Learning Objectives
By the end of this module, you will be able to:
- Assess the relative strengths of acids and bases according to their ionization constants
- Rationalize trends in acid–base strength in relation to molecular structure
- Carry out equilibrium calculations for weak acid–base systems
We can rank the strengths of acids by the extent to which they ionize in aqueous solution. The reaction of an acid with water is given by the general expression:
[latex]\text{HA}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+{\text{A}}^{-}\left(aq\right)[/latex]
Water is the base that reacts with the acid HA, A− is the conjugate base of the acid HA, and the hydronium ion is the conjugate acid of water. A strong acid yields 100% (or very nearly so) of [latex]{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}[/latex] and A− when the acid ionizes in water; Table 1 lists several strong acids. A weak acid gives small amounts of [latex]{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}[/latex] and A−.
| Table 1. Some Common Strong acids and Strong Bases | |
| Strong Acids | Strong Bases |
| HClO4 perchloric acid | LiOH lithium hydroxide |
| HCl hydrochloric acid | NaOH sodium hydroxide |
| HBr hydrobromic acid | KOH potassium hydroxide |
| HI hydroiodic acid | Ca(OH)2 calcium hydroxide |
| HNO3 nitric acid | Sr(OH)2 strontium hydroxide |
| H2SO4 sulfuric acid | Ba(OH)2 barium hydroxide |
The relative strengths of acids may be determined by measuring their equlibrium constants in aqueous solutions. In solutions of the same concentration, stronger acids ionize to a greater extent, and so yield higher concentrations of hydronium ions than do weaker acids. The equilibrium constant for an acid is called the acid-ionization constant, Ka. For the reaction of an acid HA:
[latex]\text{HA}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+{\text{A}}^{-}\left(aq\right)[/latex],
we write the equation for the ionization constant as:
[latex]{K}_{\text{a}}=\frac{\left[{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\right]\left[{\text{A}}^{-}\right]}{\text{[HA]}}[/latex]
where the concentrations are those at equilibrium. Although water is a reactant in the reaction, it is the solvent as well, so we do not include [H2O] in the equation. The larger the Ka of an acid, the larger the concentration of [latex]{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}[/latex] and A− relative to the concentration of the nonionized acid, HA. Thus a stronger acid has a larger ionization constant than does a weaker acid. The ionization constants increase as the strengths of the acids increase. (A table of ionization constants of weak acids appears in Ionization Constants of Weak Acids, with a partial listing in Table 1.)
The following data on acid-ionization constants indicate the order of acid strength CH3CO2H < HNO2 < [latex]{\text{HSO}}_{4}{}^{-}:[/latex]
[latex]{\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{CO}}_{2}\text{H}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+{\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{CO}}_{2}{}^{-}\left(aq\right){K}_{\text{a}}=1.8\times {10}^{-5}[/latex]
[latex]{\text{HNO}}_{2}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+{\text{NO}}_{2}{}^{-}\left(aq\right){K}_{\text{a}}=4.6\times {10}^{-4}[/latex]
[latex]{\text{HSO}}_{4}{}^{-}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(aq\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+{\text{SO}}_{4}{}^{2-}\left(aq\right){K}_{\text{a}}=1.2\times {10}^{-2}[/latex]
Another measure of the strength of an acid is its percent ionization. The percent ionization of a weak acid is the ratio of the concentration of the ionized acid to the initial acid concentration, times 100:
[latex]\text{% ionization}=\frac{{\left[{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\right]}_{\text{eq}}}{{\left[\text{HA}\right]}_{0}}\times 100[/latex]
Because the ratio includes the initial concentration, the percent ionization for a solution of a given weak acid varies depending on the original concentration of the acid, and actually decreases with increasing acid concentration.
Example 1: Calculation of Percent Ionization from pH
Calculate the percent ionization of a 0.125-M solution of nitrous acid (a weak acid), with a pH of 2.09.
Check Your Learning
Calculate the percent ionization of a 0.10-M solution of acetic acid with a pH of 2.89.
We can rank the strengths of bases by their tendency to form hydroxide ions in aqueous solution. The reaction of a Brønsted-Lowry base with water is given by:
[latex]\text{B}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{HB}}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+{\text{OH}}^{-}\left(aq\right)[/latex]
Water is the acid that reacts with the base, HB+ is the conjugate acid of the base B, and the hydroxide ion is the conjugate base of water. A strong base yields 100% (or very nearly so) of OH− and HB+ when it reacts with water; Table 1 lists several strong bases. A weak base yields a small proportion of hydroxide ions. Soluble ionic hydroxides such as NaOH are considered strong bases because they dissociate completely when dissolved in water.
As we did with acids, we can measure the relative strengths of bases by measuring their base-ionization constant, (Kb) in aqueous solutions. In solutions of the same concentration, stronger bases ionize to a greater extent, and so yield higher hydroxide ion concentrations than do weaker bases. A stronger base has a larger ionization constant than does a weaker base. For the reaction of a base, B:
[latex]\text{B}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{HB}}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+{\text{OH}}^{-}\left(aq\right)[/latex],
we write the equation for the ionization constant as:
[latex]{K}_{\text{b}}=\frac{\left[{\text{HB}}^{\text{+}}\right]\left[{\text{OH}}^{-}\right]}{\left[\text{B}\right]}[/latex]
where the concentrations are those at equilibrium. Again, we do not include [H2O] in the equation because water is the solvent. The chemical reactions and ionization constants of the three bases shown are:
[latex]{\text{NO}}_{2}{}^{-}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{HNO}}_{2}\left(aq\right)+{\text{OH}}^{-}\left(aq\right){K}_{\text{b}}=2.22\times {10}^{-11}[/latex]
[latex]{\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{CO}}_{2}{}^{-}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{CO}}_{2}\text{H}\left(aq\right)+{\text{OH}}^{-}\left(aq\right){K}_{\text{b}}=5.6\times {10}^{-10}[/latex]
[latex]{\text{NH}}_{3}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{NH}}_{4}{}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+{\text{OH}}^{-}\left(aq\right){K}_{\text{b}}=1.8\times {10}^{-5}[/latex]
A table of ionization constants of weak bases appears in Ionization Constants of Weak Bases (with a partial list in Table 2). As with acids, percent ionization can be measured for basic solutions, but will vary depending on the base ionization constant and the initial concentration of the solution.
Consider the ionization reactions for a conjugate acid-base pair, HA − A−:
[latex]\text{HA}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+{\text{A}}^{-}\left(aq\right){K}_{\text{a}}=\frac{\left[{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\right]\left[{\text{A}}^{-}\right]}{\left[\text{HA}\right]}[/latex]
[latex]{\text{A}}^{-}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{OH}}^{-}\left(aq\right)+\text{HA}\left(aq\right){K}_{\text{b}}=\frac{\left[\text{HA}\right]\left[\text{OH}\right]}{\left[{\text{A}}^{-}\right]}[/latex]
Adding these two chemical equations yields the equation for the autoionization for water:
[latex]\cancel{\text{HA}\left(aq\right)}+\text{H}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)+\cancel{\text{A}^{-}\left(aq\right)}+\text{H}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons\text{H}_{3}\text{O}^{+}\left(aq\right)+\cancel{\text{A}^{-}\left(aq\right)}+\text{OH}^{-}\left(aq\right)+\cancel{\text{HA}\left(aq\right)}[/latex]
[latex]{\text{2H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+{\text{OH}}^{-}\left(aq\right)[/latex]
As shown in the previous chapter on equilibrium, the K expression for a chemical equation derived from adding two or more other equations is the mathematical product of the other equations’ K expressions. Multiplying the mass-action expressions together and cancelling common terms, we see that:
[latex]{K}_{\text{a}}\times {K}_{\text{b}}=\frac{\left[{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\right]\left[{\text{A}}^{-}\right]}{\text{[HA]}}\times \frac{\text{[HA]}\left[{\text{OH}}^{-}\right]}{\left[{\text{A}}^{-}\right]}=\left[{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\right]\left[{\text{OH}}^{-}\right]={K}_{\text{w}}[/latex]
For example, the acid ionization constant of acetic acid (CH3COOH) is 1.8 × 10−5, and the base ionization constant of its conjugate base, acetate ion (CH3COO−), is 5.6 × 10−10. The product of these two constants is indeed equal to Kw:
[latex]{K}_{\text{a}}\times {K}_{\text{b}}=\left(1.8\times {10}^{-5}\right)\times \left(5.6\times {10}^{-10}\right)=1.0\times {10}^{-14}={K}_{\text{w}}[/latex]
The extent to which an acid, HA, donates protons to water molecules depends on the strength of the conjugate base, A−, of the acid. If A− is a strong base, any protons that are donated to water molecules are recaptured by A−. Thus there is relatively little A− and [latex]{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}[/latex] in solution, and the acid, HA, is weak. If A− is a weak base, water binds the protons more strongly, and the solution contains primarily A− and [latex]{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}[/latex] —the acid is strong. Strong acids form very weak conjugate bases, and weak acids form stronger conjugate bases (Figure 1).
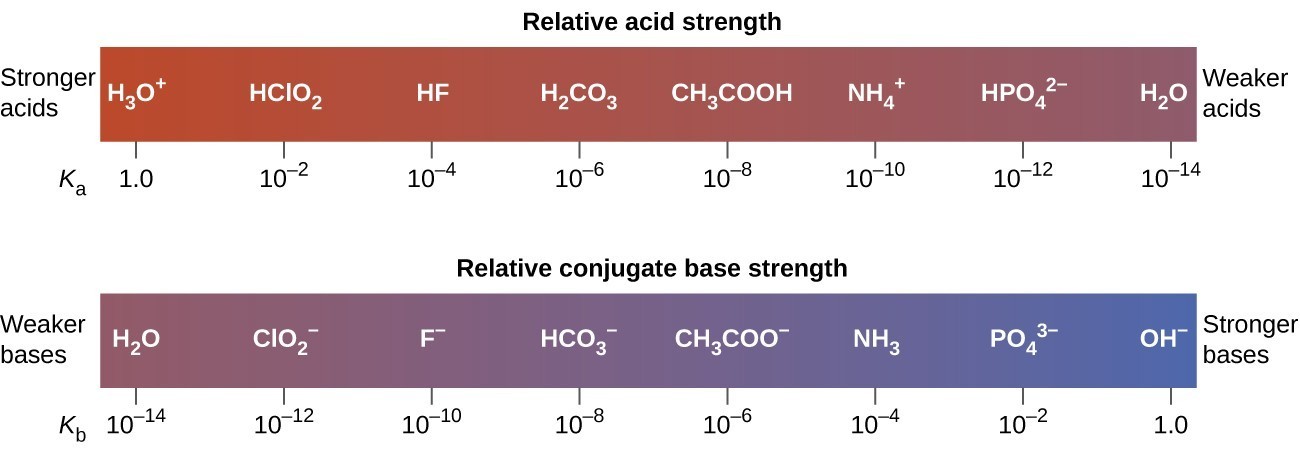
Figure 1. This diagram shows the relative strengths of conjugate acid-base pairs, as indicated by their ionization constants in aqueous solution.
Figure 2 lists a series of acids and bases in order of the decreasing strengths of the acids and the corresponding increasing strengths of the bases. The acid and base in a given row are conjugate to each other.
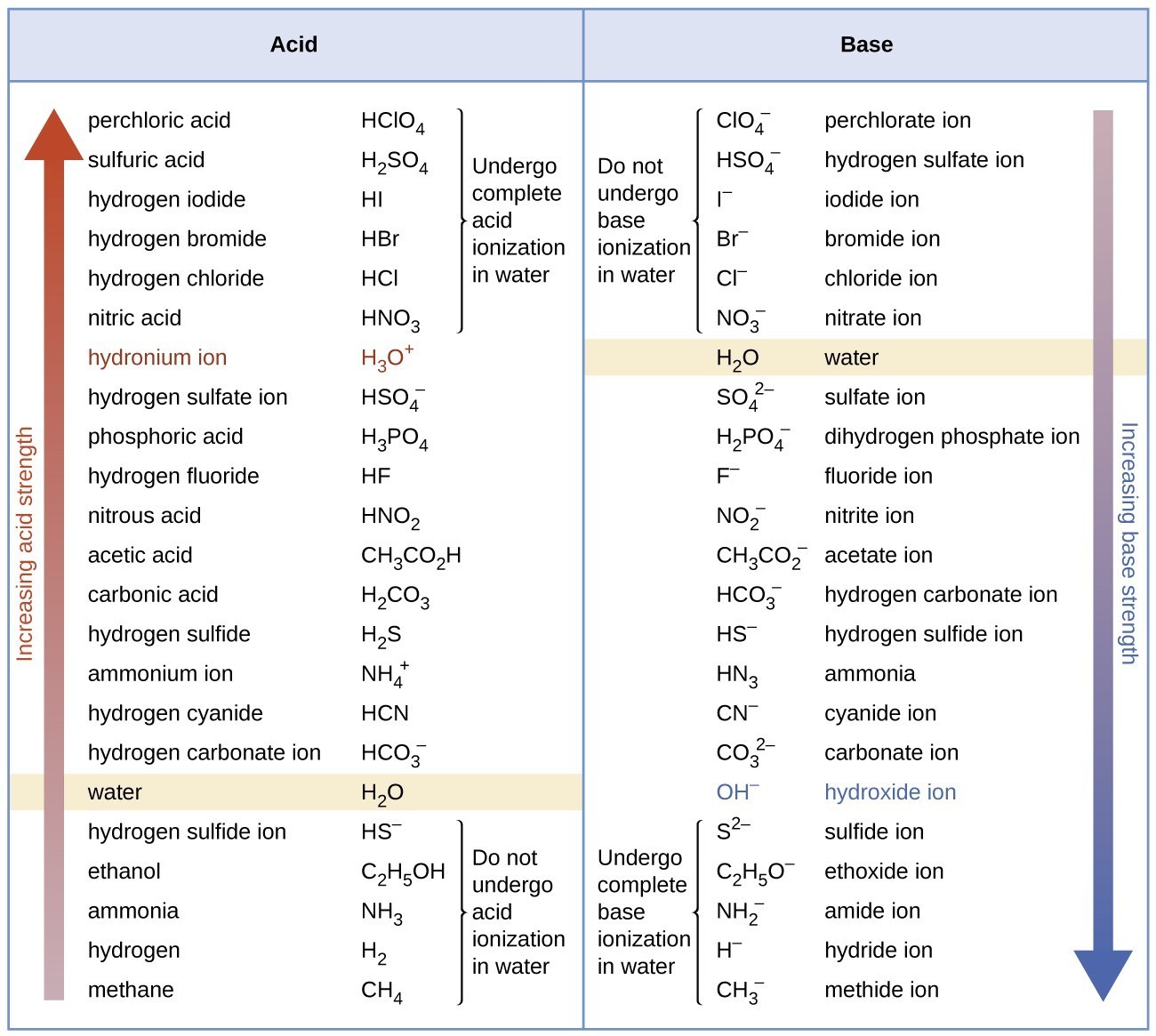
Figure 2. The chart shows the relative strengths of conjugate acid-base pairs.
The first six acids in Figure 2 are the most common strong acids. These acids are completely dissociated in aqueous solution. The conjugate bases of these acids are weaker bases than water. When one of these acids dissolves in water, their protons are completely transferred to water, the stronger base.
Those acids that lie between the hydronium ion and water in Figure 2 form conjugate bases that can compete with water for possession of a proton. Both hydronium ions and nonionized acid molecules are present in equilibrium in a solution of one of these acids. Compounds that are weaker acids than water (those found below water in the column of acids) in Figure 3 exhibit no observable acidic behavior when dissolved in water. Their conjugate bases are stronger than the hydroxide ion, and if any conjugate base were formed, it would react with water to re-form the acid.
The extent to which a base forms hydroxide ion in aqueous solution depends on the strength of the base relative to that of the hydroxide ion, as shown in the last column in Figure 2. A strong base, such as one of those lying below hydroxide ion, accepts protons from water to yield 100% of the conjugate acid and hydroxide ion. Those bases lying between water and hydroxide ion accept protons from water, but a mixture of the hydroxide ion and the base results. Bases that are weaker than water (those that lie above water in the column of bases) show no observable basic behavior in aqueous solution.
Example 2: The Product Ka ×Kb = Kw
Use the Kb for the nitrite ion, [latex]{\text{NO}}_{2}{}^{-}[/latex], to calculate the Ka for its conjugate acid.
Check Your Learning
We can determine the relative acid strengths of [latex]{\text{NH}}_{4}{}^{\text{+}}[/latex] and HCN by comparing their ionization constants. The ionization constant of HCN is given in Ionization Constants of Weak Acids as 4 × 10−10. The ionization constant of [latex]{\text{NH}}_{4}{}^{\text{+}}[/latex] is not listed, but the ionization constant of its conjugate base, NH3, is listed as 1.8 × 10−5. Determine the ionization constant of [latex]{\text{NH}}_{4}{}^{\text{+}}[/latex], and decide which is the stronger acid, HCN or [latex]{\text{NH}}_{4}{}^{\text{+}}[/latex].
The Ionization of Weak Acids and Weak Bases
Many acids and bases are weak; that is, they do not ionize fully in aqueous solution. A solution of a weak acid in water is a mixture of the nonionized acid, hydronium ion, and the conjugate base of the acid, with the nonionized acid present in the greatest concentration. Thus, a weak acid increases the hydronium ion concentration in an aqueous solution (but not as much as the same amount of a strong acid).
Acetic acid, CH3CO2H, is a weak acid. When we add acetic acid to water, it ionizes to a small extent according to the equation:
[latex]{\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{CO}}_{2}\text{H}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+{\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{CO}}_{2}{}^{-}\left(aq\right)[/latex],
giving an equilibrium mixture with most of the acid present in the nonionized (molecular) form. This equilibrium, like other equilibria, is dynamic; acetic acid molecules donate hydrogen ions to water molecules and form hydronium ions and acetate ions at the same rate that hydronium ions donate hydrogen ions to acetate ions to reform acetic acid molecules and water molecules. We can tell by measuring the pH of an aqueous solution of known concentration that only a fraction of the weak acid is ionized at any moment (Figure 3). The remaining weak acid is present in the nonionized form.
For acetic acid, at equilibrium:
[latex]{K}_{\text{a}}=\frac{\left[{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\right]\left[{\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{CO}}_{2}{}^{-}\right]}{\left[{\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{CO}}_{2}\text{H}\right]}=1.8\times {10}^{-5}[/latex]
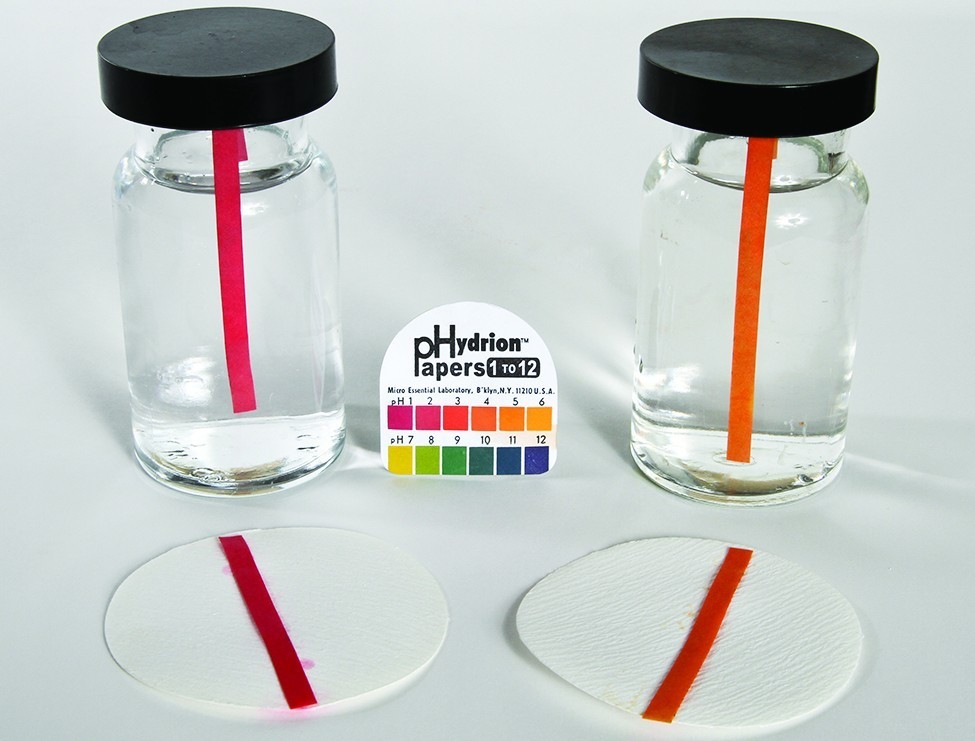

Figure 3. pH paper indicates that a 0.l-M solution of HCl (beaker on left) has a pH of 1. The acid is fully ionized and [H3O+] = 0.1 M. A 0.1-M solution of CH3CO2H (beaker on right) is has a pH of 3 ([H3O+] = 0.001 M) because the weak acid CH3CO2H is only partially ionized. In this solution, [H3O+] < [CH3CO2H]. (credit: modification of work by Sahar Atwa)
| Table 2. Ionization Constants of Some Weak Acids | |
|---|---|
| Ionization Reaction | Ka at 25 °C |
| [latex]{\text{HSO}}_{4}{}^{-}+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}+{\text{SO}}_{4}{}^{2-}[/latex] | 1.2 × 10−2 |
| [latex]\text{HF}+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}+{\text{F}}^{-}[/latex] | 7.2 × 10−4 |
| [latex]{\text{HNO}}_{2}+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}+{\text{NO}}_{2}{}^{-}[/latex] | 4.5 × 10−4 |
| [latex]\text{HNCO}+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}+{\text{NCO}}^{-}[/latex] | 3.46 × 10−4 |
| [latex]{\text{HCO}}_{2}\text{H}+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}+{\text{HCO}}_{2}{}^{-}[/latex] | 1.8 × 10−4 |
| [latex]{\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{CO}}_{2}\text{H}+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}+{\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{CO}}_{2}{}^{-}[/latex] | 1.8 × 10−5 |
| [latex]\text{HCIO}+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}+{\text{CIO}}^{-}[/latex] | 3.5 × 10−8 |
| [latex]\text{HBrO}+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}+{\text{BrO}}^{-}[/latex] | 2 × 10−9 |
| [latex]\text{HCN}+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}+{\text{CN}}^{-}[/latex] | 4 × 10−10 |
Table 2 gives the ionization constants for several weak acids; additional ionization constants can be found in Ionization Constants of Weak Acids.
At equilibrium, a solution of a weak base in water is a mixture of the nonionized base, the conjugate acid of the weak base, and hydroxide ion with the nonionized base present in the greatest concentration. Thus, a weak base increases the hydroxide ion concentration in an aqueous solution (but not as much as the same amount of a strong base).
For example, a solution of the weak base trimethylamine, (CH3)3N, in water reacts according to the equation
[latex]{\left({\text{CH}}_{3}\right)}_{3}\text{N}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\left({\text{CH}}_{3}\right)}_{3}{\text{NH}}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+{\text{OH}}^{-}\left(aq\right)[/latex],
giving an equilibrium mixture with most of the base present as the nonionized amine. This equilibrium is analogous to that described for weak acids.
We can confirm by measuring the pH of an aqueous solution of a weak base of known concentration that only a fraction of the base reacts with water (Figure 4). The remaining weak base is present as the unreacted form. The equilibrium constant for the ionization of a weak base, Kb, is called the ionization constant of the weak base, and is equal to the reaction quotient when the reaction is at equilibrium. For trimethylamine, at equilibrium:
[latex]{K}_{\text{b}}=\frac{\left[{\left({\text{CH}}_{3}\right)}_{3}{\text{NH}}^{\text{+}}\right]\left[{\text{OH}}^{-}\right]}{\left[{\left({\text{CH}}_{3}\right)}_{3}\text{N}\right]}[/latex]
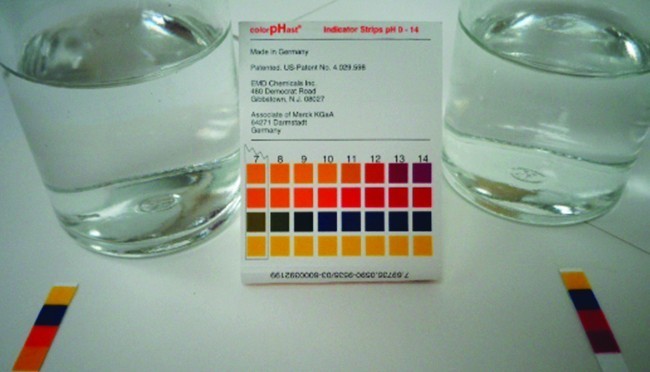
Figure 4. pH paper indicates that a 0.1-M solution of NH3 (left) is weakly basic. The solution has a pOH of 3 ([OH−] = 0.001 M) because the weak base NH3 only partially reacts with water. A 0.1-M solution of NaOH (right) has a pOH of 1 because NaOH is a strong base. (credit: modification of work by Sahar Atwa)
The ionization constants of several weak bases are given in Table 3 and in Ionization Constants of Weak Bases.
| Table 3. Ionization Constants of Some Weak Bases | |
|---|---|
| Ionization Reaction | Kb at 25 °C |
| [latex]{\left({\text{CH}}_{3}\right)}_{2}\text{NH}+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\rightleftharpoons {\left({\text{CH}}_{3}\right)}_{2}{\text{NH}}_{2}{}^{\text{+}}+{\text{OH}}^{-}[/latex] | 7.4 × 10−4 |
| [latex]{\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{NH}}_{2}+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\rightleftharpoons {\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{NH}}_{3}{}^{\text{+}}+{\text{OH}}^{-}[/latex] | 4.4 × 10−4 |
| [latex]{\left({\text{CH}}_{3}\right)}_{3}\text{N}+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\rightleftharpoons {\left({\text{CH}}_{3}\right)}_{3}{\text{NH}}^{\text{+}}+{\text{OH}}^{-}[/latex] | 7.4 × 10−5 |
| [latex]{\text{NH}}_{3}+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\rightleftharpoons {\text{NH}}_{4}{}^{\text{+}}+{\text{OH}}^{-}[/latex] | 1.8 × 10−5 |
| [latex]{\text{C}}_{6}{\text{H}}_{5}{\text{NH}}_{2}+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\rightleftharpoons {\text{C}}_{6}{\text{N}}_{5}{\text{NH}}_{3}{}^{\text{+}}+{\text{OH}}^{-}[/latex] | 4.6 × 10−10 |
Example 3: Determination of Ka from Equilibrium Concentrations
Acetic acid is the principal ingredient in vinegar (Figure 5); that’s why it tastes sour. At equilibrium, a solution contains [CH3CO2H] = 0.0787 M and [latex]\left[{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\right]=\left[{\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{CO}}_{2}{}^{-}\right]=0.00118M[/latex]. What is the value of Ka for acetic acid?

Figure 5. Vinegar is a solution of acetic acid, a weak acid. (credit: modification of work by “HomeSpot HQ”/Flickr)
Check Your Learning
What is the equilibrium constant for the ionization of the [latex]{\text{HSO}}_{4}{}^{-}[/latex] ion, the weak acid used in some household cleansers:
[latex]{\text{HSO}}_{4}{}^{-}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+{\text{SO}}_{4}{}^{2-}\left(aq\right)[/latex]
In one mixture of NaHSO4 and Na2SO4 at equilibrium, [latex]\left[{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\right][/latex] = 0.027 M; [latex]\left[{\text{HSO}}_{4}{}^{-}\right]=0.29M[/latex]; and [latex]\left[{\text{SO}}_{4}{}^{2-}\right]=0.13M[/latex].
Example 4: Determination of Kb from Equilibrium Concentrations
Caffeine, C8H10N4O2 is a weak base. What is the value of Kb for caffeine if a solution at equilibrium has [C8H10N4O2] = 0.050 M, [latex]\left[{\text{C}}_{8}{\text{H}}_{10}{\text{N}}_{4}{\text{O}}_{2}{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}\right][/latex] = 5.0 × 10−3M, and [OH−] = 2.5 × 10−3M?
Check Your Learning
What is the equilibrium constant for the ionization of the [latex]{\text{HPO}}_{4}{}^{2-}[/latex] ion, a weak base:
[latex]{\text{HPO}}_{4}{}^{2-}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{2}{\text{PO}}_{4}{}^{-}\left(aq\right)+{\text{OH}}^{-}\left(aq\right)[/latex]
In a solution containing a mixture of NaH2PO4 and Na2HPO4 at equilibrium, [OH−] = 1.3 × 10−6M; [latex]\left[{\text{H}}_{2}{\text{PO}}_{4}{}^{-}\right]=0.042M[/latex]; and [latex]\left[{\text{HPO}}_{4}{}^{2-}\right]=0.341M[/latex].
Example 5: Determination of Ka or Kb from pH
The pH of a 0.0516-M solution of nitrous acid, HNO2, is 2.34. What is its Ka?
[latex]{\text{HNO}}_{2}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+{\text{NO}}_{2}{}^{-}\left(aq\right)[/latex]
Check Your Learning
The pH of a solution of household ammonia, a 0.950-M solution of NH3, is 11.612. What is Kb for NH3.
Example 6: Equilibrium Concentrations in a Solution of a Weak Acid
Formic acid, HCO2H, is the irritant that causes the body’s reaction to ant stings (Figure 6).

Figure 6. The pain of an ant’s sting is caused by formic acid. (credit: John Tann)
What is the concentration of hydronium ion and the pH in a 0.534-M solution of formic acid?
[latex]{\text{HCO}}_{2}\text{H}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+{\text{HCO}}_{2}{}^{-}\left(aq\right){K}_{\text{a}}=1.8\times {10}^{-4}[/latex]
Check Your Learning
Only a small fraction of a weak acid ionizes in aqueous solution. What is the percent ionization of acetic acid in a 0.100-M solution of acetic acid, CH3CO2H?
[latex]{\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{CO}}_{2}\text{H}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+{\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{CO}}_{2}{}^{-}\left(aq\right){K}_{\text{a}}=1.8\times {10}^{-5}[/latex]
(Hint: Determine [latex]\left[{\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{CO}}_{2}{}^{-}\right][/latex] at equilibrium.) Recall that the percent ionization is the fraction of acetic acid that is ionized × 100, or [latex]\frac{\left[{\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{CO}}_{2}{}^{-}\right]}{{\left[{\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{CO}}_{2}\text{H}\right]}_{\text{initial}}}\times 100[/latex].
Example 7 shows that the concentration of products produced by the ionization of a weak base can be determined by the same series of steps used with a weak acid.
Example 7: Equilibrium Concentrations in a Solution of a Weak Base
Find the concentration of hydroxide ion in a 0.25-M solution of trimethylamine, a weak base:
[latex]{\left({\text{CH}}_{3}\right)}_{3}\text{N}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\left({\text{CH}}_{3}\right)}_{3}{\text{NH}}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+{\text{OH}}^{-}\left(aq\right){K}_{\text{b}}=7.4\times {10}^{-5}[/latex]
Check Your Learning
- (a) Show that the calculation in Step 2 of this example gives an x of 4.3 × 10−3 and the calculation in Step 3 shows Kb = 7.4 × 10−5.
- (b) Find the concentration of hydroxide ion in a 0.0325-M solution of ammonia, a weak base with a Kb of 1.76 × 10−5. Calculate the percent ionization of ammonia, the fraction ionized × 100, or [latex]\frac{\left[{\text{NH}}_{4}{}^{\text{+}}\right]}{\left[{\text{NH}}_{3}\right]}\times 100[/latex]
Some weak acids and weak bases ionize to such an extent that the simplifying assumption that x is small relative to the initial concentration of the acid or base is inappropriate. As we solve for the equilibrium concentrations in such cases, we will see that we cannot neglect the change in the initial concentration of the acid or base, and we must solve the equilibrium equations by using the quadratic equation.
Example 8: Equilibrium Concentrations in a Solution of a Weak Acid
Sodium bisulfate, NaHSO4, is used in some household cleansers because it contains the [latex]{\text{HSO}}_{4}{}^{-}[/latex] ion, a weak acid. What is the pH of a 0.50-M solution of [latex]{\text{HSO}}_{4}{}^{-}?[/latex]
[latex]{\text{HSO}}_{4}{}^{-}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+{\text{SO}}_{4}{}^{2-}\left(aq\right){K}_{\text{a}}=1.2\times {10}^{-2}[/latex]
Check Your Learning
- Show that the quadratic formula gives x = 7.2 × 10−2.
- Calculate the pH in a 0.010-M solution of caffeine, a weak base: [latex]{\text{C}}_{8}{\text{H}}_{10}{\text{N}}_{4}{\text{O}}_{2}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{C}}_{8}{\text{H}}_{10}{\text{N}}_{4}{\text{O}}_{2}{\text{H}}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+{\text{OH}}^{-}\left(aq\right){K}_{\text{b}}=2.5\times {10}^{-4}[/latex]
(Hint: It will be necessary to convert [OH−] to [latex]\left[{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\right][/latex] or pOH to pH toward the end of the calculation.)
The Relative Strengths of Strong Acids and Bases
Strong acids, such as HCl, HBr, and HI, all exhibit the same strength in water. The water molecule is such a strong base compared to the conjugate bases Cl−, Br−, and I− that ionization of these strong acids is essentially complete in aqueous solutions. In solvents less basic than water, we find HCl, HBr, and HI differ markedly in their tendency to give up a proton to the solvent. For example, when dissolved in ethanol (a weaker base than water), the extent of ionization increases in the order HCl < HBr < HI, and so HI is demonstrated to be the strongest of these acids. The inability to discern differences in strength among strong acids dissolved in water is known as the leveling effect of water.
Water also exerts a leveling effect on the strengths of strong bases. For example, the oxide ion, O2−, and the amide ion, [latex]{\text{NH}}_{2}{}^{-}[/latex], are such strong bases that they react completely with water:
[latex]{\text{O}}^{2-}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\longrightarrow {\text{OH}}^{-}\left(aq\right)+{\text{OH}}^{-}\left(aq\right)[/latex]
[latex]{\text{NH}}_{2}{}^{-}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\longrightarrow {\text{NH}}_{3}\left(aq\right)+{\text{OH}}^{-}\left(aq\right)[/latex]
Thus, O2− and [latex]{\text{NH}}_{2}{}^{-}[/latex] appear to have the same base strength in water; they both give a 100% yield of hydroxide ion.
Effect of Molecular Structure on Acid-Base Strength
In the absence of any leveling effect, the acid strength of binary compounds of hydrogen with nonmetals (A) increases as the H-A bond strength decreases down a group in the periodic table. For group 7A, the order of increasing acidity is HF < HCl < HBr < HI. Likewise, for group 6A, the order of increasing acid strength is H2O < H2S < H2Se < H2Te.
Across a row in the periodic table, the acid strength of binary hydrogen compounds increases with increasing electronegativity of the nonmetal atom because the polarity of the H-A bond increases. Thus, the order of increasing acidity (for removal of one proton) across the second row is CH4 < NH3 < H2O < HF; across the third row, it is SiH4 < PH3 < H2S < HCl (see Figure 7).
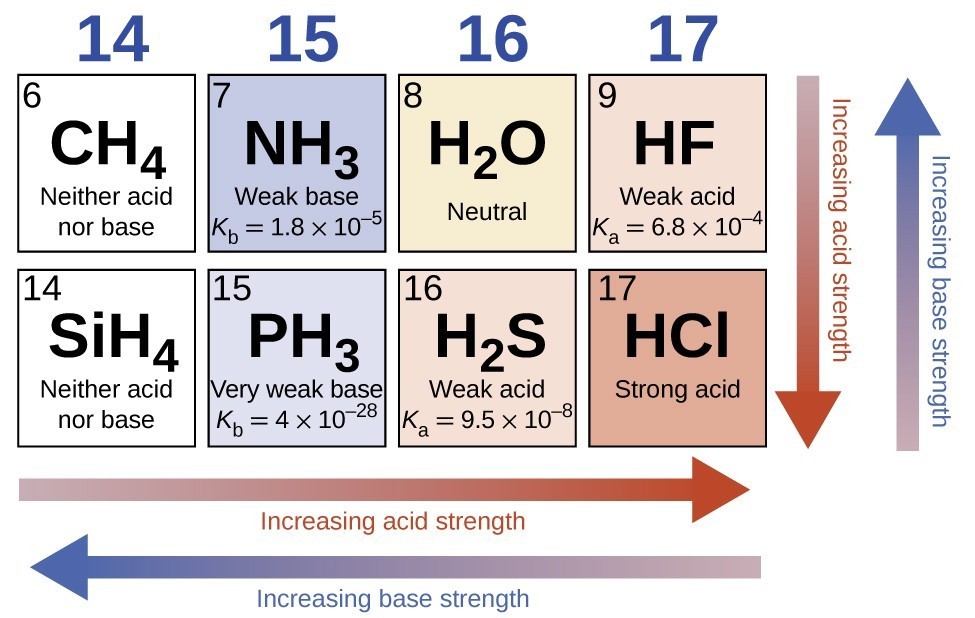
Figure 7. As you move from left to right and down the periodic table, the acid strength increases. As you move from right to left and up, the base strength increases.
Compounds containing oxygen and one or more hydroxyl (OH) groups can be acidic, basic, or amphoteric, depending on the position in the periodic table of the central atom E, the atom bonded to the hydroxyl group. Such compounds have the general formula OnE(OH)m, and include sulfuric acid, O2S(OH)2, sulfurous acid, OS(OH)2, nitric acid, O2NOH, perchloric acid, O3ClOH, aluminum hydroxide, Al(OH)3, calcium hydroxide, Ca(OH)2, and potassium hydroxide, KOH:

If the central atom, E, has a low electronegativity, its attraction for electrons is low. Little tendency exists for the central atom to form a strong covalent bond with the oxygen atom, and bond a between the element and oxygen is more readily broken than bond b between oxygen and hydrogen. Hence bond a is ionic, hydroxide ions are released to the solution, and the material behaves as a base—this is the case with Ca(OH)2 and KOH. Lower electronegativity is characteristic of the more metallic elements; hence, the metallic elements form ionic hydroxides that are by definition basic compounds.
If, on the other hand, the atom E has a relatively high electronegativity, it strongly attracts the electrons it shares with the oxygen atom, making bond a relatively strongly covalent. The oxygen-hydrogen bond, bond b, is thereby weakened because electrons are displaced toward E. Bond b is polar and readily releases hydrogen ions to the solution, so the material behaves as an acid. High electronegativities are characteristic of the more nonmetallic elements. Thus, nonmetallic elements form covalent compounds containing acidic −OH groups that are called oxyacids.
Increasing the oxidation number of the central atom E also increases the acidity of an oxyacid because this increases the attraction of E for the electrons it shares with oxygen and thereby weakens the O-H bond. Sulfuric acid, H2SO4, or O2S(OH)2 (with a sulfur oxidation number of +6), is more acidic than sulfurous acid, H2SO3, or OS(OH)2 (with a sulfur oxidation number of +4). Likewise nitric acid, HNO3, or O2NOH (N oxidation number = +5), is more acidic than nitrous acid, HNO2, or ONOH (N oxidation number = +3). In each of these pairs, the oxidation number of the central atom is larger for the stronger acid (Figure 8).
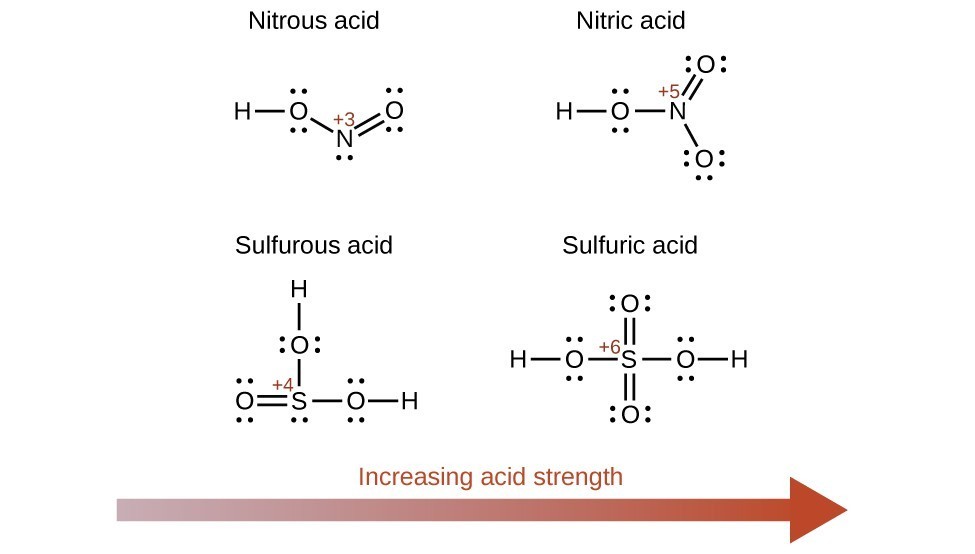
Figure 8. As the oxidation number of the central atom E increases, the acidity also increases.
Hydroxy compounds of elements with intermediate electronegativities and relatively high oxidation numbers (for example, elements near the diagonal line separating the metals from the nonmetals in the periodic table) are usually amphoteric. This means that the hydroxy compounds act as acids when they react with strong bases and as bases when they react with strong acids. The amphoterism of aluminum hydroxide, which commonly exists as the hydrate Al(H2O)3(OH)3, is reflected in its solubility in both strong acids and strong bases. In strong bases, the relatively insoluble hydrated aluminum hydroxide, Al(H2O)3(OH)3, is converted into the soluble ion, [latex]{\left[\text{Al}{\left({\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\right)}_{2}{\left(\text{OH}\right)}_{4}\right]}^{-}[/latex], by reaction with hydroxide ion:
[latex]\text{Al}{\left({\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\right)}_{3}{\left(\text{OH}\right)}_{3}\left(aq\right)+{\text{OH}}^{-}\left(aq\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)+{\left[\text{Al}{\left({\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\right)}_{2}{\left(\text{OH}\right)}_{4}\right]}^{-}\left(aq\right)[/latex]
In this reaction, a proton is transferred from one of the aluminum-bound H2O molecules to a hydroxide ion in solution. The Al(H2O)3(OH)3 compound thus acts as an acid under these conditions. On the other hand, when dissolved in strong acids, it is converted to the soluble ion [latex]{\left[\text{Al}{\left({\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\right)}_{6}\right]}^{3+}[/latex] by reaction with hydronium ion:
[latex]{\text{3H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+\text{Al}{\left({\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\right)}_{3}{\left(\text{OH}\right)}_{3}\left(aq\right)\rightleftharpoons \text{Al}{\left({\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\right)}_{6}{}^{3+}\left(aq\right)+{\text{3H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)[/latex]
In this case, protons are transferred from hydronium ions in solution to Al(H2O)3(OH)3, and the compound functions as a base.
Key Concepts and Summary
The strengths of Brønsted-Lowry acids and bases in aqueous solutions can be determined by their acid or base ionization constants. Stronger acids form weaker conjugate bases, and weaker acids form stronger conjugate bases. Thus strong acids are completely ionized in aqueous solution because their conjugate bases are weaker bases than water. Weak acids are only partially ionized because their conjugate bases are strong enough to compete successfully with water for possession of protons. Strong bases react with water to quantitatively form hydroxide ions. Weak bases give only small amounts of hydroxide ion. The strengths of the binary acids increase from left to right across a period of the periodic table (CH4 < NH3 < H2O < HF), and they increase down a group (HF < HCl < HBr < HI). The strengths of oxyacids that contain the same central element increase as the oxidation number of the element increases (H2SO3 < H2SO4). The strengths of oxyacids also increase as the electronegativity of the central element increases [H2SeO4 < H2SO4].
Key Equations
- [latex]{K}_{\text{a}}=\frac{\left[{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\right]\left[{\text{A}}^{-}\right]}{\left[\text{HA}\right]}[/latex]
- [latex]{K}_{\text{b}}=\frac{\left[{\text{HB}}^{\text{+}}\right]\left[{\text{OH}}^{-}\right]}{\left[\text{B}\right]}[/latex]
- Ka × Kb = 1.0 × 10−14 = Kw
- [latex]\text{Percent ionization}=\frac{{\left[{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\right]}_{\text{eq}}}{{\left[\text{HA}\right]}_{0}}\times 100[/latex]
Exercises
- Explain why the neutralization reaction of a strong acid and a weak base gives a weakly acidic solution.
- Explain why the neutralization reaction of a weak acid and a strong base gives a weakly basic solution.
- Use this list of important industrial compounds (and Figure 2) to answer the following questions regarding: CaO, Ca(OH)2, CH3CO2H, CO2, HCl, H2CO3, HF, HNO2, HNO3, H3PO4, H2SO4, NH3, NaOH, Na2CO3.
- Identify the strong Brønsted-Lowry acids and strong Brønsted-Lowry bases.
- List those compounds in (a) that can behave as Brønsted-Lowry acids with strengths lying between those of [latex]{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}[/latex] and H2O.
- List those compounds in (a) that can behave as Brønsted-Lowry bases with strengths lying between those of H2O and OH−.
- The odor of vinegar is due to the presence of acetic acid, CH3CO2H, a weak acid. List, in order of descending concentration, all of the ionic and molecular species present in a 1-M aqueous solution of this acid.
- Household ammonia is a solution of the weak base NH3 in water. List, in order of descending concentration, all of the ionic and molecular species present in a 1-M aqueous solution of this base.
- Explain why the ionization constant, Ka, for H2SO4 is larger than the ionization constant for H2SO3.
- Explain why the ionization constant, Ka, for HI is larger than the ionization constant for HF.
- Gastric juice, the digestive fluid produced in the stomach, contains hydrochloric acid, HCl. Milk of Magnesia, a suspension of solid Mg(OH)2 in an aqueous medium, is sometimes used to neutralize excess stomach acid. Write a complete balanced equation for the neutralization reaction, and identify the conjugate acid-base pairs.
- Nitric acid reacts with insoluble copper(II) oxide to form soluble copper(II) nitrate, Cu(NO3)2, a compound that has been used to prevent the growth of algae in swimming pools. Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of an aqueous solution of HNO3 with CuO.
- What is the ionization constant at 25 °C for the weak acid [latex]{\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{NH}}_{3}{}^{\text{+}}[/latex], the conjugate acid of the weak base CH3NH2, Kb = 4.4 × 10−4.
- What is the ionization constant at 25 °C for the weak acid [latex]{\left({\text{CH}}_{3}\right)}_{2}{\text{NH}}_{2}{}^{\text{+}}[/latex], the conjugate acid of the weak base (CH3)2NH, Kb = 7.4 × 10−4?
- Which base, CH3NH2 or (CH3)2NH, is the strongest base? Which conjugate acid, [latex]{\left({\text{CH}}_{3}\right)}_{2}{\text{NH}}_{2}{}^{\text{+}}[/latex] or (CH3)2NH, is the strongest acid?
- Which is the stronger acid, [latex]{\text{NH}}_{4}{}^{\text{+}}[/latex] or HBrO?
- Which is the stronger base, (CH3)3N or [latex]{\text{H}}_{2}{\text{BO}}_{3}{}^{-}?[/latex]
- Predict which acid in each of the following pairs is the stronger and explain your reasoning for each.
- H2O or HF
- B(OH)3 or Al(OH)3
- [latex]{\text{HSO}}_{3}^{-}[/latex] or [latex]{\text{HSO}}_{4}{}^{-}[/latex]
- NH3 or H2S
- H2O or H2Te
- Predict which compound in each of the following pairs of compounds is more acidic and explain your reasoning for each.
- [latex]{\text{HSO}}_{4}^{-}[/latex] or [latex]{\text{HSeO}}_{4}^{-}[/latex]
- NH3 or H2O
- PH3 or HI
- NH3 or PH3
- H2S or HBr
- Rank the compounds in each of the following groups in order of increasing acidity or basicity, as indicated, and explain the order you assign.
- acidity: HCl, HBr, HI
- basicity: H2O, OH−, H−, Cl−
- basicity: Mg(OH)2, Si(OH)4, ClO3(OH) (Hint: Formula could also be written as HClO4).
- acidity: HF, H2O, NH3, CH4
- Rank the compounds in each of the following groups in order of increasing acidity or basicity, as indicated, and explain the order you assign.
- acidity: NaHSO3, NaHSeO3, NaHSO4
- basicity: [latex]{\text{BrO}}_{2}{}^{-}[/latex], [latex]{\text{ClO}}_{2}{}^{-}[/latex], [latex]{\text{IO}}_{2}{}^{-}[/latex]
- acidity: HOCl, HOBr, HOI
- acidity: HOCl, HOClO, HOClO2, HOClO3
- basicity: [latex]{\text{NH}}_{2}{}^{-}[/latex], HS−, HTe−, [latex]{\text{PH}}_{2}{}^{-}[/latex]
- basicity: BrO−, [latex]{\text{BrO}}_{2}{}^{-}[/latex], [latex]{\text{BrO}}_{3}{}^{-}[/latex], [latex]{\text{BrO}}_{4}{}^{-}[/latex]
- Both HF and HCN ionize in water to a limited extent. Which of the conjugate bases, F− or CN−, is the stronger base? See Table 3.
- The active ingredient formed by aspirin in the body is salicylic acid, C6H4OH(CO2H). The carboxyl group (−CO2H) acts as a weak acid. The phenol group (an OH group bonded to an aromatic ring) also acts as an acid but a much weaker acid. List, in order of descending concentration, all of the ionic and molecular species present in a 0.001-M aqueous solution of C6H4OH(CO2H).
- What do we represent when we write: [latex]{\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{CO}}_{2}\text{H}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+{\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{CO}}_{2}{}^{-}\left(aq\right)?[/latex]
- Explain why equilibrium calculations are not necessary to determine ionic concentrations in solutions of certain strong electrolytes such as NaOH and HCl. Under what conditions are equilibrium calculations necessary as part of the determination of the concentrations of all ions of some other strong electrolytes in solution?
- Are the concentrations of hydronium ion and hydroxide ion in a solution of an acid or a base in water directly proportional or inversely proportional? Explain your answer.
- What two common assumptions can simplify calculation of equilibrium concentrations in a solution of a weak acid?
- What two common assumptions can simplify calculation of equilibrium concentrations in a solution of a weak base?
- Which of the following will increase the percent of NH3 that is converted to the ammonium ion in water (Hint: Use LeChâtelier’s principle.)?
- addition of NaOH
- addition of HCl
- addition of NH4Cl
- Which of the following will increase the percent of HF that is converted to the fluoride ion in water?
- addition of NaOH
- addition of HCl
- addition of NaF
- What is the effect on the concentrations of [latex]{\text{NO}}_{2}{}^{-}[/latex], HNO2, and OH− when the following are added to a solution of KNO2 in water:
- HCl
- HNO2
- NaOH
- NaCl
- KNO
The equation for the equilibrium is: [latex]{\text{NO}}_{2}{}^{-}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{HNO}}_{2}\left(aq\right)+{\text{OH}}^{-}\left(aq\right)[/latex]
- What is the effect on the concentration of hydrofluoric acid, hydronium ion, and fluoride ion when the following are added to separate solutions of hydrofluoric acid?
- HCl
- KF
- NaCl
- KOH
- HF
The equation for the equilibrium is: [latex]\text{HF}\left(aq\right)+{\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\left(l\right)\rightleftharpoons {\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\left(aq\right)+{\text{F}}^{-}\left(aq\right)[/latex]
- Why is the hydronium ion concentration in a solution that is 0.10 M in HCl and 0.10 M in HCOOH determined by the concentration of HCl?
- From the equilibrium concentrations given, calculate Ka for each of the weak acids and Kb for each of the weak bases.
- CH3CO2H: [latex]\left[{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\right][/latex] = 1.34 × 10−3M;
[latex]\left[{\text{CH}}_{3}{\text{CO}}_{2}{}^{-}\right][/latex] = 1.34 × 10−3M;
[CH3CO2H] = 9.866 × 10−2M; - ClO−: [OH−] = 4.0 × 10−4M;
[HClO] = 2.38 × 10−5M;
[ClO−] = 0.273 M; - HCO2H: [HCO2H] = 0.524 M;
[latex]\left[{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\right][/latex] = 9.8 × 10−3M;
[latex]\left[{\text{HCO}}_{2}{}^{-}\right][/latex] = 9.8 × 10−3M; - [latex]{\text{C}}_{6}{\text{H}}_{5}{\text{NH}}_{3}{}^{\text{+}}:[/latex] [latex]\left[{\text{C}}_{6}{\text{H}}_{5}{\text{NH}}_{3}{}^{\text{+}}\right][/latex] = 0.233 M;
[C6H5NH2] = 2.3 × 10−3M;
[latex]\left[{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\right][/latex] = 2.3 × 10−3M
- CH3CO2H: [latex]\left[{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\right][/latex] = 1.34 × 10−3M;
- From the equilibrium concentrations given, calculate Ka for each of the weak acids and Kb for each of the weak bases.
- NH3: [OH−] = 3.1 × 10−3M;
[latex]\left[{\text{NH}}_{4}{}^{\text{+}}\right][/latex] = 3.1 × 10−3M;
[NH3] = 0.533 M; - HNO2: [latex]\left[{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\right][/latex] = 0.011 M;
[latex]\left[{\text{NO}}_{2}{}^{-}\right][/latex] = 0.0438 M;
[HNO2] = 1.07 M; - (CH3)3N: [(CH3)3N] = 0.25 M;
[latex]\left[{\left({\text{CH}}_{3}\right)}_{3}{\text{NH}}^{\text{+}}\right][/latex] = 4.3 × 10−3M;
[OH−] = 4.3 × 10−3M; - [latex]{\text{NH}}_{4}{}^{\text{+}}:[/latex] [latex]\left[{\text{NH}}_{4}{}^{\text{+}}\right][/latex] = 0.100 M;
[NH3] = 7.5 × 10−6M;
[latex]\left[{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}\right][/latex] = 7.5 × 10−6M
- NH3: [OH−] = 3.1 × 10−3M;
- Determine Kb for the nitrite ion, [latex]{\text{NO}}_{2}{}^{-}[/latex]. In a 0.10-M solution this base is 0.0015% ionized.
- Determine Ka for hydrogen sulfate ion, [latex]{\text{HSO}}_{4}{}^{-}[/latex]. In a 0.10-M solution the acid is 29% ionized.
- Calculate the ionization constant for each of the following acids or bases from the ionization constant of its conjugate base or conjugate acid:
- F−
- [latex]{\text{NH}}_{4}{}^{\text{+}}[/latex]
- [latex]{\text{AsO}}_{4}{}^{3-}[/latex]
- [latex]{\left({\text{CH}}_{3}\right)}_{2}{\text{NH}}_{2}{}^{\text{+}}[/latex]
- [latex]{\text{NO}}_{2}{}^{-}[/latex]
- [latex]{\text{HC}}_{2}{\text{O}}_{4}{}^{-}[/latex] (as a base)
- Calculate the ionization constant for each of the following acids or bases from the ionization constant of its conjugate base or conjugate acid:
- HTe− (as a base)
- [latex]{\left({\text{CH}}_{3}\right)}_{3}{\text{NH}}^{\text{+}}[/latex]
- [latex]{\text{HAsO}}_{4}{}^{3-}[/latex] (as a base)
- [latex]{\text{HO}}_{2}{}^{-}[/latex] (as a base)
- [latex]{\text{C}}_{6}{\text{H}}_{5}{\text{NH}}_{3}{}^{\text{+}}[/latex]
- [latex]{\text{HSO}}_{3}{}^{-}[/latex] (as a base)
- For which of the following solutions must we consider the ionization of water when calculating the pH or pOH?
- 3 × 10−8M HNO3
- 0.10 g HCl in 1.0 L of solution
- 0.00080 g NaOH in 0.50 L of solution
- 1 × 10−7M Ca(OH)2
- 0.0245 M KNO3
- Even though both NH3 and C6H5NH2 are weak bases, NH3 is a much stronger acid than C6H5NH2. Which of the following is correct at equilibrium for a solution that is initially 0.10 M in NH3 and 0.10 M in C6H5NH2?
- [latex]\left[{\text{OH}}^{-}\right]=\left[{\text{NH}}_{4}{}^{\text{+}}\right][/latex]
- [latex]\left[{\text{NH}}_{4}{}^{\text{+}}\right]=\left[{\text{C}}_{6}{\text{H}}_{5}{\text{NH}}_{3}{}^{\text{+}}\right][/latex]
- [latex]\left[{\text{OH}}^{-}\right]=\left[{\text{C}}_{6}{\text{H}}_{5}{\text{NH}}_{3}{}^{\text{+}}\right][/latex]
- [NH3] = [C6H5NH2]
- both a and b are correct
Exercises: Calculating Equilibrium Concenration
- Calculate the equilibrium concentration of the nonionized acids and all ions in a solution that is 0.25 M in HCO2H and 0.10 M in HClO.
- Calculate the equilibrium concentration of the nonionized acids and all ions in a solution that is 0.134 M in HNO2 and 0.120 M in HBrO.
- Calculate the equilibrium concentration of the nonionized bases and all ions in a solution that is 0.25 M in CH3NH2 and 0.10 M in C5H5N (Kb = 1.7 × 10−9).
- Calculate the equilibrium concentration of the nonionized bases and all ions in a solution that is 0.115 M in NH3 and 0.100 M in C6H5NH2.
- Using the Ka values in Ionization Constants of Weak Acids, place [latex]\text{Al}{\left({\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\right)}_{6}{}^{3+}[/latex] in the correct location in Figure 3.
- Calculate the concentration of all solute species in each of the following solutions of acids or bases. Assume that the ionization of water can be neglected, and show that the change in the initial concentrations can be neglected. Ionization constants can be found in Ionization Constants of Weak Acids and Ionization Constants of Weak Bases.
- 0.0092 M HClO, a weak acid
- 0.0784 M C6H5NH2, a weak base
- 0.0810 M HCN, a weak acid
- 0.11 M (CH3)3N, a weak base
- 0.120 M [latex]\text{Fe}{\left({\text{H}}_{2}\text{O}\right)}_{6}{}^{2+}[/latex] a weak acid, Ka = 1.6 × 10−7
- Propionic acid, C2H5CO2H (Ka = 1.34 × 10−5), is used in the manufacture of calcium propionate, a food preservative. What is the hydronium ion concentration in a 0.698-M solution of C2H5CO2H?
- White vinegar is a 5.0% by mass solution of acetic acid in water. If the density of white vinegar is 1.007 g/cm3, what is the pH?
- The ionization constant of lactic acid, CH3CH(OH)CO2H, an acid found in the blood after strenuous exercise, is 1.36 × 10−4. If 20.0 g of lactic acid is used to make a solution with a volume of 1.00 L, what is the concentration of hydronium ion in the solution?
- Nicotine, C10H14N2, is a base that will accept two protons (K1 = 7 × 10−7, K2 = 1.4 × 10−11). What is the concentration of each species present in a 0.050-M solution of nicotine?
- The pH of a 0.20-M solution of HF is 1.92. Determine Ka for HF from these data.
- The pH of a 0.15-M solution of [latex]{\text{HSO}}_{4}{}^{-}[/latex] is 1.43. Determine Ka for [latex]{\text{HSO}}_{4}{}^{-}[/latex] from these data.
- The pH of a 0.10-M solution of caffeine is 11.16. Determine Kb for caffeine from these data:
- The pH of a solution of household ammonia, a 0.950 M solution of NH3, is 11.612. Determine Kb for NH3 from these data.
Glossary
acid ionization constant (Ka): equilibrium constant for the ionization of a weak acid
base ionization constant (Kb): equilibrium constant for the ionization of a weak base
leveling effect of water: any acid stronger than [latex]{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}[/latex], or any base stronger than OH− will react with water to form [latex]{\text{H}}_{3}{\text{O}}^{\text{+}}[/latex], or OH−, respectively; water acts as a base to make all strong acids appear equally strong, and it acts as an acid to make all strong bases appear equally strong
oxyacid: compound containing a nonmetal and one or more hydroxyl groups
percent ionization: ratio of the concentration of the ionized acid to the initial acid concentration, times 100
Candela Citations
- Chemistry. Provided by: OpenStax College. Located at: http://openstaxcollege.org. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at https://openstaxcollege.org/textbooks/chemistry/get
![A diagram is shown that includes six rust-red rectangles. The first rectangle is labeled, “p H,” and there is an arrow that points to the right to the second rectangle. The second rectangle is labeled, “[ H subscript 3 O superscript plus ].” There is an arrow that points right to the third rectangle. The third rectangle is labeled, “Calculate x subscript [ H subscript 3 O superscript plus ].” There is an arrow that points right to the fourth rectangle. The fourth rectangle is labeled, “Calculate x subscript [ H N O subscript 2 ] and x subscript [ N O subscript 2 superscript negative sign ].” There is an arrow that points down to the fifth rectangle. The fifth rectangle is labeled, “Calculate equilibrium concentrations.” There is an arrow that points down to the sixth rectangle. The sixth rectangle is labeled, “Calculate K subscript a.”](https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images-archive-read-only/wp-content/uploads/sites/887/2015/05/23213738/CNX_Chem_14_03_steps_img.jpg)
![This table has two main columns and four rows. The first row for the first column does not have a heading and then has the following in the first column: Initial concentration ( M ), Change ( M ), Equilibrium concentration ( M ). The second column has the header of, “H N O subscript 2 plus sign H subscript 2 O equilibrium arrow H subscript 3 O superscript positive sign plus sign N O subscript 2 superscript negative sign.” Under the second column is a subgroup of four columns and three rows. The first column has the following: 0.0516, negative x, [ H N O subscript 2 ] subscript i plus ( negative x ) equals 0.0516 plus sign ( negative x ). The second column is blank in the first row, positive sign, blank for the third row. The third column has the following: approximately 0, x, [ H subscript 3 O ] superscript positive sign plus sign x [ N O subscript 2 ] superscript negative sign plus sign x plus sign 0 plus sign x. The fourth column has the following: 0, x, 0.0046.](https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images-archive-read-only/wp-content/uploads/sites/887/2015/05/23213740/CNX_Chem_14_03_ICETable1_img.jpg)






![This table has two main columns and four rows. The first row for the first column does not have a heading and then has the following in the first column: Initial concentration ( M ), Change ( M ), Equilibrium ( M ). The second column has the header of “[ H N O subscript 2 ] [ H subscript 3 O superscript positive sign ] [ N O subscript 2 superscript negative sign ].” Under the second column is a subgroup of three columns and three rows. The first column has the following: 0.134, negative x, 0.134 minus sign x. The second column has the following: 0, x, x. The third column has the following: 0, x, x.](https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images-archive-read-only/wp-content/uploads/sites/887/2015/05/23213758/CNX_Chem_14_03_ICETable7_img.jpg)
![This table has two main columns and four rows. The first row for the first column does not have a heading and then has the following in the first column: Initial concentration ( M ), Change ( M ), Equilibrium ( M ). The second column has the header of “[ N H subscript 3 ] [ O H superscript negative sign ] [ N H subscript 4 superscript positive sign ].” Under the second column is a subgroup of three columns and three rows. The first column has the following: 0.115, negative x, 0.115 minus sign x. The second column has the following: 0, x, x. The third column has the following: 0, x, x.](https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images-archive-read-only/wp-content/uploads/sites/887/2015/05/23213801/CNX_Chem_14_03_ICETable9_img.jpg)
![This table has two main columns and four rows. The first row for the first column does not have a heading and then has the following in the first column: Initial concentration ( M ), Change ( M ), Equilibrium ( M ). The second column has the header of “[ H C l O ] [ H subscript 3 O superscript positive sign ] [ C l O superscript negative sign ].” Under the second column is a subgroup of three columns and three rows. The first column has the following: 0.0092, negative x, 0.0092 minus sign x. The second column has the following: 0, x, x. The third column has the following: 0, x, x.](https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images-archive-read-only/wp-content/uploads/sites/887/2015/05/23213802/CNX_Chem_14_03_ICETable11_img.jpg)
![This table has two main columns and four rows. The first row for the first column does not have a heading and then has the following in the first column: Initial concentration ( M ), Change ( M ), Equilibrium ( M ). The second column has the header of “[ C subscript 6 H subscript 5 H subscript 2 ] [ C subscript five H subscript 5 N H subscript 3 superscript positive sign ] [ O H superscript negative sign ].” Under the second column is a subgroup of three rows and three columns. The first column has the following: 0.0784, negative sign x, 0.0784 minus sign x. The second column has the following: 0, x, x. The third column has the following: 0, x, x.](https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images-archive-read-only/wp-content/uploads/sites/887/2015/05/23213803/CNX_Chem_14_03_ICETable12_img.jpg)
![This table has two main columns and four rows. The first row for the first column does not have a heading and then has the following in the first column: Initial concentration ( M ), Change ( M ), Equilibrium ( M ). The second column has the header of “[ H C l O ] [ H subscript 3 O superscript positive sign ] [ C N superscript negative sign ].” Under the second column is a subgroup of three columns and three rows. The first column has the following: 0.0810, negative x, 0.0810 minus sign x. The second column has the following: 0, x, x. The third column has the following: 0, x, x.](https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images-archive-read-only/wp-content/uploads/sites/887/2015/05/23213805/CNX_Chem_14_03_ICETable13_img.jpg)
![This table has two main columns and four rows. The first row for the first column does not have a heading and then has the following in the first column: Initial concentration ( M ), Change ( M ), Equilibrium ( M ). The second column has the header of “[ ( C H subscript 3 ) subscript 3 N ] [ ( C H subscript ) subscript 3 N H superscript positive sign ] [ O H ].” Under the second column is a subgroup of three columns and three rows. The first column has the following: 0.11, negative sign x, 0.11 minus sign x. The second column has the following: 0, x, x. The third column has the following: 0, x, x.](https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images-archive-read-only/wp-content/uploads/sites/887/2015/05/23213807/CNX_Chem_14_03_ICETable14_img.jpg)
![This table has two main columns and four rows. The first row for the first column does not have a heading and then has the following in the first column: Initial concentration ( M ), Change ( M ), Equilibrium ( M ). The second column has the header of “[ F e ( H subscript 2 O ) subscript 6 superscript 2 superscript positive sign ] [ H subscript 3 O superscript positive sign ] [ F e ( H subscript 2 O ) subscript 5 (O H) superscript positive sign ].” Under the second column is a subgroup of three columns and three rows. The first column has the following: 0.120, negative sign x, 0.120 minus sign x. The second column has the following: 0, x, x. The third column has the following: 0, x, x.](https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images-archive-read-only/wp-content/uploads/sites/887/2015/05/23213808/CNX_Chem_14_03_ICETable15_img.jpg)
![This table has two main columns and four rows. The first row for the first column does not have a heading and then has the following in the first column: Initial concentration ( M ), Change ( M ), Equilibrium ( M ). The second column has the header of “[ C H subscript 3 C O subscript 2 H ] [ H subscript 3 O superscript positive sign ] [ C H subscript 3 C O subscript 2 superscript negative sign ].” Under the second column is a subgroup of three rows and three columns. The first column has the following: 0.838, negative sign x, 0.838 minus sign x. The second column has the following: 0, x, x. The third column has the following: 0, x, x.](https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images-archive-read-only/wp-content/uploads/sites/887/2015/05/23213811/CNX_Chem_14_03_ICETable32_img.jpg)
![This table has two main columns and four rows. The first row for the first column does not have a heading and then has the following in the first column: Initial concentration ( M ), Change ( M ), Equilibrium ( M ). The second column has the header of “[ C subscript 10 H subscript 14 N subscript 2 ] [ C subscript 10 H subscript 14 N subscript 2 H superscript positive sign ] [ O H superscript negative sign ].” Under the second column is a subgroup of three rows and three columns. The first column has the following: 0.050, negative sign x, 0.050 minus sign x. The second column has the following: 0, x, x. The third column has the following: 0, x, x.](https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images-archive-read-only/wp-content/uploads/sites/887/2015/05/23213816/CNX_Chem_14_03_ICETable34_img.jpg)