1. Explain how to determine the reduction identities from the double-angle identity [latex]\cos \left(2x\right)={\cos }^{2}x-{\sin }^{2}x[/latex].
2. Explain how to determine the double-angle formula for [latex]\tan \left(2x\right)[/latex] using the double-angle formulas for [latex]\cos \left(2x\right)[/latex] and [latex]\sin \left(2x\right)[/latex].
3. We can determine the half-angle formula for [latex]\tan \left(\frac{x}{2}\right)=\frac{\sqrt{1-\cos x}}{\sqrt{1+\cos x}}[/latex] by dividing the formula for [latex]\sin \left(\frac{x}{2}\right)[/latex] by [latex]\cos \left(\frac{x}{2}\right)[/latex]. Explain how to determine two formulas for [latex]\tan \left(\frac{x}{2}\right)[/latex] that do not involve any square roots.
4. For the half-angle formula given in the previous exercise for [latex]\tan \left(\frac{x}{2}\right)[/latex], explain why dividing by 0 is not a concern. (Hint: examine the values of [latex]\cos x[/latex] necessary for the denominator to be 0.)
For the following exercises, find the exact values of a) [latex]\sin \left(2x\right)[/latex], b) [latex]\cos \left(2x\right)[/latex], and c) [latex]\tan \left(2x\right)[/latex] without solving for [latex]x[/latex].
5. If [latex]\sin x=\frac{1}{8}[/latex], and [latex]x[/latex] is in quadrant I.
6. If [latex]\cos x=\frac{2}{3}[/latex], and [latex]x[/latex] is in quadrant I.
7. If [latex]\cos x=-\frac{1}{2}[/latex], and [latex]x[/latex] is in quadrant III.
8. If [latex]\tan x=-8[/latex], and [latex]x[/latex] is in quadrant IV.
For the following exercises, find the values of the six trigonometric functions if the conditions provided hold.
9. [latex]\cos \left(2\theta \right)=\frac{3}{5}[/latex] and [latex]{90}^{\circ }\le \theta \le {180}^{\circ }[/latex]
10. [latex]\cos \left(2\theta \right)=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}[/latex] and [latex]{180}^{\circ }\le \theta \le {270}^{\circ }[/latex]
For the following exercises, simplify to one trigonometric expression.
11. [latex]2\sin \left(\frac{\pi }{4}\right)2\cos \left(\frac{\pi }{4}\right)[/latex]
12. [latex]4\sin \left(\frac{\pi }{8}\right)\cos \left(\frac{\pi }{8}\right)[/latex]
For the following exercises, find the exact value using half-angle formulas.
13. [latex]\sin \left(\frac{\pi }{8}\right)[/latex]
14. [latex]\cos \left(-\frac{11\pi }{12}\right)[/latex]
15. [latex]\sin \left(\frac{11\pi }{12}\right)[/latex]
16. [latex]\cos \left(\frac{7\pi }{8}\right)[/latex]
17. [latex]\tan \left(\frac{5\pi }{12}\right)[/latex]
18. [latex]\tan \left(-\frac{3\pi }{12}\right)[/latex]
19. [latex]\tan \left(-\frac{3\pi }{8}\right)[/latex]
For the following exercises, find the exact values of a) [latex]\sin \left(\frac{x}{2}\right)[/latex], b) [latex]\cos \left(\frac{x}{2}\right)[/latex], and c) [latex]\tan \left(\frac{x}{2}\right)[/latex] without solving for [latex]x[/latex].
20. If [latex]\tan x=-\frac{4}{3}[/latex], and [latex]x[/latex] is in quadrant IV.
21. If [latex]\sin x=-\frac{12}{13}[/latex], and [latex]x[/latex] is in quadrant III.
22. If [latex]\csc x=7[/latex], and [latex]x[/latex] is in quadrant II.
23. If [latex]\sec x=-4[/latex], and [latex]x[/latex] is in quadrant II.
For the following exercises, use Figure 5 to find the requested half and double angles.
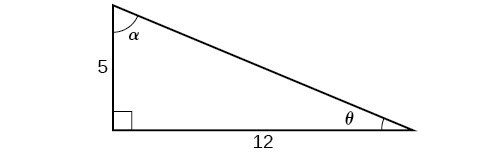
Figure 5
24. Find [latex]\sin \left(2\theta \right),\cos \left(2\theta \right)[/latex], and [latex]\tan \left(2\theta \right)[/latex].
25. Find [latex]\sin \left(2\alpha \right),\cos \left(2\alpha \right)[/latex], and [latex]\tan \left(2\alpha \right)[/latex].
26. Find [latex]\sin \left(\frac{\theta }{2}\right),\cos \left(\frac{\theta }{2}\right)[/latex], and [latex]\tan \left(\frac{\theta }{2}\right)[/latex].
27. Find [latex]\sin \left(\frac{\alpha }{2}\right),\cos \left(\frac{\alpha }{2}\right)[/latex], and [latex]\tan \left(\frac{\alpha }{2}\right)[/latex].
For the following exercises, simplify each expression. Do not evaluate.
28. [latex]{\cos }^{2}\left({28}^{\circ }\right)-{\sin }^{2}\left({28}^{\circ }\right)[/latex]
29. [latex]2{\cos }^{2}\left({37}^{\circ }\right)-1[/latex]
30. [latex]1 - 2{\sin }^{2}\left({17}^{\circ }\right)[/latex]
31. [latex]{\cos }^{2}\left(9x\right)-{\sin }^{2}\left(9x\right)[/latex]
32. [latex]4\sin \left(8x\right)\cos \left(8x\right)[/latex]
33. [latex]6\sin \left(5x\right)\cos \left(5x\right)[/latex]
For the following exercises, prove the identity given.
34. [latex]{\left(\sin t-\cos t\right)}^{2}=1-\sin \left(2t\right)[/latex]
35. [latex]\sin \left(2x\right)=-2\sin \left(-x\right)\cos \left(-x\right)[/latex]
36. [latex]\cot x-\tan x=2\cot \left(2x\right)[/latex]
37. [latex]\frac{\sin \left(2\theta \right)}{1+\cos \left(2\theta \right)}{\tan }^{2}\theta =\tan \theta[/latex]
For the following exercises, rewrite the expression with an exponent no higher than 1.
38. [latex]{\cos }^{2}\left(5x\right)[/latex]
39. [latex]{\cos }^{2}\left(6x\right)[/latex]
40. [latex]{\sin }^{4}\left(8x\right)[/latex]
41. [latex]{\sin }^{4}\left(3x\right)[/latex]
42. [latex]{\cos }^{2}x{\sin }^{4}x[/latex]
43. [latex]{\cos }^{4}x{\sin }^{2}x[/latex]
44. [latex]{\tan }^{2}x{\sin }^{2}x[/latex]
For the following exercises, reduce the equations to powers of one, and then check the answer graphically.
45. [latex]{\tan }^{4}x[/latex]
46. [latex]{\sin }^{2}\left(2x\right)[/latex]
47. [latex]{\sin }^{2}x{\cos }^{2}x[/latex]
48. [latex]{\tan }^{2}x\sin x[/latex]
49. [latex]{\tan }^{4}x{\cos }^{2}x[/latex]
50. [latex]{\cos }^{2}x\sin \left(2x\right)[/latex]
51. [latex]{\cos }^{2}\left(2x\right)\sin x[/latex]
52. [latex]{\tan }^{2}\left(\frac{x}{2}\right)\sin x[/latex]
For the following exercises, algebraically find an equivalent function, only in terms of [latex]\sin x[/latex] and/or [latex]\cos x[/latex], and then check the answer by graphing both equations.
53. [latex]\sin \left(4x\right)[/latex]
54. [latex]\cos \left(4x\right)[/latex]
For the following exercises, prove the identities.
55. [latex]\sin \left(2x\right)=\frac{2\tan x}{1+{\tan }^{2}x}[/latex]
56. [latex]\cos \left(2\alpha \right)=\frac{1-{\tan }^{2}\alpha }{1+{\tan }^{2}\alpha }[/latex]
57. [latex]\tan \left(2x\right)=\frac{2\sin x\cos x}{2{\cos }^{2}x - 1}[/latex]
58. [latex]{\left({\sin }^{2}x - 1\right)}^{2}=\cos \left(2x\right)+{\sin }^{4}x[/latex]
59. [latex]\sin \left(3x\right)=3\sin x{\cos }^{2}x-{\sin }^{3}x[/latex]
60. [latex]\cos \left(3x\right)={\cos }^{3}x - 3{\sin }^{2}x\cos x[/latex]
61. [latex]\frac{1+\cos \left(2t\right)}{\sin \left(2t\right)-\cos t}=\frac{2\cos t}{2\sin t - 1}[/latex]
62. [latex]\sin \left(16x\right)=16\sin x\cos x\cos \left(2x\right)\cos \left(4x\right)\cos \left(8x\right)[/latex]
63. [latex]\cos \left(16x\right)=\left({\cos }^{2}\left(4x\right)-{\sin }^{2}\left(4x\right)-\sin \left(8x\right)\right)\left({\cos }^{2}\left(4x\right)-{\sin }^{2}\left(4x\right)+\sin \left(8x\right)\right)[/latex]
Candela Citations
- Precalculus. Authored by: Jay Abramson, et al.. Provided by: OpenStax. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/fd53eae1-fa23-47c7-bb1b-972349835c3c@5.175:1/Preface. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at: http://cnx.org/contents/fd53eae1-fa23-47c7-bb1b-972349835c3c@5.175:1/Preface