Graphs of the Parent Functions



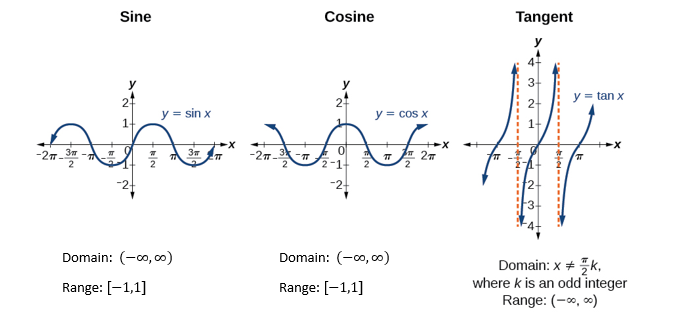
Graphs of the Trigonometric Functions



Trigonometric Identities
| Pythagorean Identities | [latex]\begin{array}{l}{\mathrm{cos}}^{2}t+{\mathrm{sin}}^{2}t=1\\ 1+{\mathrm{tan}}^{2}t={\mathrm{sec}}^{2}t\\ 1+{\mathrm{cot}}^{2}t={\mathrm{csc}}^{2}t\end{array}[/latex] |
| Even-Odd Identities | [latex]\begin{array}{l}\mathrm{cos}\left(-t\right)=\mathrm{cos}\text{ }t\hfill \\ \mathrm{sec}\left(-t\right)=\mathrm{sec}\text{ }t\hfill \\ \mathrm{sin}\left(-t\right)=-\mathrm{sin}\text{ }t\hfill \\ \mathrm{tan}\left(-t\right)=-\mathrm{tan}\text{ }t\hfill \\ \mathrm{csc}\left(-t\right)=-\mathrm{csc}\text{ }t\hfill \\ \mathrm{cot}\left(-t\right)=-\mathrm{cot}\text{ }t\hfill \end{array}[/latex] |
| Cofunction Identities | [latex]\begin{array}{l}\mathrm{cos}\text{ }t=\mathrm{sin}\left(\frac{\pi }{2}-t\right)\hfill \\ \mathrm{sin}\text{ }t=\mathrm{cos}\left(\frac{\pi }{2}-t\right)\hfill \\ \mathrm{tan}\text{ }t=\mathrm{cot}\left(\frac{\pi }{2}-t\right)\hfill \\ \mathrm{cot}\text{ }t=\mathrm{tan}\left(\frac{\pi }{2}-t\right)\hfill \\ \mathrm{sec}\text{ }t=\mathrm{csc}\left(\frac{\pi }{2}-t\right)\hfill \\ \mathrm{csc}\text{ }t=\mathrm{sec}\left(\frac{\pi }{2}-t\right)\hfill \end{array}[/latex] |
| Fundamental Identities | [latex]\begin{array}{l}\mathrm{tan}\text{ }t=\frac{\mathrm{sin}\text{ }t}{\mathrm{cos}\text{ }t}\hfill \\ \mathrm{sec}\text{ }t=\frac{1}{\mathrm{cos}\text{ }t}\hfill \\ \mathrm{csc}\text{ }t=\frac{1}{\mathrm{sin}\text{ }t}\hfill \\ \text{cot}\text{ }t=\frac{1}{\text{tan}\text{ }t}=\frac{\text{cos}\text{ }t}{\text{sin}\text{ }t}\hfill \end{array}[/latex] |
| Sum and Difference Identities | [latex]\begin{array}{l}\mathrm{cos}\left(\alpha +\beta \right)=\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\alpha \text{ }\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\beta -\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\alpha \text{ }\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\beta \hfill \\ \mathrm{cos}\left(\alpha -\beta \right)=\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\alpha \text{ }\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\beta +\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\alpha \text{ }\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\beta \hfill \\ \mathrm{sin}\left(\alpha +\beta \right)=\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\alpha \text{ }\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\beta +\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\alpha \text{ }\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\beta \hfill \\ \mathrm{sin}\left(\alpha -\beta \right)=\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\alpha \text{ }\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\beta -\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\alpha \text{ }\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\beta \hfill \\ \mathrm{tan}\left(\alpha +\beta \right)=\frac{\mathrm{tan}\text{ }\alpha +\mathrm{tan}\text{ }\beta }{1-\mathrm{tan}\text{ }\alpha \text{ }\mathrm{tan}\text{ }\beta }\hfill \\ \mathrm{tan}\left(\alpha -\beta \right)=\frac{\mathrm{tan}\text{ }\alpha -\mathrm{tan}\text{ }\beta }{1+\mathrm{tan}\text{ }\alpha \text{ }\mathrm{tan}\text{ }\beta }\hfill \end{array}[/latex] |
| Double-Angle Formulas | [latex]\begin{array}{l}\mathrm{sin}\left(2\theta \right)=2\text{ }\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\theta \text{ }\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\theta \hfill \\ \mathrm{cos}\left(2\theta \right)={\mathrm{cos}}^{2}\theta -{\mathrm{sin}}^{2}\theta \hfill \\ \mathrm{cos}\left(2\theta \right)=1-2\text{ }{\mathrm{sin}}^{2}\theta \hfill \\ \mathrm{cos}\left(2\theta \right)=2\text{ }{\mathrm{cos}}^{2}\theta -1\hfill \\ \mathrm{tan}\left(2\theta \right)=\frac{2\text{ }\mathrm{tan}\text{ }\theta }{1-{\mathrm{tan}}^{2}\theta }\hfill \end{array}[/latex] |
| Half-Angle Formulas | [latex]\begin{array}{l}\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\frac{\alpha }{2}=±\sqrt{\frac{1-\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\alpha }{2}}\hfill \\ \mathrm{cos}\text{ }\frac{\alpha }{2}=±\sqrt{\frac{1+\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\alpha }{2}}\hfill \\ \mathrm{tan}\text{ }\frac{\alpha }{2}=±\sqrt{\frac{1-\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\alpha }{1+\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\alpha }}\hfill \\ \mathrm{tan}\text{ }\frac{\alpha }{2}=\frac{\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\alpha }{1+\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\alpha }\hfill \\ \mathrm{tan}\text{ }\frac{\alpha }{2}=\frac{1-\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\alpha }{\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\alpha }\hfill \end{array}[/latex] |
| Reduction Formulas | [latex]\begin{array}{l}{\mathrm{sin}}^{2}\theta =\frac{1-\mathrm{cos}\left(2\theta \right)}{2}\\ {\mathrm{cos}}^{2}\theta =\frac{1+\mathrm{cos}\left(2\theta \right)}{2}\\ {\mathrm{tan}}^{2}\theta =\frac{1-\mathrm{cos}\left(2\theta \right)}{1+\mathrm{cos}\left(2\theta \right)}\end{array}[/latex] |
| Product-to-Sum Formulas | [latex]\begin{array}{l}\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\alpha \text{ }\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\beta =\frac{1}{2}\left[\mathrm{cos}\left(\alpha -\beta \right)+\mathrm{cos}\left(\alpha +\beta \right)\right]\hfill \\ \mathrm{sin}\text{ }\alpha \text{ }\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\beta =\frac{1}{2}\left[\mathrm{sin}\left(\alpha +\beta \right)+\mathrm{sin}\left(\alpha -\beta \right)\right]\hfill \\ \mathrm{sin}\text{ }\alpha \text{ }\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\beta =\frac{1}{2}\left[\mathrm{cos}\left(\alpha -\beta \right)-\mathrm{cos}\left(\alpha +\beta \right)\right]\hfill \\ \mathrm{cos}\text{ }\alpha \text{ }\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\beta =\frac{1}{2}\left[\mathrm{sin}\left(\alpha +\beta \right)-\mathrm{sin}\left(\alpha -\beta \right)\right]\hfill \end{array}[/latex] |
| Sum-to-Product Formulas | [latex]\begin{array}{l}\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\alpha +\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\beta =2\text{ }\mathrm{sin}\left(\frac{\alpha +\beta }{2}\right)\text{ }\mathrm{cos}\left(\frac{\alpha -\beta }{2}\right)\hfill \\ \mathrm{sin}\text{ }\alpha -\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\beta =2\text{ }\mathrm{sin}\left(\frac{\alpha -\beta }{2}\right)\text{ }\mathrm{cos}\left(\frac{\alpha +\beta }{2}\right)\hfill \\ \mathrm{cos}\text{ }\alpha -\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\beta =-2\text{ }\mathrm{sin}\left(\frac{\alpha +\beta }{2}\right)\text{ }\mathrm{sin}\left(\frac{\alpha -\beta }{2}\right)\hfill \\ \mathrm{cos}\text{ }\alpha +\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\beta =2\text{ }\mathrm{cos}\left(\frac{\alpha +\beta }{2}\right)\text{ }\mathrm{cos}\left(\frac{\alpha -\beta }{2}\right)\hfill \end{array}[/latex] |
| Law of Sines | [latex]\begin{array}{l}\frac{\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\alpha }{a}=\frac{\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\beta }{b}=\frac{\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\gamma }{c}\hfill \\ \frac{a}{\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\alpha }=\frac{b}{\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\beta }=\frac{c}{\mathrm{sin}\text{ }\gamma }\hfill \end{array}[/latex] |
| Law of Cosines | [latex]\begin{array}{l}{a}^{2}={b}^{2}+{c}^{2}-2bc\text{ }\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\alpha \hfill \\ {b}^{2}={a}^{2}+{c}^{2}-2ac\text{ }\mathrm{cos}\text{ }\beta \hfill \\ {c}^{2}={a}^{2}+{b}^{2}-2ab\text{ }\text{cos}\text{ }\gamma \hfill \end{array}[/latex] |
Candela Citations
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- Basic Functions and Identities. Authored by: Douglas Hoffman. Provided by: Openstax. Located at: https://cnx.org/contents/8si1Yf2B@2.21:EyqJ6FuE@4/Basic-Functions-and-Identities. Project: Essential Precalcus, Part 2. License: CC BY: Attribution
