Learning Objectives
- Use the slope intercept form to plot and write equations of lines
- Use the point-slope formula to write the equation of a line
- Write the equation of a line in standard form
- Recognize vertical and horizontal lines from their graphs and equations
Slope-Intercept Form
Perhaps the most familiar form of a linear equation is the slope-intercept form, written as [latex]y=mx+b[/latex], where [latex]m=\text{slope}[/latex] and [latex]b=y\text{-intercept}[/latex]. Let us begin with the slope.
The Slope of a Line
The slope of a line refers to the ratio of the vertical change in y over the horizontal change in x between any two points on a line. It indicates the direction in which a line slants as well as its steepness. Slope is sometimes described as rise over run.
If the slope is positive, the line slants to the right. If the slope is negative, the line slants to the left. As the slope increases, the line becomes steeper. Some examples are shown below. The lines indicate the following slopes: [latex]m=-3[/latex], [latex]m=2[/latex], and [latex]m=\frac{1}{3}[/latex].
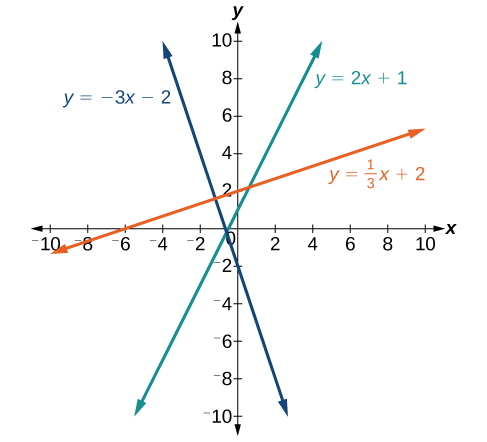
A General Note: The Slope of a Line
The slope of a line, m, represents the change in y over the change in x. Given two points, [latex]\left({x}_{1},{y}_{1}\right)[/latex] and [latex]\left({x}_{2},{y}_{2}\right)[/latex], the following formula determines the slope of a line containing these points:
Example: Finding the Slope of a Line Given Two Points
Find the slope of a line that passes through the points [latex]\left(2,-1\right)[/latex] and [latex]\left(-5,3\right)[/latex].
Try It
Find the slope of the line that passes through the points [latex]\left(-2,6\right)[/latex] and [latex]\left(1,4\right)[/latex].
Example: Identifying the Slope and y-intercept of a Line Given an Equation
Identify the slope and y-intercept, given the equation [latex]y=-\frac{3}{4}x - 4[/latex].
The Point-Slope Formula
Given the slope and one point on a line, we can find the equation of the line using the point-slope formula.
This is an important formula, as it will be used in other areas of college algebra and often in calculus to find the equation of a tangent line. We need only one point and the slope of the line to use the formula. After substituting the slope and the coordinates of one point into the formula, we simplify it and write it in slope-intercept form.
A General Note: The Point-Slope Formula
Given one point and the slope, the point-slope formula will lead to the equation of a line:
Example: Finding the Equation of a Line Given the Slope and One Point
Write the equation of the line with slope [latex]m=-3[/latex] and passing through the point [latex]\left(4,8\right)[/latex]. Write the final equation in slope-intercept form.
Try It
Given [latex]m=4[/latex], find the equation of the line in slope-intercept form passing through the point [latex]\left(2,5\right)[/latex].
Example: Finding the Equation of a Line Passing Through Two Given Points
Find the equation of the line passing through the points [latex]\left(3,4\right)[/latex] and [latex]\left(0,-3\right)[/latex]. Write the final equation in slope-intercept form.
Standard Form of a Line
Another way that we can represent the equation of a line is in standard form. Standard form is given as
where [latex]A[/latex], [latex]B[/latex], and [latex]C[/latex] are integers. The x- and y-terms are on one side of the equal sign and the constant term is on the other side.
Example: Finding the Equation of a Line and Writing It in Standard Form
Find the equation of the line with [latex]m=-6[/latex] and passing through the point [latex]\left(\frac{1}{4},-2\right)[/latex]. Write the equation in standard form.
Try It
Find the equation of the line in standard form with slope [latex]m=-\frac{1}{3}[/latex] and passing through the point [latex]\left(1,\frac{1}{3}\right)[/latex].
Vertical and Horizontal Lines
The equations of vertical and horizontal lines do not require any of the preceding formulas, although we can use the formulas to prove that the equations are correct. The equation of a vertical line is given as
where c is a constant. The slope of a vertical line is undefined, and regardless of the y-value of any point on the line, the x-coordinate of the point will be c.
Suppose that we want to find the equation of a line containing the following points: [latex]\left(-3,-5\right),\left(-3,1\right),\left(-3,3\right)[/latex], and [latex]\left(-3,5\right)[/latex]. First, we will find the slope.
Zero in the denominator means that the slope is undefined and, therefore, we cannot use the point-slope formula. However, we can plot the points. Notice that all of the x-coordinates are the same and we find a vertical line through [latex]x=-3[/latex].
The equation of a horizontal line is given as
where c is a constant. The slope of a horizontal line is zero, and for any x-value of a point on the line, the y-coordinate will be c.
Suppose we want to find the equation of a line that contains the following set of points: [latex]\left(-2,-2\right),\left(0,-2\right),\left(3,-2\right)[/latex], and [latex]\left(5,-2\right)[/latex]. We can use the point-slope formula. First, we find the slope using any two points on the line.
Use any point for [latex]\left({x}_{1},{y}_{1}\right)[/latex] in the formula, or use the y-intercept.
The graph is a horizontal line through [latex]y=-2[/latex]. Notice that all of the y-coordinates are the same.
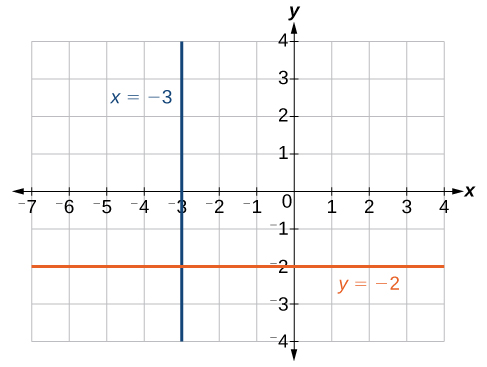
The line x = −3 is a vertical line. The line y = −2 is a horizontal line.
try it now
Use the Desmos calculator to graph the following:
- A horizontal line that passes through the point (-5,2)
- A vertical line that passes through the point (3,3)
Example: Finding the Equation of a Line Passing Through the Given Points
Find the equation of the line passing through the given points: [latex]\left(1,-3\right)[/latex] and [latex]\left(1,4\right)[/latex].
Try It
Find the equation of the line passing through [latex]\left(-5,2\right)[/latex] and [latex]\left(2,2\right)[/latex].
Candela Citations
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution
- College Algebra. Authored by: Abramson, Jay et al.. Provided by: OpenStax. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/9b08c294-057f-4201-9f48-5d6ad992740d@5.2. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/9b08c294-057f-4201-9f48-5d6ad992740d@5.2
- Question ID 1719. Authored by: Barbara Goldner. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: IMathAS Community License CC- BY + GPL
- Question ID 110942, 110946, 110951, 110952. Authored by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: IMathAS Community License CC- BY + GPL
- College Algebra. Authored by: OpenStax College Algebra. Provided by: OpenStax. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/9b08c294-057f-4201-9f48-5d6ad992740d@3.278:1/Preface. License: CC BY: Attribution