandth, what will the population of India be in 2031?
Try It
The population of China was about 1.39 billion in the year 2013, with an annual growth rate of about 0.6%. This situation is represented by the growth function [latex]P\left(t\right)=1.39{\left(1.006\right)}^{t}[/latex], where t is the number of years since 2013. To the nearest thousandth, what will the population of China be for the year 2031? How does this compare to the population prediction we made for India in the previous example?
Use a Compound Interest Formula
Savings instruments in which earnings are continually reinvested, such as mutual funds and retirement accounts, use compound interest. The term compounding refers to interest earned not only on the original value, but on the accumulated value of the account.
The annual percentage rate (APR) of an account, also called the nominal rate, is the yearly interest rate earned by an investment account. The term nominal is used when the compounding occurs a number of times other than once per year. In fact, when interest is compounded more than once a year, the effective interest rate ends up being greater than the nominal rate! This is a powerful tool for investing.
We can calculate the compound interest using the compound interest formula, which is an exponential function of the variables time t, principal P, APR r, and number of compounding periods in a year n:
[latex]A\left(t\right)=P{\left(1+\frac{r}{n}\right)}^{nt}[/latex]
For example, observe the table below, which shows the result of investing $1,000 at 10% for one year. Notice how the value of the account increases as the compounding frequency increases.
| Frequency | Value after 1 year |
|---|---|
| Annually | $1100 |
| Semiannually | $1102.50 |
| Quarterly | $1103.81 |
| Monthly | $1104.71 |
| Daily | $1105.16 |
A General Note: The Compound Interest Formula
Compound interest can be calculated using the formula
[latex]A\left(t\right)=P{\left(1+\frac{r}{n}\right)}^{nt}[/latex]
where
- A(t) is the account value,
- t is measured in years,
- P is the starting amount of the account, often called the principal, or more generally present value,
- r is the annual percentage rate (APR) expressed as a decimal, and
- n is the number of compounding periods in one year.
Example: Calculating Compound Interest
If we invest $3,000 in an investment account paying 3% interest compounded quarterly, how much will the account be worth in 10 years?
Try It
An initial investment of $100,000 at 12% interest is compounded weekly (use 52 weeks in a year). What will the investment be worth in 30 years?
Example: Using the Compound Interest Formula to Solve for the Principal
A 529 Plan is a college-savings plan that allows relatives to invest money to pay for a child’s future college tuition; the account grows tax-free. Lily wants to set up a 529 account for her new granddaughter and wants the account to grow to $40,000 over 18 years. She believes the account will earn 6% compounded semi-annually (twice a year). To the nearest dollar, how much will Lily need to invest in the account now?
Try It
Refer to the previous example. To the nearest dollar, how much would Lily need to invest if the account is compounded quarterly?
Evaluate exponential functions with base e
As we saw earlier, the amount earned on an account increases as the compounding frequency increases. The table below shows that the increase from annual to semi-annual compounding is larger than the increase from monthly to daily compounding. This might lead us to ask whether this pattern will continue.
Examine the value of $1 invested at 100% interest for 1 year, compounded at various frequencies.
| Frequency | [latex]A\left(t\right)={\left(1+\frac{1}{n}\right)}^{n}[/latex] | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Annually | [latex]{\left(1+\frac{1}{1}\right)}^{1}[/latex] | $2 |
| Semiannually | [latex]{\left(1+\frac{1}{2}\right)}^{2}[/latex] | $2.25 |
| Quarterly | [latex]{\left(1+\frac{1}{4}\right)}^{4}[/latex] | $2.441406 |
| Monthly | [latex]{\left(1+\frac{1}{12}\right)}^{12}[/latex] | $2.613035 |
| Daily | [latex]{\left(1+\frac{1}{365}\right)}^{365}[/latex] | $2.714567 |
| Hourly | [latex]{\left(1+\frac{1}{\text{8766}}\right)}^{\text{8766}}[/latex] | $2.718127 |
| Once per minute | [latex]{\left(1+\frac{1}{\text{525960}}\right)}^{\text{525960}}[/latex] | $2.718279 |
| Once per second | [latex]{\left(1+\frac{1}{31557600}\right)}^{31557600}[/latex] | $2.718282 |
These values appear to be approaching a limit as n increases without bound. In fact, as n gets larger and larger, the expression [latex]{\left(1+\frac{1}{n}\right)}^{n}[/latex] approaches a number used so frequently in mathematics that it has its own name: the letter [latex]e[/latex]. This value is an irrational number, which means that its decimal expansion goes on forever without repeating. Its approximation to six decimal places is shown below.
A General Note: The Number e
The letter e represents the irrational number
[latex]{\left(1+\frac{1}{n}\right)}^{n},\text{as}n\text{increases without bound}[/latex]
The letter e is used as a base for many real-world exponential models. To work with base e, we use the approximation, [latex]e\approx 2.718282[/latex]. The constant was named by the Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler (1707–1783) who first investigated and discovered many of its properties.
Example: Using a Calculator to Find Powers of e
Calculate [latex]{e}^{3.14}[/latex]. Round to five decimal places.
Try It
Use a calculator to find [latex]{e}^{-0.5}[/latex]. Round to five decimal places.
Candela Citations
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Question ID 1495. Authored by: WebWork-Rochester. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: IMathAS Community License CC-BY + GPL
- College Algebra. Authored by: Abramson, Jay et al.. Provided by: OpenStax. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/9b08c294-057f-4201-9f48-5d6ad992740d@5.2. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/9b08c294-057f-4201-9f48-5d6ad992740d@5.2
- Question ID 2453. Authored by: Anderson,Tophe, mb Sousa,James. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: IMathAS Community License CC-BY + GPL
- http://www.worldometers.info/world-population/. Accessed February 24, 2014. ↵