High Medieval Music (1150–1300)
Ars Antiqua
The flowering of the Notre Dame school of polyphony from around 1150 to 1250 corresponded to the equally impressive achievements in Gothic architecture: indeed the centre of activity was at the cathedral of Notre Dame itself. Sometimes the music of this period is called the Parisian school, or Parisian organum, and represents the beginning of what is conventionally known as Ars antiqua. This was the period in which rhythmic notation first appeared in western music, mainly a context-based method of rhythmic notation known as the rhythmic modes.
This was also the period in which concepts of formal structure developed which were attentive to proportion, texture, and architectural effect. Composers of the period alternated florid and discant organum (more note-against-note, as opposed to the succession of many-note melismas against long-held notes found in the florid type), and created several new musical forms:clausulae, which were melismatic sections of organa extracted and fitted with new words and further musical elaboration; conductus, which was a song for one or more voices to be sung rhythmically, most likely in a procession of some sort; and tropes, which were additions of new words and sometimes new music to sections of older chants. All of these genres save one were based upon chant; that is, one of the voices, (usually three, though sometimes four) nearly always the lowest (the tenor at this point) sang a chant melody, though with freely composed note-lengths, over which the other voices sang organum. The exception to this method was the conductus, a two-voice composition that was freely composed in its entirety.
The motet, one of the most important musical forms of the high Middle Ages and Renaissance, developed initially during the Notre Dame period out of the clausula, especially the form using multiple voices as elaborated by Pérotin, who paved the way for this particularly by replacing many of his predecessor (as canon of the cathedral) Léonin’s lengthy florid clausulae with substitutes in a discant style. Gradually, there came to be entire books of these substitutes, available to be fitted in and out of the various chants. Since, in fact, there were more than can possibly have been used in context, it is probable that the clausulae came to be performed independently, either in other parts of the mass, or in private devotions. The clausulae, thus practised, became the motet when troped with non-liturgical words, and were further developed into a form of great elaboration, sophistication and subtlety in the fourteenth century, the period of Ars nova.
Surviving manuscripts from this era include the Montpellier Codex, Bamberg Codex, and Las Huelgas Codex.
Composers of this time include Léonin, Pérotin, W. de Wycombe, Adam de St. Victor, and Petrus de Cruce (Pierre de la Croix). Petrus is credited with the innovation of writing more than three semibreves to fit the length of a breve. Coming before the innovation of imperfect tempus, this practice inaugurated the era of what are now called “Petronian” motets. These late 13th-century works are in three to four parts and have multiple texts sung simultaneously. Originally, the tenor line (from the Latin tenere, “to hold”) held a preexisting liturgical chant line in the original Latin, while the text of the one, two, or even three voices above, called the voces organales, provided commentary on the liturgical subject either in Latin or in the vernacular French. The rhythmic values of the voces organales decreased as the parts multiplied, with the duplum (the part above the tenor) having smaller rhythmic values than the tenor, the triplum(the line above the duplum) having smaller rhythmic values than the duplum, and so on. As time went by, the texts of the voces organales became increasingly secular in nature and had less and less overt connection to the liturgical text in the tenor line.
The Petronian motet is a highly complex genre, given its mixture of several semibreve breves with rhythmic modes and sometimes (with increasing frequency) substitution of secular songs for chant in the tenor. Indeed, ever-increasing rhythmic complexity would be a fundamental characteristic of the 14th century, though music in France, Italy, and England would take quite different paths during that time.
Cantigas de Santa Maria
The Cantigas de Santa Maria (“Canticles of Holy Mary”) are 420 poems with musical notation, written in Galician-Portuguese during the reign of Alfonso X El Sabio (1221–1284) and often attributed to him.
It is one of the largest collections of monophonic (solo) songs from the Middle Ages and is characterized by the mention of the Virgin Mary in every song, while every tenth song is a hymn.
The manuscripts have survived in four codices: two at El Escorial, one at Madrid’s National Library, and one in Florence, Italy. Some have colored miniatures showing pairs of musicians playing a wide variety of instruments.
Troubadours and Trouvères
The music of the troubadours and trouvères was a vernacular tradition of monophonic secular song, probably accompanied by instruments, sung by professional, occasionally itinerant, musicians who were as skilled as poets as they were singers and instrumentalists. The language of the troubadours was Occitan (also known as the langue d’oc, or Provençal); the language of the trouvères was Old French (also known as langue d’oil). The period of the troubadours corresponded to the flowering of cultural life in Provence which lasted through the twelfth century and into the first decade of the thirteenth. Typical subjects of troubadour song were war, chivalry and courtly love. The period of the troubadours wound down after theAlbigensian Crusade, the fierce campaign by Pope Innocent III to eliminate the Cathar heresy (and northern barons’ desire to appropriate the wealth of the south). Surviving troubadours went either to Portugal,Spain, northern Italy or northern France (where the trouvère tradition lived on), where their skills and techniques contributed to the later developments of secular musical culture in those places.
The music of the trouvères was similar to that of the troubadours, but was able to survive into the thirteenth century unaffected by the Albigensian Crusade. Most of the more than two thousand surviving trouvère songs include music, and show a sophistication as great as that of the poetry it accompanies.
The Minnesinger tradition was the Germanic counterpart to the activity of the troubadours and trouvères to the west. Unfortunately, few sources survive from the time; the sources of Minnesang are mostly from two or three centuries after the peak of the movement, leading to some controversy over their accuracy. Among the Minnesingers with surviving music areWolfram von Eschenbach, Walther von der Vogelweide, and Niedhart von Reuenthal.
Trovadorismo
In the Middle Ages, Galician-Portuguese was the language used in nearly all of Iberia for lyric poetry. From this language derive both modern Galician and Portuguese. The Galician-Portuguese school, which was influenced to some extent (mainly in certain formal aspects) by the Occitan troubadours, is first documented at the end of the twelfth century and lasted until the middle of the fourteenth.
The earliest extant composition in this school is usually agreed to be Ora faz ost’ o senhor de Navarra by the Portuguese João Soares de Paiva, usually dated just before or after 1200. The troubadours of the movement, not to be confused with the Occitan troubadours (who frequented courts in nearby León and Castile), wrote almost entirely cantigas. Beginning probably around the middle of the thirteenth century, these songs, known also as cantares or trovas, began to be compiled in collections known as cancioneiros (songbooks). Three such anthologies are known: the Cancioneiro da Ajuda, the Cancioneiro Colocci-Brancuti (or Cancioneiro da Biblioteca Nacional de Lisboa), and the Cancioneiro da Vaticana. In addition to these there is the priceless collection of over 400 Galician-Portugues cantigas in the Cantigas de Santa Maria, which tradition attributes to Alfonso X.
The Galician-Portuguese cantigas can be divided into three basic genres: male-voiced love poetry, called cantigas de amor (or cantigas d’amor) female-voiced love poetry, called cantigas de amigo (cantigas d’amigo); and poetry of insult and mockery called cantigas d’escarnho e de mal dizer. All three are lyric genres in the technical sense that they were strophic songs with either musical accompaniment or introduction on a stringed instrument. But all three genres also have dramatic elements, leading early scholars to characterize them as lyric-dramatic.
The origins of the cantigas d’amor are usually traced to Provençal and Old French lyric poetry, but formally and rhetorically they are quite different. The cantigas d’amigo are probably rooted in a native song tradition, though this view has been contested. The cantigas d’escarnho e maldizer may also (according to Lang) have deep local roots. The latter two genres (totalling around 900 texts) make the Galician-Portuguese lyric unique in the entire panorama of medieval Romance poetry.
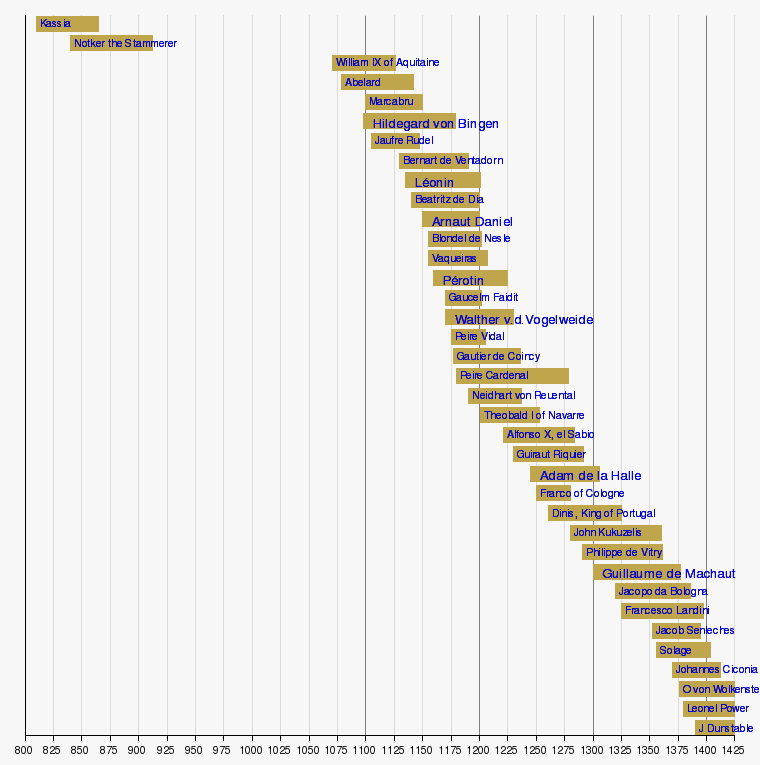
- Troubadours with surviving melodies:
|
|
|
|
- Composers of the high and late medieval era:
Late Medieval Music (1300–1400)
France: Ars Nova
The beginning of the Ars nova is one of the few clean chronological divisions in medieval music, since it corresponds to the publication of the Roman de Fauvel, a huge compilation of poetry and music, in 1310 and 1314. The Roman de Fauvel is a satire on abuses in the medieval church, and is filled with medieval motets, lais, rondeaux and other new secular forms. While most of the music is anonymous, it contains several pieces by Philippe de Vitry, one of the first composers of the isorhythmic motet, a development which distinguishes the fourteenth century. The isorhythmic motet was perfected by Guillaume de Machaut, the finest composer of the time.

Page of the French manuscript Livres de Fauvel, Paris (ca. 1318), “the first practical source of Ars nova music.”
During the Ars nova era, secular music acquired a polyphonic sophistication formerly found only in sacred music, a development not surprising considering the secular character of the early Renaissance (while this music is typically considered “medieval”, the social forces that produced it were responsible for the beginning of the literary and artistic Renaissance in Italy—the distinction between Middle Ages and Renaissance is a blurry one, especially considering arts as different as music and painting). The term “Ars nova” (new art, or new technique) was coined by Philippe de Vitry in his treatise of that name (probably written in 1322), in order to distinguish the practice from the music of the immediately preceding age.
The dominant secular genre of the Ars Nova was the chanson, as it would continue to be in France for another two centuries. These chansons were composed in musical forms corresponding to the poetry they set, which were in the so-called formes fixes of rondeau, ballade, and virelai. These forms significantly affected the development of musical structure in ways that are felt even today; for example, the ouvert-clos rhyme-scheme shared by all three demanded a musical realization which contributed directly to the modern notion of antecedent and consequent phrases. It was in this period, too, in which began the long tradition of setting the mass ordinary. This tradition started around mid-century with isolated or paired settings of Kyries, Glorias, etc., but Machaut composed what is thought to be the first complete mass conceived as one composition. The sound world of Ars Nova music is very much one of linear primacy and rhythmic complexity. “Resting” intervals are the fifth and octave, with thirds and sixths considered dissonances. Leaps of more than a sixth in individual voices are not uncommon, leading to speculation of instrumental participation at least in secular performance.
Surviving French manuscripts include the Ivrea Codex and the Apt Codex.
Italy: Trecento
Most of the music of Ars nova was French in origin; however, the term is often loosely applied to all of the music of the fourteenth century, especially to include the secular music in Italy. There this period was often referred to as Trecento.
Italian music has always, it seems, been known for its lyrical or melodic character, and this goes back to the fourteenth century in many respects. Italian secular music of this time (what little surviving liturgical music there is, is similar to the French except for somewhat different notation) featured what has been called the cantalina style, with a florid top voice supported by two (or even one; a fair amount of Italian Trecento music is for only two voices) that are more regular and slower moving. This type of texture remained a feature of Italian music in the popular fifteenth- and sixteenth-century secular genres as well, and was an important influence on the eventual development of the trio texture that revolutionized music in the seventeenth.
There were three main forms for secular works in the Trecento. One was the madrigal, not the same as that of 150–250 years later, but with a verse/refrain-like form. Three-line stanzas, each with different words, alternated with a two-line ritornello, with the same text at each appearance. Perhaps we can see the seeds of the subsequent late-Renaissance and Baroque ritornello in this device; it too returns again and again, recognizable each time, in contrast with its surrounding disparate sections. Another form, the caccia (“chase,”) was written for two voices in a canon at the unison. Sometimes, this form also featured a ritornello, which was occasionally also in a canonic style. Usually, the name of this genre provided a double meaning, since the texts of caccia were primarily about hunts and related outdoor activities, or at least action-filled scenes. The third main form was the ballata, which was roughly equivalent to the French virelai.
Surviving Italian manuscripts include the Squarcialupi Codex and the Rossi Codex.
For information about specific Italian composers writing in the late medieval era, see Francesco Landini, Gherardello da Firenze, Andrea da Firenze, Lorenzo da Firenze, Giovanni da Firenze (aka Giovanni da Cascia), Bartolino da Padova, Jacopo da Bologna, Donato da Cascia, Lorenzo Masini, Niccolò da Perugia, and Maestro Piero.
Germany: Geisslerlieder
The Geisslerlieder were the songs of wandering bands of flagellants, who sought to appease the wrath of an angry God by penitential music accompanied by mortification of their bodies. There were two separate periods of activity of Geisslerlied: one around the middle of the thirteenth century, from which, unfortunately, no music survives (although numerous lyrics do); and another from 1349, for which both words and music survive intact due to the attention of a single priest who wrote about the movement and recorded its music. This second period corresponds to the spread of the Black Death in Europe, and documents one of the most terrible events in European history. Both periods of Geisslerlied activity were mainly in Germany.
There was also French-influenced polyphony written in German areas at this time, but it was somewhat less sophisticated than its models. In fairness to the mostly anonymous composers of this repertoire, however, most of the surviving manuscripts seem to have been copied with extreme incompetence, and are filled with errors that make a truly thorough evaluation of the music’s quality impossible.
Mannerism and Ars Subtilior

The chanson Belle, bonne, sage by Baude Cordier, an Ars subtilior piece included in the Chantilly Codex
As often seen at the end of any musical era, the end of the medieval era is marked by a highly manneristic style known as Ars subtilior. In some ways, this was an attempt to meld the French and Italian styles. This music was highly stylized, with a rhythmic complexity that was not matched until the twentieth century. In fact, not only was the rhythmic complexity of this repertoire largely unmatched for five and a half centuries, with extreme syncopations, mensural trickery, and even examples of augenmusik (such as a chanson by Baude Cordier written out in manuscript in the shape of a heart), but also its melodic material was quite complex as well, particularly in its interaction with the rhythmic structures. Already discussed under Ars Nova has been the practice of isorhythm, which continued to develop through late-century and in fact did not achieve its highest degree of sophistication until early in the fifteenth century. Instead of using isorhythmic techniques in one or two voices, or trading them among voices, some works came to feature a pervading isorhythmic texture which rivals the integral serialism of the twentieth century in its systematic ordering of rhythmic and tonal elements. The term “mannerism” was applied by later scholars, as it often is, in response to an impression of sophistication being practised for its own sake, a malady which some authors have felt infected the Ars subtilior.
One of the most important extant sources of Ars Subtilior chansons is the Chantilly Codex.
For information about specific composers writing music in Ars subtilior style, see Anthonello de Caserta, Philippus de Caserta (aka Philipoctus de Caserta), Johannes Ciconia, Matteo da Perugia, Lorenzo da Firenze, Grimace, Jacob Senleches, and Baude Cordier.
Transitioning to the Renaissance
Demarcating the end of the medieval era and the beginning of the Renaissance, with regard to the composition of music, is difficult. While the music of the fourteenth century is fairly obviously medieval in conception, the music of the early fifteenth century is often conceived as belonging to a transitional period, not only retaining some of the ideals of the end of the Middle Ages (such as a type of polyphonic writing in which the parts differ widely from each other in character, as each has its specific textural function), but also showing some of the characteristic traits of the Renaissance (such as the international style developing through the diffusion of Franco-Flemish musicians throughout Europe, and in terms of texture an increasing equality of parts).
Music historians do not agree on when the Renaissance era began, but most historians agree that England was still a medieval society in the early fifteenth century (see periodization issues of the Middle Ages). While there is no consensus, 1400 is a useful marker, because it was around that time that the Renaissance came into full swing in Italy.
The increasing reliance on the interval of the third as a consonance is one of the most pronounced features of transition into the Renaissance. Polyphony, in use since the twelfth century, became increasingly elaborate with highly independent voices throughout the fourteenth century. With John Dunstaple and other English composers, partly through the local technique offaburden (an improvisatory process in which a chant melody and a written part predominantly in parallel sixths above it are ornamented by one sung in perfect fourths below the latter, and which later took hold on the continent as “fauxbordon”), the interval of the third emerges as an important musical development; because of this Contenance Angloise (“English countenance”), English composers’ music is often regarded as the first to sound less truly bizarre to modern, unschooled audiences. English stylistic tendencies in this regard had come to fruition and began to influence continental composers as early as the 1420s, as can be seen in works of the young Dufay, among others. While the Hundred Years’ War continued, English nobles, armies, their chapels and retinues, and therefore some of their composers, travelled in France and performed their music there; it must also of course be remembered that the English controlled portions of northern France at this time.
English manuscripts include the Worcester Fragments, the Old St. Andrews Music Book, the Old Hall Manuscript, and Egerton Manuscript.
For information about specific composers who are considered transitional between the medieval and the Renaissance, see Zacara da Teramo, Paolo da Firenze, Giovanni Mazzuoli,Antonio da Cividale, Antonius Romanus, Bartolomeo da Bologna, Roy Henry, Arnold de Lantins, Leonel Power, and John Dunstaple.
Mass
The earliest musical settings of the Mass are Gregorian chant. The different portions of the Ordinary came into the liturgy at different times, with the Kyrie probably being first (perhaps as early as the seventh century) and the Credo being last (it did not become part of the Roman mass until 1014).
In the early fourteenth century, composers began writing polyphonic versions of the sections of the Ordinary. The reason for this surge in interest is not known, but it has been suggested that there was a shortage of new music since composers were increasingly attracted to secular music, and overall interest in writing sacred music had entered a period of decline. The non-changing part of the mass, the Ordinary, then would have music which was available for performance all the time.
Two manuscripts of the fourteenth century, the Ivrea Codex and the Apt Codex, are the primary sources for polyphonic settings of the Ordinary. Stylistically these settings are similar to bothmotets and secular music of the time, with a three-voice texture dominated by the highest part. Most of this music was written or assembled at the papal court at Avignon.
Several anonymous complete masses from the foureenth century survive, including the Tournai Mass; however, discrepancies in style indicate that the movements of these masses were written by several composers and later compiled by scribes into a single set. The first complete Mass we know of whose composer can be identified was the Messe de Nostre Dame (Mass of Our Lady) by Guillaume de Machaut in the fourteenth century.
Candela Citations
- Medieval music. Provided by: Wiipedia. Located at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Medieval_music. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Mass (music). Provided by: Wikipedia. Located at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mass_(music). License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Partitura de Alleluia Nativitas. Authored by: Marta and Laura. Located at: https://www.flickr.com/photos/54863957@N07/5147906673/. License: CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial
- CantigasDeSantaMariaPanPipes. Provided by: Wikimedia. Located at: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:CantigasDeSantaMariaPanPipes.jpg. License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright
- Peire Raimon de Toulouse. Provided by: Wikimedia. Located at: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:BnF_ms._12473_fol._68v_-_Peire_Raimon_de_Toulouse_(1).jpg. License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright
- Roman de Fauvel. Provided by: Wikimedia. Located at: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Roman_de_Fauvel.jpg. License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright


