Learning Outcomes
- Understand and use the inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions.
- Find the exact value of expressions involving the inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions.
- Use a calculator to evaluate inverse trigonometric functions.
- Use inverse trigonometric functions to solve right triangles.
- Find exact values of composite functions with inverse trigonometric functions.
Understanding and Using the Inverse Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Functions
In order to use inverse trigonometric functions, we need to understand that an inverse trigonometric function “undoes” what the original trigonometric function “does,” as is the case with any other function and its inverse. In other words, the domain of the inverse function is the range of the original function, and vice versa, as summarized in Figure 1.

Figure 1
For example, if [latex]f(x)=\sin x[/latex], then we would write [latex]f^{1}(x)={\sin}^{-1}{x}[/latex]. Be aware that [latex]{\sin}^{-1}x[/latex] does not mean [latex]\frac{1}{\sin{x}}[/latex]. The following examples illustrate the inverse trigonometric functions:
- Since [latex]\sin\left(\frac{\pi}{6}\right)=\frac{1}{2}[/latex], then [latex]\frac{\pi}{6}=\sin^{−1}(\frac{1}{2})[/latex].
- Since [latex]\cos(\pi)=−1[/latex], then [latex]\pi=\cos^{−1}(−1)[/latex].
- Since [latex]\tan\left(\frac{\pi}{4}\right)=1[/latex], then [latex]\frac{\pi}{4}=\tan^{−1}(1)[/latex].
In previous sections, we evaluated the trigonometric functions at various angles, but at times we need to know what angle would yield a specific sine, cosine, or tangent value. For this, we need inverse functions. Recall that, for a one-to-one function, if [latex]f(a)=b[/latex], then an inverse function would satisfy [latex]f^{−1}(b)=a[/latex].
Bear in mind that the sine, cosine, and tangent functions are not one-to-one functions. The graph of each function would fail the horizontal line test. In fact, no periodic function can be one-to-one because each output in its range corresponds to at least one input in every period, and there are an infinite number of periods. As with other functions that are not one-to-one, we will need to restrict the domain of each function to yield a new function that is one-to-one. We choose a domain for each function that includes the number 0. Figure 2 shows the graph of the sine function limited to [latex]\left[\frac{−\pi}{2}\text{, }\frac{\pi}{2}\right][/latex] and the graph of the cosine function limited to [0, π].
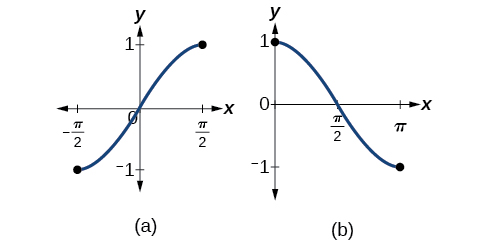
Figure 2. (a) Sine function on a restricted domain of [latex]\left[−\frac{\pi}{2}\text{, }\frac{\pi}{2}\right][/latex]; (b) Cosine function on a restricted domain of [0, π]
Figure 3 shows the graph of the tangent function limited to [latex]\left(−\frac{\pi}{2}\text{, }\frac{\pi}{2}\right)[/latex].
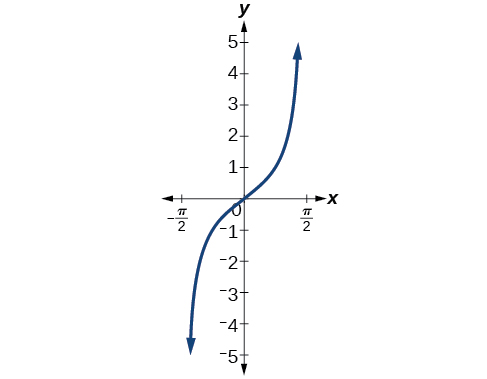
Figure 3. Tangent function on a restricted domain of [latex]\left(−\frac{\pi}{2}\text{, }\frac{\pi}{2}\right)[/latex]
These conventional choices for the restricted domain are somewhat arbitrary, but they have important, helpful characteristics. Each domain includes the origin and some positive values, and most importantly, each results in a one-to-one function that is invertible. The conventional choice for the restricted domain of the tangent function also has the useful property that it extends from one vertical asymptote to the next instead of being divided into two parts by an asymptote.
On these restricted domains, we can define the inverse trigonometric functions.
- The inverse sine function [latex]y=\sin^{−1}x[/latex] means [latex]x=\sin y[/latex]. The inverse sine function is sometimes called the arcsine function, and notated arcsin x.
[latex]y=\sin^{−1}x[/latex] has domain [−1, 1] and range [latex]\left[−\frac{\pi}{2}\text{, }\frac{\pi}{2}\right][/latex]
- The inverse cosine function [latex]y=\cos^{−1}x[/latex] means [latex]x=\cos y[/latex]. The inverse cosine function is sometimes called the arccosine function, and notated arccos x.
[latex]y=\cos^{−1}x[/latex] has domain [−1, 1] and range [0, π]
- The inverse tangent function [latex]y=\tan^{−1}x[/latex] means [latex]x=\tan y[/latex]. The inverse tangent function is sometimes called the arctangent function, and notated arctan x.
[latex]y=\tan^{−1}x[/latex] has domain (−∞, ∞) and range [latex]\left(−\frac{\pi}{2}\text{, }\frac{\pi}{2}\right)[/latex]
The graphs of the inverse functions are shown in Figure 4, Figure 5, and Figure 6. Notice that the output of each of these inverse functions is a number, an angle in radian measure. We see that [latex]\sin^{−1}x[/latex] has domain [−1, 1] and range [latex]\left[−\frac{\pi}{2}\text{, }\frac{\pi}{2}\right][/latex], [latex]\cos^{−1}x[/latex] has domain [−1, 1] and range [0, π], and [latex]\tan^{−1}x[/latex] has domain of all real numbers and range [latex]\left(−\frac{\pi}{2}\text{, }\frac{\pi}{2}\right)[/latex]. To find the domain and range of inverse trigonometric functions, switch the domain and range of the original functions. Each graph of the inverse trigonometric function is a reflection of the graph of the original function about the line [latex]y=x[/latex].
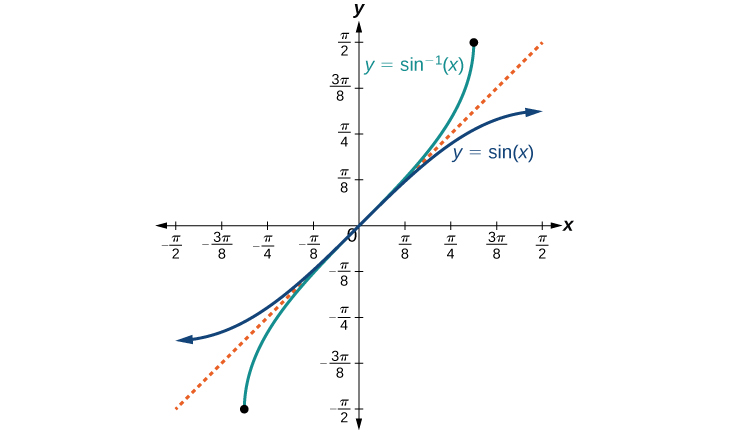
Figure 4. The sine function and inverse sine (or arcsine) function
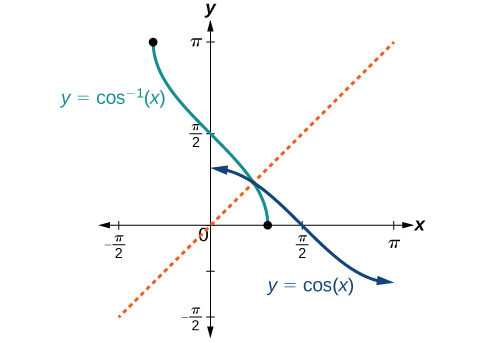
Figure 5. The cosine function and inverse cosine (or arccosine) function
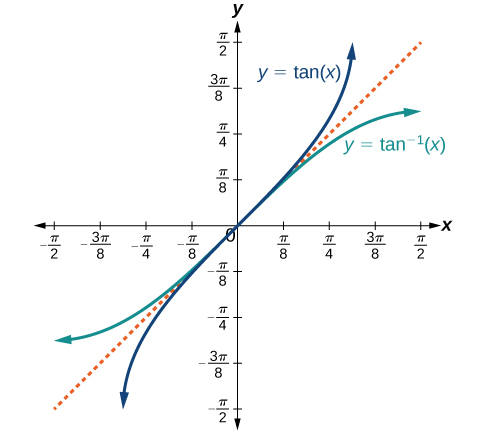
Figure 6. The tangent function and inverse tangent (or arctangent) function
A General Note: Relations for Inverse Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Functions
For angles in the interval [latex]\left[−\frac{\pi}{2}\text{, }\frac{\pi}{2}\right][/latex], if [latex]\sin y=x[/latex], then [latex]\sin^{−1}x=y[/latex].
For angles in the interval [0, π], if [latex]\cos y=x[/latex], then [latex]\cos^{−1}x=y[/latex].
For angles in the interval [latex]\left(−\frac{\pi}{2}\text{, }\frac{\pi}{2}\right)[/latex], if [latex]\tan y=x[/latex], then [latex]\tan^{−1}x=y[/latex].
Example 1: Writing a Relation for an Inverse Function
Given [latex]\sin\left(\frac{5\pi}{12}\right)\approx 0.96593[/latex], write a relation involving the inverse sine.
Try It
Given [latex]\cos(0.5)\approx 0.8776[/latex], write a relation involving the inverse cosine.
Finding the Exact Value of Expressions Involving the Inverse Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Functions
Now that we can identify inverse functions, we will learn to evaluate them. For most values in their domains, we must evaluate the inverse trigonometric functions by using a calculator, interpolating from a table, or using some other numerical technique. Just as we did with the original trigonometric functions, we can give exact values for the inverse functions when we are using the special angles, specifically [latex]\frac{\pi}{ 6} (30^\circ)\text{, }\frac{\pi}{ 4} (45^\circ),\text{ and } \frac{\pi}{ 3} (60^\circ)[/latex], and their reflections into other quadrants.
How To: Given a “special” input value, evaluate an inverse trigonometric function.
- Find angle x for which the original trigonometric function has an output equal to the given input for the inverse trigonometric function.
- If x is not in the defined range of the inverse, find another angle y that is in the defined range and has the same sine, cosine, or tangent as x, depending on which corresponds to the given inverse function.
Example 2: Evaluating Inverse Trigonometric Functions for Special Input Values
Evaluate each of the following.
a. [latex]\sin−1\left(\frac{1}{2}\right)[/latex]
b. [latex]\sin−1\left(−\frac{2}{\sqrt{2}}\right)[/latex]
c. [latex]\cos−1\left(−\frac{3}{\sqrt{2}}\right)[/latex]
d. [latex]\tan^{− 1}(1)[/latex]
Try It
Evaluate each of the following.
- [latex]\sin^{−1}(−1)[/latex]
- [latex]\tan^{−1}(−1)[/latex]
- [latex]\cos^{−1}(−1)[/latex]
- [latex]\cos^{−1}(\frac{1}{2})[/latex]
Try It
Using a Calculator to Evaluate Inverse Trigonometric Functions
To evaluate inverse trigonometric functions that do not involve the special angles discussed previously, we will need to use a calculator or other type of technology. Most scientific calculators and calculator-emulating applications have specific keys or buttons for the inverse sine, cosine, and tangent functions. These may be labeled, for example, SIN-1, ARCSIN, or ASIN.
In the previous chapter, we worked with trigonometry on a right triangle to solve for the sides of a triangle given one side and an additional angle. Using the inverse trigonometric functions, we can solve for the angles of a right triangle given two sides, and we can use a calculator to find the values to several decimal places.
In these examples and exercises, the answers will be interpreted as angles and we will use θ as the independent variable. The value displayed on the calculator may be in degrees or radians, so be sure to set the mode appropriate to the application.
Example 3: Evaluating the Inverse Sine on a Calculator
Evaluate [latex]\sin^{−1}(0.97)[/latex] using a calculator.
Try It
Evaluate [latex]\cos^{−1}(−0.4)[/latex] using a calculator.
Try It
How To: Given two sides of a right triangle like the one shown in Figure 7, find an angle.
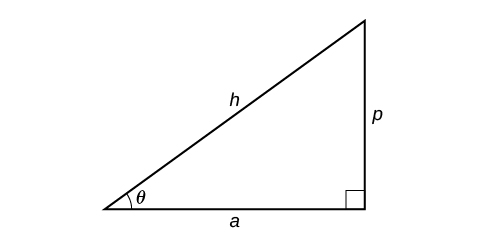
Figure 7
- If one given side is the hypotenuse of length h and the side of length a adjacent to the desired angle is given, use the equation [latex]\theta=\cos^{−1}\left(\frac{a}{h}\right)[/latex].
- If one given side is the hypotenuse of length h and the side of length p opposite to the desired angle is given, use the equation [latex]\theta=\sin^{−1}\left(\frac{p}{h}\right)[/latex].
- If the two legs (the sides adjacent to the right angle) are given, then use the equation [latex]\theta=\tan^{−1}\left(\frac{p}{a}\right)[/latex].
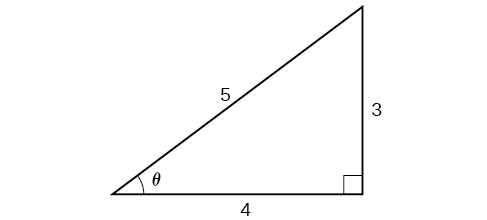
Example 4: Applying the Inverse Cosine to a Right Triangle
Solve the triangle in Figure 8 for the angle θ.
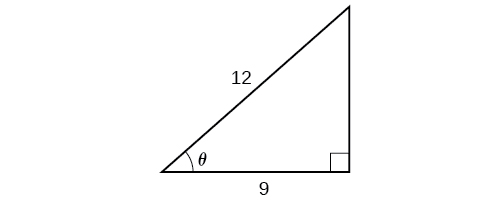
Figure 8
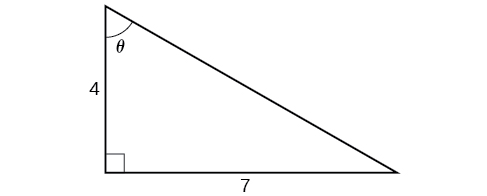
Try It
Solve the triangle in Figure 9 for the angle θ.
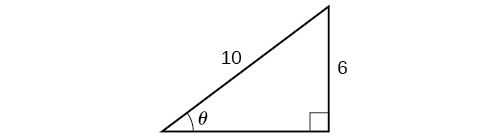
Figure 9
Try It
Finding Exact Values of Composite Functions with Inverse Trigonometric Functions
There are times when we need to compose a trigonometric function with an inverse trigonometric function. In these cases, we can usually find exact values for the resulting expressions without resorting to a calculator. Even when the input to the composite function is a variable or an expression, we can often find an expression for the output. To help sort out different cases, let f(x) and g(x) be two different trigonometric functions belonging to the set {sin(x), cos(x), tan(x)} and let [latex]f^{−1}(y)[/latex] and [latex]g^{−1}(y)[/latex] be their inverses.
Evaluating Compositions of the Form [latex]f\left(f^{−1}(y)\right)[/latex] and [latex]f^{−1}(f(x))[/latex]
For any trigonometric function, [latex]f(f^{−1}(y))=y[/latex] for all y in the proper domain for the given function. This follows from the definition of the inverse and from the fact that the range of f was defined to be identical to the domain of [latex]f^{−1}[/latex]. However, we have to be a little more careful with expressions of the form [latex]f^{−1}(f(x))[/latex].
A General Note: Compositions of a trigonometric function and its inverse
[latex]\begin{align} &\sin(\sin^{−1}x)=x\text{ for }−1\leq x\leq1\\ &\cos(\cos^{−1}x)=x\text{ for }−\infty\leq x\leq1 \\ &\tan(\tan^{−1}x)=x\text{ for }−\infty\text{ < }x\text{ < }\infty \end{align}[/latex]
[latex]\begin{align} \hfill &\sin^{−1}(\sin x)=x\text{ only for }−\frac{\pi}{2} \leq x \leq \frac{\pi}{2} \hfill \\ &\cos^{−1}(\cos x)=x\text{ only for }0\leq x\leq\pi \hfill \\ &\tan^{−1}(\tan x)=x\text{ only for }−\frac{\pi}{2}\text{ < }x\text{ < }\frac{\pi}{2} \end{align}[/latex]
Q & A
Is it correct that [latex]\sin^{−1}(\sin x)=x[/latex]?
No. This equation is correct if x belongs to the restricted domain [latex]\left[−\frac{\pi}{2},\frac{\pi}{2}\right][/latex], but sine is defined for all real input values, and for x outside the restricted interval, the equation is not correct because its inverse always returns a value in [latex]\left[−\frac{\pi}{2},\frac{\pi}{2}\right][\latex]. The situation is similar for cosine and tangent and their inverses. For example, [latex]\sin^{−1}\left(\sin\left(\frac{3\pi}{4}\right)\right)=\frac{\pi}{4}[/latex].
How To:
Given an expression of the form [latex]f^{−1}(f(\theta))[/latex] where [latex]f(\theta)=\sin\theta\text{, }\cos\theta\text{, or }\tan\theta[/latex], evaluate.
- If θ is in the restricted domain of f, then [latex]f^{−1}(f(\theta))=\theta[/latex].
- If not, then find an angle ϕ within the restricted domain of f such that [latex]f(\phi)=f(\theta)[/latex]. Then [latex]f^{−1}(f(\theta))=\phi[/latex].
Example 5: Using Inverse Trigonometric Functions
Evaluate the following:
- [latex]\sin^{−1}(\sin(\frac{\pi}{3}))[/latex]
- [latex]\sin^{−1}(\sin(\frac{2\pi}{3}))[/latex]
- [latex]\cos^{−1}(\cos(\frac{2\pi}{3}))[/latex]
- [latex]\cos^{−1}(\cos(−\frac{\pi}{3}))[/latex]
Try It
Evaluate [latex]\tan^{−1}\left(\tan\left(\frac{\pi}{8}\right)\right)[/latex] and [latex]\tan^{−1}\left(\tan\left(\frac{11\pi}{9}\right)\right)[/latex].
Evaluating Compositions of the Form [latex]f^{−1}(g(x))[/latex]
Now that we can compose a trigonometric function with its inverse, we can explore how to evaluate a composition of a trigonometric function and the inverse of another trigonometric function. We will begin with compositions of the form [latex]f^{−1}(g(x))[/latex]. For special values of x, we can exactly evaluate the inner function and then the outer, inverse function. However, we can find a more general approach by considering the relation between the two acute angles of a right triangle where one is θ, making the other [latex]\frac{\pi}{2}−\theta[/latex]. Consider the sine and cosine of each angle of the right triangle in Figure 10.
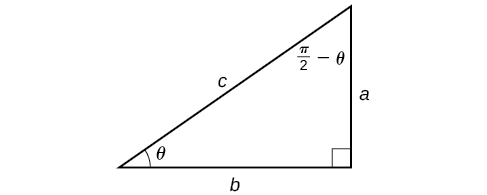
Figure 10. Right triangle illustrating the cofunction relationships
Because [latex]\cos\theta=\frac{b}{c}=\sin\left(\frac{\pi}{2}−\theta\right)[/latex], we have [latex]\sin^{−1}(\cos\theta)=\frac{\pi}{2}−\theta\text{ if }0\leq\theta\leq\pi[/latex]. If θ is not in this domain, then we need to find another angle that has the same cosine as θ and does belong to the restricted domain; we then subtract this angle from [latex]\frac{\pi}{2}[/latex]. Similarly, [latex]\sin\theta=\frac{a}{c}=\cos\left(\frac{\pi}{2}−\theta\right)[/latex], so [latex]\cos^{−1}(\sin\theta)=\frac{\pi}{2}−\theta\text{ if }−\frac{\pi}{2}\leq\theta\leq\frac{\pi}{2}[/latex]. These are just the function-cofunction relationships presented in another way.
How To: Given functions of the form [latex]\sin^{−1}(\cos x)\text{ and }\cos^{−1}(\sin x)[/latex], evaluate them.
- If x is in [0,π], then [latex]\sin^{−1}(\cos x)=\frac{\pi}{2}−x[/latex].
- If x is not in [0,π], then find another angle y in [0,π] such that [latex]\cos y=\cos x[/latex].
[latex]\sin^{−1}(\cos x)=\frac{\pi}{2}−y[/latex]
- If x is in [latex]\left[−\frac{\pi}{2},\frac{\pi}{2}\right][/latex], then [latex]\cos^{−1}(\sin x)=\frac{\pi}{2}−x[/latex].
- If x is not in [latex]\left[−\frac{\pi}{2},\frac{\pi}{2}\right][/latex], then find another angle y in [latex]\left[−\frac{\pi}{2}\text{, }\frac{\pi}{2}\right][/latex] such that [latex]\sin y=\sin x[/latex].
[latex]\cos^{−1}(\sin x)=\frac{\pi}{2}−y[/latex]
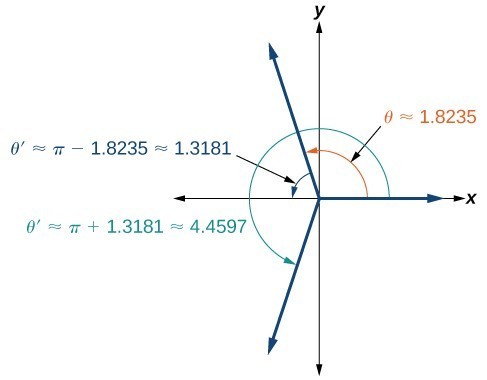
Example 6: Evaluating the Composition of an Inverse Sine with a Cosine
Evaluate [latex]\sin^{−1}(\cos(\frac{13\pi}{6}))[/latex]
- by direct evaluation.
- by the method described previously.
Try It
Evaluate [latex]\cos^{−1}(\sin(−\frac{11\pi}{4}))[/latex].
Try It
Evaluating Compositions of the Form [latex]f(g^{−1}(x))[/latex]
To evaluate compositions of the form [latex]f(g^{−1}(x))[/latex], where f and g are any two of the functions sine, cosine, or tangent and x is any input in the domain of [latex]g−1[/latex], we have exact formulas, such as [latex]\sin\left({\cos}^{−1}x\right)=\sqrt{1−{x}^{2}}[/latex]. When we need to use them, we can derive these formulas by using the trigonometric relations between the angles and sides of a right triangle, together with the use of Pythagoras’s relation between the lengths of the sides. We can use the Pythagorean identity, [latex]\sin^{2}x+cos^{2}x=1[/latex], to solve for one when given the other. We can also use the inverse trigonometric functions to find compositions involving algebraic expressions.
Example 7: Evaluating the Composition of a Sine with an Inverse Cosine
Find an exact value for [latex]\sin\left(\cos^{−1}\left(\frac{4}{5}\right)\right)[/latex].
Try It
Evaluate [latex]\cos(\tan^{−1}(\frac{5}{12}))[/latex].
Example 8: Evaluating the Composition of a Sine with an Inverse Tangent
Find an exact value for [latex]\sin\left(\tan^{−1}\left(\frac{7}{4}\right)\right)[/latex].
Try It
Evaluate [latex]\cos(\sin^{−1}(\frac{7}{9}))[/latex].
Try It
Example 9: Finding the Cosine of the Inverse Sine of an Algebraic Expression
Find a simplified expression for [latex]\cos\left(\sin^{−1}\left(\frac{x}{3}\right)\right)[/latex] for [latex]−3\leq x\leq3[/latex].
Try It
Find a simplified expression for [latex]\sin\left(\tan^{−1}\left(4x\right)\right)\\[/latex] for [latex]−\frac{1}{4}\leq x \leq\frac{1}{4}[/latex].
Try It
Solving Linear Trigonometric Equations in Sine and Cosine
Trigonometric equations are, as the name implies, equations that involve trigonometric functions. Similar in many ways to solving polynomial equations or rational equations, only specific values of the variable will be solutions, if there are solutions at all. Often we will solve a trigonometric equation over a specified interval. However, just as often, we will be asked to find all possible solutions, and as trigonometric functions are periodic, solutions are repeated within each period. In other words, trigonometric equations may have an infinite number of solutions. Additionally, like rational equations, the domain of the function must be considered before we assume that any solution is valid. The period of both the sine function and the cosine function is [latex]2\pi[/latex]. In other words, every [latex]2\pi[/latex] units, the y-values repeat. If we need to find all possible solutions, then we must add [latex]2\pi k[/latex], where [latex]k[/latex] is an integer, to the initial solution. Recall the rule that gives the format for stating all possible solutions for a function where the period is [latex]2\pi :[/latex]
There are similar rules for indicating all possible solutions for the other trigonometric functions. Solving trigonometric equations requires the same techniques as solving algebraic equations. We read the equation from left to right, horizontally, like a sentence. We look for known patterns, factor, find common denominators, and substitute certain expressions with a variable to make solving a more straightforward process. However, with trigonometric equations, we also have the advantage of using the identities we developed in the previous sections.
Example 10: Solving a Linear Trigonometric Equation Involving the Cosine Function
Find all possible exact solutions for the equation [latex]\cos \theta =\frac{1}{2}[/latex].
Example 11: Solving a Linear Equation Involving the Sine Function
Find all possible exact solutions for the equation [latex]\sin t=\frac{1}{2}[/latex].
How To: Given a trigonometric equation, solve using algebra.
- Look for a pattern that suggests an algebraic property, such as the difference of squares or a factoring opportunity.
- Substitute the trigonometric expression with a single variable, such as [latex]x[/latex] or [latex]u[/latex].
- Solve the equation the same way an algebraic equation would be solved.
- Substitute the trigonometric expression back in for the variable in the resulting expressions.
- Solve for the angle.
Example 12: Solve the Trigonometric Equation in Linear Form
Solve the equation exactly: [latex]2\cos \theta -3=-5,0\le \theta <2\pi[/latex].
Try It
Solve exactly the following linear equation on the interval [latex]\left[0,2\pi \right):2\sin x+1=0[/latex].
Try It
Solve Trigonometric Equations Using a Calculator
Not all functions can be solved exactly using only the unit circle. When we must solve an equation involving an angle other than one of the special angles, we will need to use a calculator. Make sure it is set to the proper mode, either degrees or radians, depending on the criteria of the given problem.
Example 13: Using a Calculator to Solve a Trigonometric Equation Involving Sine
Use a calculator to solve the equation [latex]\sin \theta =0.8[/latex], where [latex]\theta[/latex] is in radians.
Example 14: Using a Calculator to Solve a Trigonometric Equation Involving Secant
Use a calculator to solve the equation [latex]\sec \theta =-4[/latex], giving your answer in radians.
Try It
Solve [latex]\cos \theta =-0.2[/latex].
Try It
Solving Equations Involving a Single Trigonometric Function
When we are given equations that involve only one of the six trigonometric functions, their solutions involve using algebraic techniques and the unit circle. We need to make several considerations when the equation involves trigonometric functions other than sine and cosine. Problems involving the reciprocals of the primary trigonometric functions need to be viewed from an algebraic perspective. In other words, we will write the reciprocal function, and solve for the angles using the function. Also, an equation involving the tangent function is slightly different from one containing a sine or cosine function. First, as we know, the period of tangent is [latex]\pi[/latex], not [latex]2\pi[/latex]. Further, the domain of tangent is all real numbers with the exception of odd integer multiples of [latex]\frac{\pi }{2}[/latex], unless, of course, a problem places its own restrictions on the domain.
Example 15: Solving a Problem Involving a Single Trigonometric Function
Solve the problem exactly: [latex]2{\sin }^{2}\theta -1=0,0\le \theta <2\pi[/latex].
Example 16: Solving a Trigonometric Equation Involving Cosecant
Solve the following equation exactly: [latex]\csc \theta =-2,0\le \theta <4\pi[/latex].
Example 17: Solving an Equation Involving Tangent
Solve the equation exactly: [latex]\tan \left(\theta -\frac{\pi }{2}\right)=1,0\le \theta <2\pi[/latex].
Try It
Find all solutions for [latex]\tan x=\sqrt{3}[/latex].
Try It
Example 18: Identify all Solutions to the Equation Involving Tangent
Identify all exact solutions to the equation [latex]2\left(\tan x+3\right)=5+\tan x,0\le x<2\pi[/latex].
Solving Trigonometric Equations in Quadratic Form
Solving a quadratic equation may be more complicated, but once again, we can use algebra as we would for any quadratic equation. Look at the pattern of the equation. Is there more than one trigonometric function in the equation, or is there only one? Which trigonometric function is squared? If there is only one function represented and one of the terms is squared, think about the standard form of a quadratic. Replace the trigonometric function with a variable such as [latex]x[/latex] or [latex]u[/latex]. If substitution makes the equation look like a quadratic equation, then we can use the same methods for solving quadratics to solve the trigonometric equations.
Example 19: Solving a Trigonometric Equation in Quadratic Form
Solve the equation exactly: [latex]{\cos }^{2}\theta +3\cos \theta -1=0,0\le \theta <2\pi[/latex].
Example 20: Solving a Trigonometric Equation in Quadratic Form by Factoring
Solve the equation exactly: [latex]2{\sin }^{2}\theta -5\sin \theta +3=0,0\le \theta \le 2\pi[/latex].
Try It
Solve [latex]{\sin }^{2}\theta =2\cos \theta +2,0\le \theta \le 2\pi[/latex]. [Hint: Make a substitution to express the equation only in terms of cosine.]
Try It
Example 21: Solving a Trigonometric Equation Using Algebra
Solve exactly:
[latex]2{\sin }^{2}\theta +\sin \theta =0;0\le \theta <2\pi[/latex]
Example 22: Solving a Trigonometric Equation Quadratic in Form
Solve the equation quadratic in form exactly: [latex]2{\sin }^{2}\theta -3\sin \theta +1=0,0\le \theta <2\pi[/latex].
Try It
Solve the quadratic equation [latex]2{\cos }^{2}\theta +\cos \theta =0[/latex].
Key Concepts
- An inverse function is one that “undoes” another function. The domain of an inverse function is the range of the original function and the range of an inverse function is the domain of the original function.
- Because the trigonometric functions are not one-to-one on their natural domains, inverse trigonometric functions are defined for restricted domains.
- For any trigonometric function [latex]f(x)[/latex], if [latex]x=f^{−1}(y)[/latex], then [latex]f(x)=y[/latex]. However, [latex]f(x)=y[/latex] only implies [latex]x=f^{−1}(y)[/latex] if x is in the restricted domain of f.
- Special angles are the outputs of inverse trigonometric functions for special input values; for example, [latex]\frac{\pi}{4}=\tan^{−1}( 1 )\text{ and }\frac{\pi}{6}=\sin^{−1}(\frac{1}{2})[/latex].
- A calculator will return an angle within the restricted domain of the original trigonometric function.
- Inverse functions allow us to find an angle when given two sides of a right triangle.
- In function composition, if the inside function is an inverse trigonometric function, then there are exact expressions; for example, [latex]\sin\left(\cos^{−1}\left(x\right)\right)=\sqrt{1−x^{2}}[/latex].
- If the inside function is a trigonometric function, then the only possible combinations are [latex]\sin^{−1}\left(\cos x\right)=\frac{\pi}{2}−x[/latex] if [latex]0\leq x\leq\pi[/latex] and [latex]\cos^{−1}\left(\sin x\right)=\frac{\pi}{2}−x[/latex] if [latex]−\frac{\pi}{2}\leq x \leq\frac{\pi}{2}[/latex].
- When evaluating the composition of a trigonometric function with an inverse trigonometric function, draw a reference triangle to assist in determining the ratio of sides that represents the output of the trigonometric function.
- When evaluating the composition of a trigonometric function with an inverse trigonometric function, you may use trig identities to assist in determining the ratio of sides.
- When solving linear trigonometric equations, we can use algebraic techniques just as we do solving algebraic equations. Look for patterns, like the difference of squares, quadratic form, or an expression that lends itself well to substitution.
- Equations involving a single trigonometric function can be solved or verified using the unit circle.
- We can also solve trigonometric equations using a graphing calculator.
- Many equations appear quadratic in form. We can use substitution to make the equation appear simpler, and then use the same techniques we use solving an algebraic quadratic: factoring, the quadratic formula, etc.
Glossary
- arccosine
- another name for the inverse cosine; [latex]\arccos x=\cos^{−1}x[/latex]
- arcsine
- another name for the inverse sine; [latex]\arcsin x=\sin^{−1}x[/latex]
- arctangent
- another name for the inverse tangent; [latex]\arctan x=\tan^{−1}x[/latex]
- inverse cosine function
- the function [latex]\cos^{−1}x[/latex], which is the inverse of the cosine function and the angle that has a cosine equal to a given number
- inverse sine function
- the function [latex]\sin^{−1}x[/latex], which is the inverse of the sine function and the angle that has a sine equal to a given number
- inverse tangent function
- the function [latex]\tan^{−1}x[/latex], which is the inverse of the tangent function and the angle that has a tangent equal to a given number
Candela Citations
- Precalculus. Authored by: OpenStax College. Provided by: OpenStax. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/fd53eae1-fa23-47c7-bb1b-972349835c3c@5.175:1/Preface. License: CC BY: Attribution