The function of the digestive system is to break down the foods you eat, release their nutrients, and absorb those nutrients into the body. Although the small intestine is the workhorse of the system, where the majority of digestion occurs, and where most of the released nutrients are absorbed into the blood or lymph, each of the digestive system organs makes a vital contribution to this process.

Figure 1. All digestive organs play integral roles in the life-sustaining process of digestion.
As is the case with all body systems, the digestive system does not work in isolation; it functions cooperatively with the other systems of the body. Consider for example, the interrelationship between the digestive and cardiovascular systems. Arteries supply the digestive organs with oxygen and processed nutrients, and veins drain the digestive tract. These intestinal veins, constituting the hepatic portal system, are unique; they do not return blood directly to the heart. Rather, this blood is diverted to the liver where its nutrients are off-loaded for processing before blood completes its circuit back to the heart. At the same time, the digestive system provides nutrients to the heart muscle and vascular tissue to support their functioning. The interrelationship of the digestive and endocrine systems is also critical. Hormones secreted by several endocrine glands, as well as endocrine cells of the pancreas, the stomach, and the small intestine, contribute to the control of digestion and nutrient metabolism. In turn, the digestive system provides the nutrients to fuel endocrine function. Table 1 gives a quick glimpse at how these other systems contribute to the functioning of the digestive system.
| Table 1. Contribution of Other Body Systems to the Digestive System | |
|---|---|
| Body system | Benefits received by the digestive system |
| Cardiovascular | Blood supplies digestive organs with oxygen and processed nutrients |
| Endocrine | Endocrine hormones help regulate secretion in digestive glands and accessory organs |
| Integumentary | Skin helps protect digestive organs and synthesizes vitamin D for calcium absorption |
| Lymphatic | Mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue and other lymphatic tissue defend against entry of pathogens; lacteals absorb lipids; and lymphatic vessels transport lipids to bloodstream |
| Muscular | Skeletal muscles support and protect abdominal organs |
| Nervous | Sensory and motor neurons help regulate secretions and muscle contractions in the digestive tract |
| Respiratory | Respiratory organs provide oxygen and remove carbon dioxide |
| Skeletal | Bones help protect and support digestive organs |
| Urinary | Kidneys convert vitamin D into its active form, allowing calcium absorption in the small intestine |
Digestive System Organs
The easiest way to understand the digestive system is to divide its organs into two main categories. The first group is the organs that make up the alimentary canal. Accessory digestive organs comprise the second group and are critical for orchestrating the breakdown of food and the assimilation of its nutrients into the body. Accessory digestive organs, despite their name, are critical to the function of the digestive system.
Alimentary Canal Organs
Also called the gastrointestinal (GI) tract or gut, the alimentary canal (aliment- = “to nourish”) is a one-way tube about 7.62 meters (25 feet) in length during life and closer to 10.67 meters (35 feet) in length when measured after death, once smooth muscle tone is lost. The main function of the organs of the alimentary canal is to nourish the body. This tube begins at the mouth and terminates at the anus. Between those two points, the canal is modified as the oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, and small and large intestines to fit the functional needs of the body. Both the mouth and anus are open to the external environment; thus, food and wastes within the alimentary canal are technically considered to be outside the body. Only through the process of absorption do the nutrients in food enter into and nourish the body’s “inner space.”
Accessory Structures
Each accessory digestive organ aids in the breakdown of food. Within the mouth, the teeth and tongue begin mechanical digestion, whereas the salivary glands begin chemical digestion. Once food products enter the small intestine, the gallbladder, liver, and pancreas release secretions—such as bile and enzymes—essential for digestion to continue. Together, these are called accessory organs because they sprout from the lining cells of the developing gut (mucosa) and augment its function; indeed, you could not live without their vital contributions, and many significant diseases result from their malfunction. Even after development is complete, they maintain a connection to the gut by way of ducts.
Digestive Processes
The processes of digestion include six activities: ingestion, propulsion, secretion, digestion, absorption, and defecation.
The first of these processes, ingestion, refers to the entry of food into the alimentary canal through the mouth. There, the food is chewed and mixed with saliva, which contains enzymes that begin breaking down the carbohydrates in the food plus some lipid digestion via lingual lipase. Chewing increases the surface area of the food and allows an appropriately sized bolus to be produced.

Figure 2. Peristalsis moves food through the digestive tract with alternating waves of muscle contraction and relaxation.
Food leaves the mouth when the tongue and pharyngeal muscles propel it into the esophagus. This act of swallowing, the last voluntary act until defecation, is an example of propulsion, which refers to the movement of food through the digestive tract. It includes both the voluntary process of swallowing and the involuntary process of peristalsis. Peristalsis consists of sequential, alternating waves of contraction and relaxation of alimentary wall smooth muscles, which act to propel food along (Figure 2). These waves also play a role in mixing food with digestive juices. Peristalsis is so powerful that foods and liquids you swallow enter your stomach even if you are standing on your head.
Secretion of substances that aid in digestion occurs along the length of the alimentary canal. These substances include saliva, mucus, bile, and various digestive enzymes. Secretion is accomplished by structures in the alimentary canal and by some of the accessory organs.
Digestion includes both mechanical and chemical processes. Mechanical digestion is a purely physical process that does not change the chemical nature of the food. Instead, it makes the food smaller to increase both surface area and mobility. It includes mastication, or chewing, as well as tongue movements that help break food into smaller bits and mix food with saliva. Although there may be a tendency to think that mechanical digestion is limited to the first steps of the digestive process, it occurs after the food leaves the mouth, as well. The mechanical churning of food in the stomach serves to further break it apart and expose more of its surface area to digestive juices, creating an acidic “soup” called chyme. Segmentation, which occurs mainly in the small intestine, consists of localized contractions of circular muscle of the muscularis layer of the alimentary canal. These contractions isolate small sections of the intestine, moving their contents back and forth while continuously subdividing, breaking up, and mixing the contents. By moving food back and forth in the intestinal lumen, segmentation mixes food with digestive juices and facilitates absorption.
In chemical digestion, starting in the mouth, digestive secretions break down complex food molecules into their chemical building blocks (for example, proteins into separate amino acids). These secretions vary in composition, but typically contain water, various enzymes, acids, and salts. The process is completed in the small intestine.
Food that has been broken down is of no value to the body unless it enters the bloodstream and its nutrients are put to work. This occurs through the process of absorption, which takes place primarily within the small intestine. There, most nutrients are absorbed from the lumen of the alimentary canal into the bloodstream through the epithelial cells that make up the mucosa. Lipids are absorbed into lacteals and are transported via the lymphatic vessels to the bloodstream (the subclavian veins near the heart). The details of these processes will be discussed later.
In defecation, the final step in digestion, undigested materials are removed from the body as feces.
Aging and the Digestive System: From Appetite Suppression to Constipation
Age-related changes in the digestive system begin in the mouth and can affect virtually every aspect of the digestive system. Taste buds become less sensitive, so food isn’t as appetizing as it once was. A slice of pizza is a challenge, not a treat, when you have lost teeth, your gums are diseased, and your salivary glands aren’t producing enough saliva. Swallowing can be difficult, and ingested food moves slowly through the alimentary canal because of reduced strength and tone of muscular tissue. Neurosensory feedback is also dampened, slowing the transmission of messages that stimulate the release of enzymes and hormones.
Pathologies that affect the digestive organs—such as hiatal hernia, gastritis, and peptic ulcer disease—can occur at greater frequencies as you age. Problems in the small intestine may include duodenal ulcers, maldigestion, and malabsorption. Problems in the large intestine include hemorrhoids, diverticular disease, and constipation. Conditions that affect the function of accessory organs—and their abilities to deliver pancreatic enzymes and bile to the small intestine—include jaundice, acute pancreatitis, cirrhosis, and gallstones.
In some cases, a single organ is in charge of a digestive process. For example, ingestion occurs only in the mouth and defecation only at the end of the large intestine. However, most digestive processes involve the interaction of several organs and occur gradually as food moves through the alimentary canal (Figure 3).
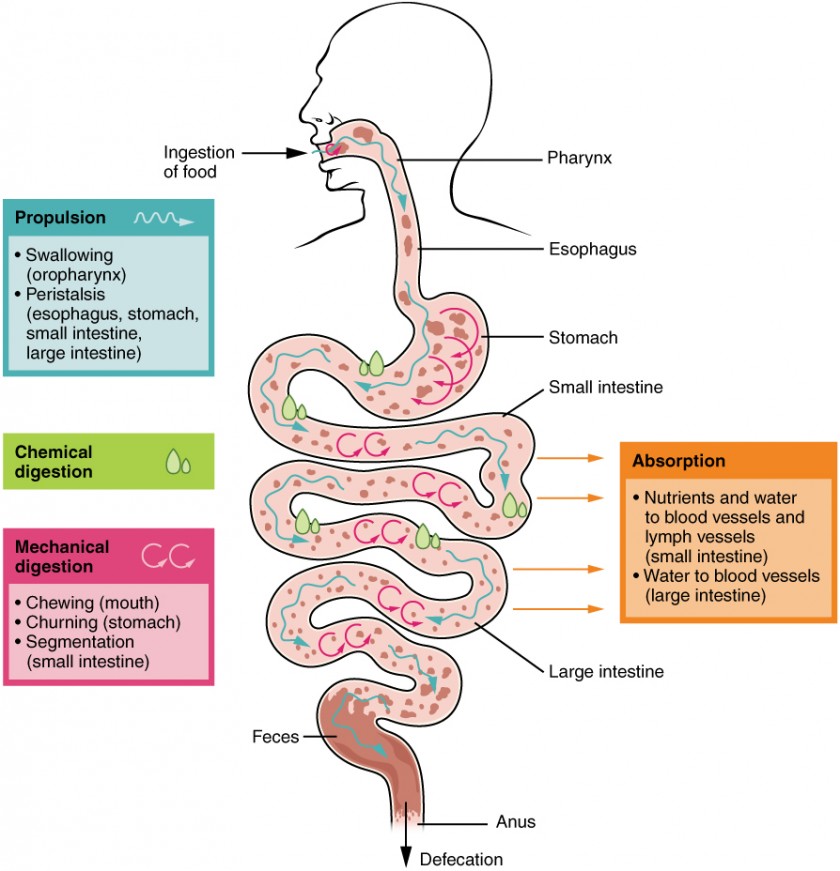
Figure 3. The digestive processes are ingestion, propulsion, mechanical digestion, chemical digestion, absorption, and defecation.
Some chemical digestion occurs in the mouth. Some absorption can occur in the mouth and stomach, for example, alcohol and aspirin.
Histology of the Alimentary Canal
Throughout its length, the alimentary tract is composed of the same four tissue layers; the details of their structural arrangements vary to fit their specific functions. Starting from the lumen and moving outwards, these layers are the mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, and serosa, which is continuous with the mesentery.

Figure 4. The wall of the alimentary canal has four basic tissue layers: the mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, and serosa.
The mucosa is referred to as a mucous membrane, because mucus production is a characteristic feature of gut epithelium. The membrane consists of epithelium, which is in direct contact with ingested food, and the lamina propria, a layer of connective tissue analogous to the dermis. In addition, the mucosa has a thin, smooth muscle layer, called the muscularis mucosa (not to be confused with the muscularis layer, described below).
- Epithelium—In the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, and anal canal, the epithelium is primarily a non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium. In the stomach and intestines, it is a simple columnar epithelium. Notice that the epithelium is in direct contact with the lumen, the space inside the alimentary canal. Interspersed among its epithelial cells are goblet cells, which secrete mucus and fluid into the lumen, and enteroendocrine cells, which secrete hormones into the interstitial spaces between cells. Epithelial cells have a very brief lifespan, averaging from only a couple of days (in the mouth) to about a week (in the gut). This process of rapid renewal helps preserve the health of the alimentary canal, despite the wear and tear resulting from continued contact with foodstuffs.
- Lamina propria—In addition to loose connective tissue, the lamina propria contains numerous blood and lymphatic vessels that transport nutrients absorbed through the alimentary canal to other parts of the body. The lamina propria also serves an immune function by housing clusters of lymphocytes, making up the mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT). These lymphocyte clusters are particularly substantial in the distal ileum where they are known as Peyer’s patches. When you consider that the alimentary canal is exposed to foodborne bacteria and other foreign matter, it is not hard to appreciate why the immune system has evolved a means of defending against the pathogens encountered within it.
- Muscularis mucosa—This thin layer of smooth muscle is in a constant state of tension, pulling the mucosa of the stomach and small intestine into undulating folds. These folds dramatically increase the surface area available for digestion and absorption.
As its name implies, the submucosa lies immediately beneath the mucosa. A broad layer of dense connective tissue, it connects the overlying mucosa to the underlying muscularis. It includes blood and lymphatic vessels (which transport absorbed nutrients), and a scattering of submucosal glands that release digestive secretions. Additionally, it serves as a conduit for a dense branching network of nerves, the submucosal plexus.
The third layer of the alimentary canal is the muscalaris (also called the muscularis externa). The muscularis in the small intestine is made up of a double layer of smooth muscle: an inner circular layer and an outer longitudinal layer. The contractions of these layers promote mechanical digestion, expose more of the food to digestive chemicals, and move the food along the canal. In the most proximal and distal regions of the alimentary canal, including the mouth, pharynx, anterior part of the esophagus, and external anal sphincter, the muscularis is made up of skeletal muscle, which gives you voluntary control over swallowing and defecation. The basic two-layer structure found in the small intestine is modified in the organs proximal and distal to it. The stomach is equipped for its churning function by the addition of a third layer, the oblique muscle. While the colon has two layers like the small intestine, its longitudinal layer is segregated into three narrow parallel bands, the tenia coli, which make it look like a series of pouches rather than a simple tube.
The serosa is the portion of the alimentary canal superficial to the muscularis. Present only in the region of the alimentary canal within the abdominal cavity, it consists of a layer of visceral peritoneum overlying a layer of loose connective tissue. Instead of serosa, the mouth, pharynx, and esophagus have a dense sheath of collagen fibers called the adventitia. These tissues serve to hold the alimentary canal in place near the ventral surface of the vertebral column.
The Peritoneum
The digestive organs within the abdominal cavity are held in place by the peritoneum, a broad serous membranous sac made up of squamous epithelial tissue surrounded by connective tissue. It is composed of two different regions: the parietal peritoneum, which lines the abdominal wall, and the visceral peritoneum, which envelopes the abdominal organs. The peritoneal cavity is the space bounded by the visceral and parietal peritoneal surfaces. A few milliliters of watery fluid act as a lubricant to minimize friction between the serosal surfaces of the peritoneum.

Figure 5. A cross-section of the abdomen shows the relationship between abdominal organs and the peritoneum (darker lines).
Disorders of the Digestive System: Peritonitis
Inflammation of the peritoneum is called peritonitis. Chemical peritonitis can develop any time the wall of the alimentary canal is breached, allowing the contents of the lumen entry into the peritoneal cavity. For example, when an ulcer perforates the stomach wall, gastric juices spill into the peritoneal cavity. Hemorrhagic peritonitis occurs after a ruptured tubal pregnancy or traumatic injury to the liver or spleen fills the peritoneal cavity with blood. Even more severe peritonitis is associated with bacterial infections seen with appendicitis, colonic diverticulitis, and pelvic inflammatory disease (infection of uterine tubes, usually by sexually transmitted bacteria). Peritonitis is life threatening and often results in emergency surgery to correct the underlying problem and intensive antibiotic therapy. When your great grandparents and even your parents were young, the mortality from peritonitis was high. Aggressive surgery, improvements in anesthesia safety, the advance of critical care expertise, and antibiotics have greatly improved the mortality rate from this condition. Even so, the mortality rate still ranges from 30 to 40 percent.
The visceral peritoneum includes multiple large folds that envelope various abdominal organs, holding them to the dorsal surface of the body wall. Within these folds are blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerves that innervate the organs with which they are in contact, supplying their adjacent organs. The five major peritoneal folds are described in Table 2. Note that during fetal development, certain digestive structures, including the first portion of the small intestine (called the duodenum), the pancreas, and portions of the large intestine (the ascending and descending colon, and the rectum) remain completely or partially posterior to the peritoneum. Thus, the location of these organs is described as retroperitoneal.
| Table 2. The Five Major Peritoneal Folds | |
|---|---|
| Fold | Description |
| Greater omentum | Apron-like structure that lies superficial to the small intestine and transverse colon; a site of fat deposition in people who are overweight |
| Falciform ligament | Anchors the liver to the anterior abdominal wall and inferior border of the diaphragm |
| Lesser omentum | Suspends the stomach from the inferior border of the liver; provides a pathway for structures connecting to the liver |
| Mesentery | Vertical band of tissue anterior to the lumbar vertebrae and anchoring all of the small intestine except the initial portion (the duodenum) |
| Mesocolon | Attaches two portions of the large intestine (the transverse and sigmoid colon) to the posterior abdominal wall |
Chapter Review
The digestive system includes the organs of the alimentary canal and accessory structures. The alimentary canal forms a continuous tube that is open to the outside environment at both ends. The organs of the alimentary canal are the mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine. The accessory digestive structures include the teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, pancreas, and gallbladder. The wall of the alimentary canal is composed of four basic tissue layers: mucosa, submucosa, muscularis, and serosa. The enteric nervous system provides intrinsic innervation, and the autonomic nervous system provides extrinsic innervation.
Glossary
accessory digestive organ: includes teeth, tongue, salivary glands, gallbladder, liver, and pancreas
alimentary canal: continuous muscular digestive tube that extends from the mouth to the anus
motility: movement of food through the GI tract
mucosa: innermost lining of the alimentary canal
muscularis: muscle (skeletal or smooth) layer of the alimentary canal wall
myenteric plexus: (plexus of Auerbach) major nerve supply to alimentary canal wall; controls motility
retroperitoneal: located posterior to the peritoneum
serosa: outermost layer of the alimentary canal wall present in regions within the abdominal cavity
submucosa: layer of dense connective tissue in the alimentary canal wall that binds the overlying mucosa to the underlying muscularis
submucosal plexus: (plexus of Meissner) nerve supply that regulates activity of glands and smooth muscle
Candela Citations
- Anatomy & Physiology. Provided by: OpenStax CNX. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/14fb4ad7-39a1-4eee-ab6e-3ef2482e3e22@8.25. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/14fb4ad7-39a1-4eee-ab6e-3ef2482e3e22@8.25