The leukocyte, commonly known as a white blood cell (or WBC), is a major component of the body’s defenses against disease. Leukocytes protect the body against invading microorganisms and body cells with mutated DNA, and they clean up debris. Platelets are essential for the repair of blood vessels when damage to them has occurred; they also provide growth factors for healing and repair.

Figure 1. Leukocytes. (Micrographs provided by the Regents of University of Michigan Medical School © 2012)
Characteristics of Leukocytes
Although leukocytes and erythrocytes both originate from hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow, they are very different from each other in many significant ways. For instance, leukocytes are far less numerous than erythrocytes: Typically there are only 5000 to 10,000 per µL. They are also larger than erythrocytes and are the only formed elements that are complete cells, possessing a nucleus and organelles. And although there is just one type of erythrocyte, there are many types of leukocytes. Most of these types have a much shorter lifespan than that of erythrocytes, some as short as a few hours or even a few minutes in the case of acute infection.
One of the most distinctive characteristics of leukocytes is their movement. Whereas erythrocytes spend their days circulating within the blood vessels, leukocytes routinely leave the bloodstream to perform their defensive functions in the body’s tissues. For leukocytes, the vascular network is simply a highway they travel and soon exit to reach their true destination. When they arrive, they are often given distinct names, such as macrophage or microglia, depending on their function. As shown in Figure 2, they leave the capillaries—the smallest blood vessels—or other small vessels through a process known as emigration (from the Latin for “removal”) or diapedesis (dia- = “through”; -pedan = “to leap”) in which they squeeze through adjacent cells in a blood vessel wall.

Figure 2. Leukocytes exit the blood vessel and then move through the connective tissue of the dermis toward the site of a wound. Some leukocytes, such as the eosinophil and neutrophil, are characterized as granular leukocytes. They release chemicals from their granules that destroy pathogens; they are also capable of phagocytosis. The monocyte, an agranular leukocyte, differentiates into a macrophage that then phagocytizes the pathogens.
Once they have exited the capillaries, some leukocytes will take up fixed positions in lymphatic tissue, bone marrow, the spleen, the thymus, or other organs. Others will move about through the tissue spaces very much like amoebas, continuously extending their plasma membranes, sometimes wandering freely, and sometimes moving toward the direction in which they are drawn by chemical signals. This attracting of leukocytes occurs because of positive chemotaxis (literally “movement in response to chemicals”), a phenomenon in which injured or infected cells and nearby leukocytes emit the equivalent of a chemical “911” call, attracting more leukocytes to the site. In clinical medicine, the differential counts of the types and percentages of leukocytes present are often key indicators in making a diagnosis and selecting a treatment.
Classification of Leukocytes
When scientists first began to observe stained blood slides, it quickly became evident that leukocytes could be divided into two groups, according to whether their cytoplasm contained highly visible granules:
- Granular leukocytes contain abundant granules within the cytoplasm. They include neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils.
- While granules are not totally lacking in agranular leukocytes, they are far fewer and less obvious. Agranular leukocytes include monocytes, which mature into macrophages that are phagocytic, and lymphocytes, which arise from the lymphoid stem cell line.
Granular Leukocytes
We will consider the granular leukocytes in order from most common to least common. All of these are produced in the red bone marrow and have a short lifespan of hours to days. They typically have a lobed nucleus and are classified according to which type of stain best highlights their granules (Figure 3).

Figure 3. A neutrophil has small granules that stain light lilac and a nucleus with two to five lobes. An eosinophil’s granules are slightly larger and stain reddish-orange, and its nucleus has two to three lobes. A basophil has large granules that stain dark blue to purple and a two-lobed nucleus.
The most common of all the leukocytes, neutrophils will normally comprise 50–70 percent of total leukocyte count. They are 10–12 µm in diameter, significantly larger than erythrocytes. They are called neutrophils because their granules show up most clearly with stains that are chemically neutral (neither acidic nor basic). The granules are numerous but quite fine and normally appear light lilac. The nucleus has a distinct lobed appearance and may have two to five lobes, the number increasing with the age of the cell. Older neutrophils have increasing numbers of lobes and are often referred to as polymorphonuclear (a nucleus with many forms), or simply “polys.” Younger and immature neutrophils begin to develop lobes and are known as “bands.”
Neutrophils are rapid responders to the site of infection and are efficient phagocytes with a preference for bacteria. Their granules include lysozyme, an enzyme capable of lysing, or breaking down, bacterial cell walls; oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide; and defensins, proteins that bind to and puncture bacterial and fungal plasma membranes, so that the cell contents leak out. Abnormally high counts of neutrophils indicate infection and/or inflammation, particularly triggered by bacteria, but are also found in burn patients and others experiencing unusual stress. A burn injury increases the proliferation of neutrophils in order to fight off infection that can result from the destruction of the barrier of the skin. Low counts may be caused by drug toxicity and other disorders, and may increase an individual’s susceptibility to infection.
Eosinophils typically represent 2–4 percent of total leukocyte count. They are also 10–12 µm in diameter. The granules of eosinophils stain best with an acidic stain known as eosin. The nucleus of the eosinophil will typically have two to three lobes and, if stained properly, the granules will have a distinct red to orange color.
The granules of eosinophils include antihistamine molecules, which counteract the activities of histamines, inflammatory chemicals produced by basophils and mast cells. Some eosinophil granules contain molecules toxic to parasitic worms, which can enter the body through the integument, or when an individual consumes raw or undercooked fish or meat. Eosinophils are also capable of phagocytosis and are particularly effective when antibodies bind to the target and form an antigen-antibody complex. High counts of eosinophils are typical of patients experiencing allergies, parasitic worm infestations, and some autoimmune diseases. Low counts may be due to drug toxicity and stress.
Basophils are the least common leukocytes, typically comprising less than one percent of the total leukocyte count. They are slightly smaller than neutrophils and eosinophils at 8–10 µm in diameter. The granules of basophils stain best with basic (alkaline) stains. Basophils contain large granules that pick up a dark blue stain and are so common they may make it difficult to see the two-lobed nucleus.
In general, basophils intensify the inflammatory response. They share this trait with mast cells. In the past, mast cells were considered to be basophils that left the circulation. However, this appears not to be the case, as the two cell types develop from different lineages.
The granules of basophils release histamines, which contribute to inflammation, and heparin, which opposes blood clotting. High counts of basophils are associated with allergies, parasitic infections, and hypothyroidism. Low counts are associated with pregnancy, stress, and hyperthyroidism.
Agranular Leukocytes
Agranular leukocytes contain smaller, less-visible granules in their cytoplasm than do granular leukocytes. The nucleus is simple in shape, sometimes with an indentation but without distinct lobes. There are two major types of agranulocytes: lymphocytes and monocytes.
Lymphocytes are the only formed element of blood that arises from lymphoid stem cells. Although they form initially in the bone marrow, much of their subsequent development and reproduction occurs in the lymphatic tissues. Lymphocytes are the second most common type of leukocyte, accounting for about 20–30 percent of all leukocytes, and are essential for the immune response. The size range of lymphocytes is quite extensive, with some authorities recognizing two size classes and others three. Typically, the large cells are 10–14 µm and have a smaller nucleus-to-cytoplasm ratio and more granules. The smaller cells are typically 6–9 µm with a larger volume of nucleus to cytoplasm, creating a “halo” effect. A few cells may fall outside these ranges, at 14–17 µm. This finding has led to the three size range classification.
The three major groups of lymphocytes include natural killer cells, B cells, and T cells. Natural killer (NK) cells are capable of recognizing cells that do not express “self” proteins on their plasma membrane or that contain foreign or abnormal markers. These “nonself” cells include cancer cells, cells infected with a virus, and other cells with atypical surface proteins. Thus, they provide generalized, nonspecific immunity. The larger lymphocytes are typically NK cells.
B cells and T cells, also called B lymphocytes and T lymphocytes, play prominent roles in defending the body against specific pathogens (disease-causing microorganisms) and are involved in specific immunity. One form of B cells (plasma cells) produces the antibodies or immunoglobulins that bind to specific foreign or abnormal components of plasma membranes. This is also referred to as humoral (body fluid) immunity. T cells provide cellular-level immunity by physically attacking foreign or diseased cells. A memory cell is a variety of both B and T cells that forms after exposure to a pathogen and mounts rapid responses upon subsequent exposures. Unlike other leukocytes, memory cells live for many years. B cells undergo a maturation process in the bone marrow, whereas T cells undergo maturation in the thymus. This site of the maturation process gives rise to the name B and T cells. The functions of lymphocytes are complex and will be covered in detail in the chapter covering the lymphatic system and immunity. Smaller lymphocytes are either B or T cells, although they cannot be differentiated in a normal blood smear.
Abnormally high lymphocyte counts are characteristic of viral infections as well as some types of cancer. Abnormally low lymphocyte counts are characteristic of prolonged (chronic) illness or immunosuppression, including that caused by HIV infection and drug therapies that often involve steroids.
Monocytes originate from myeloid stem cells. They normally represent 2–8 percent of the total leukocyte count. They are typically easily recognized by their large size of 12–20 µm and indented or horseshoe-shaped nuclei. Macrophages are monocytes that have left the circulation and phagocytize debris, foreign pathogens, worn-out erythrocytes, and many other dead, worn out, or damaged cells. Macrophages also release antimicrobial defensins and chemotactic chemicals that attract other leukocytes to the site of an infection. Some macrophages occupy fixed locations, whereas others wander through the tissue fluid.
Abnormally high counts of monocytes are associated with viral or fungal infections, tuberculosis, and some forms of leukemia and other chronic diseases. Abnormally low counts are typically caused by suppression of the bone marrow.
Platelets
You may occasionally see platelets referred to as thrombocytes, but because this name suggests they are a type of cell, it is not accurate. A platelet is not a cell but rather a fragment of the cytoplasm of a cell called a megakaryocyte that is surrounded by a plasma membrane. Megakaryocytes are descended from myeloid stem cells and are large, typically 50–100 µm in diameter, and contain an enlarged, lobed nucleus. As noted earlier, thrombopoietin, a glycoprotein secreted by the kidneys and liver, stimulates the proliferation of megakaryoblasts, which mature into megakaryocytes.
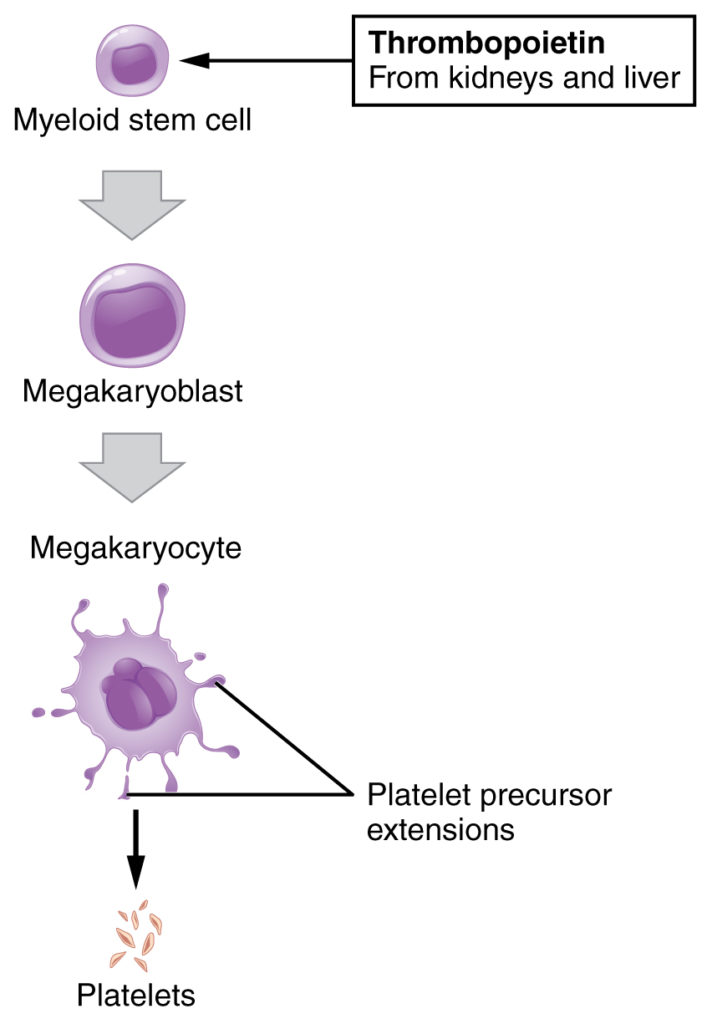
Figure 4. Platelets are derived from cells called megakaryocytes.
These remain within bone marrow tissue (Figure 4) and ultimately form platelet-precursor extensions that extend through the walls of bone marrow capillaries to release into the circulation thousands of cytoplasmic fragments, each enclosed by a bit of plasma membrane. These enclosed fragments are platelets. Each megakarocyte releases 2000–3000 platelets during its lifespan. Following platelet release, megakaryocyte remnants, which are little more than a cell nucleus, are consumed by macrophages.
Platelets are relatively small, 2–4 µm in diameter, but numerous, with typically 150,000–160,000 per µL of blood. After entering the circulation, approximately one-third migrate to the spleen for storage for later release in response to any rupture in a blood vessel. They then become activated to perform their primary function, which is to limit blood loss. Platelets remain only about 10 days, then are phagocytized by macrophages.
Platelets are critical to hemostasis, the stoppage of blood flow following damage to a vessel. They also secrete a variety of growth factors essential for growth and repair of tissue, particularly connective tissue. Infusions of concentrated platelets are now being used in some therapies to stimulate healing.
Thrombocytosis is a condition in which there are too many platelets. This may trigger formation of unwanted blood clots (thrombosis), a potentially fatal disorder. If there is an insufficient number of platelets, called thrombocytopenia, blood may not clot properly, and excessive bleeding may result.
Chapter Review
Leukocytes function in body defenses. They squeeze out of the walls of blood vessels through emigration or diapedesis, then may move through tissue fluid or become attached to various organs where they fight against pathogenic organisms, diseased cells, or other threats to health. Granular leukocytes, which include neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils, originate with myeloid stem cells, as do the agranular monocytes. The other agranular leukocytes, NK cells, B cells, and T cells, arise from the lymphoid stem cell line. The most abundant leukocytes are the neutrophils, which are first responders to infections, especially with bacteria. About 20–30 percent of all leukocytes are lymphocytes, which are critical to the body’s defense against specific threats. Leukemia and lymphoma are malignancies involving leukocytes. Platelets are fragments of cells known as megakaryocytes that dwell within the bone marrow. While many platelets are stored in the spleen, others enter the circulation and are essential for hemostasis; they also produce several growth factors important for repair and healing.
Glossary
agranular leukocytes: leukocytes with few granules in their cytoplasm; specifically, monocytes, lymphocytes, and NK cells
B lymphocytes: (also, B cells) lymphocytes that defend the body against specific pathogens and thereby provide specific immunity
basophils: granulocytes that stain with a basic (alkaline) stain and store histamine and heparin
defensins: antimicrobial proteins released from neutrophils and macrophages that create openings in the plasma membranes to kill cells
diapedesis: (also, emigration) process by which leukocytes squeeze through adjacent cells in a blood vessel wall to enter tissues
emigration: (also, diapedesis) process by which leukocytes squeeze through adjacent cells in a blood vessel wall to enter tissues
eosinophils: granulocytes that stain with eosin; they release antihistamines and are especially active against parasitic worms
granular leukocytes: leukocytes with abundant granules in their cytoplasm; specifically, neutrophils, eosinophils, and basophils
leukemia: cancer involving leukocytes
leukocyte: (also, white blood cell) colorless, nucleated blood cell, the chief function of which is to protect the body from disease
leukocytosis: excessive leukocyte proliferation
leukopenia: below-normal production of leukocytes
lymphocytes: agranular leukocytes of the lymphoid stem cell line, many of which function in specific immunity
lymphoma: form of cancer in which masses of malignant T and/or B lymphocytes collect in lymph nodes, the spleen, the liver, and other tissues
lysozyme: digestive enzyme with bactericidal properties
megakaryocyte: bone marrow cell that produces platelets
memory cell: type of B or T lymphocyte that forms after exposure to a pathogen
monocytes: agranular leukocytes of the myeloid stem cell line that circulate in the bloodstream; tissue monocytes are macrophages
natural killer (NK) cells: cytotoxic lymphocytes capable of recognizing cells that do not express “self” proteins on their plasma membrane or that contain foreign or abnormal markers; provide generalized, nonspecific immunity
neutrophils: granulocytes that stain with a neutral dye and are the most numerous of the leukocytes; especially active against bacteria
polymorphonuclear: having a lobed nucleus, as seen in some leukocytes
positive chemotaxis: process in which a cell is attracted to move in the direction of chemical stimuli
T lymphocytes: (also, T cells) lymphocytes that provide cellular-level immunity by physically attacking foreign or diseased cells
thrombocytes: platelets, one of the formed elements of blood that consists of cell fragments broken off from megakaryocytes
thrombocytopenia: condition in which there are too few platelets, resulting in abnormal bleeding (hemophilia)
thrombocytosis: condition in which there are too many platelets, resulting in abnormal clotting (thrombosis)
Candela Citations
- Anatomy & Physiology. Provided by: OpenStax CNX. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/14fb4ad7-39a1-4eee-ab6e-3ef2482e3e22@8.25. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/14fb4ad7-39a1-4eee-ab6e-3ef2482e3e22@8.25