Learning Objectives
In this section, you will:
- Determine and be able to explain whether a relation represents a function given a table or a graph.
- Evaluate functions and solve equations involving functions.
- Determine whether a function given numerically or graphically is one-to-one, and explain your rationale.
- Graph and name the functions listed in the library of functions.
A jetliner changes altitude as its distance from the starting point of a flight increases. The weight of a growing child increases with time. In each case, one quantity depends on another. There is a relationship between the two quantities that we can describe, analyze, and use to make predictions. In this section, we will analyze such relationships.
Determining Whether a Relation Represents a Function
A relation is a set of ordered pairs. The set of the first components of each ordered pair is called the domain and the set of the second components of each ordered pair is called the range. Consider the following set of ordered pairs. The first numbers in each pair are the first five natural numbers. The second number in each pair is twice that of the first.
[latex]\left\{\left(1,\text{ }2\right),\text{ }\left(2,\text{ }4\right),\text{ }\left(3,\text{ }6\right),\text{ }\left(4,\text{ }8\right),\text{ }\left(5,\text{ }10\right)\right\}[/latex]
The domain is [latex]\left\{1,\text{ }2,\text{ }3,\text{ }4,\text{ }5\right\}.[/latex] The range is [latex]\left\{2,\text{ }4,\text{ }6,\text{ }8,\text{ }10\right\}.[/latex]
Note that each value in the domain is also known as an input value, or independent variable, and is often labeled with the lowercase letter [latex]x.[/latex] Each value in the range is also known as an output value, or dependent variable, and is often labeled lowercase letter [latex]y.[/latex]
A function [latex]f[/latex] is a relation that assigns a single value in the range to each value in the domain. In other words, no [latex]x[/latex]-values are repeated. For our example that relates the first five natural numbers to numbers double their values, this relation is a function because each element in the domain, [latex]\left\{1,\text{ }2,\text{ }3,\text{ }4,\text{ }5\right\},[/latex] is paired with exactly one element in the range, [latex]\left\{2,\text{ }4,\text{ }6,\text{ }8,\text{ }10\right\}.[/latex]
Now let’s consider the set of ordered pairs that relates the terms “even” and “odd” to the first five natural numbers. It would appear as
[latex]\left\{\left(\text{odd},\text{ }1\right),\text{ }\left(\text{even},\text{ }2\right),\text{ }\left(\text{odd},\text{ }3\right),\text{ }\left(\text{even},\text{ }4\right),\text{ }\left(\text{odd},\text{ }5\right)\right\}[/latex]
Notice that each element in the domain, [latex]\left\{\text{even,}\text{ }\text{odd}\right\}[/latex] is not paired with exactly one element in the range, [latex]\left\{1,\text{ }2,\text{ }3,\text{ }4,\text{ }5\right\}.[/latex] For example, the term “odd” corresponds to three values from the range, [latex]\left\{1,\text{ }3,\text{ }5\right\}[/latex] and the term “even” corresponds to two values from the range, [latex]\left\{2,\text{ }4\right\}.[/latex] This violates the definition of a function, so this relation is not a function.
Figure 1 compares relations that are functions and not functions.
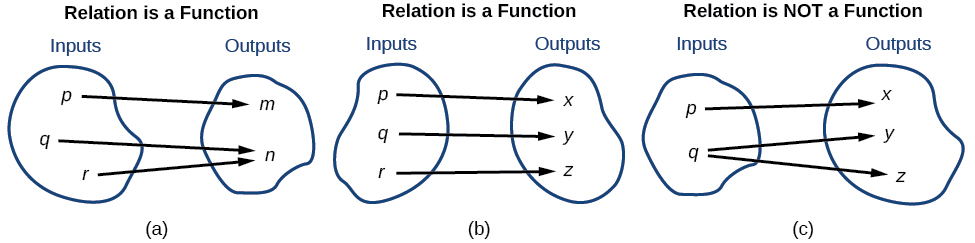
Figure 1: (a) This relationship is a function because each input is associated with a single output. Note that input [latex]q[/latex] and [latex]r[/latex] both give output [latex]n.[/latex] (b) This relationship is also a function. In this case, each input is associated with a single output. (c) This relationship is not a function because input [latex]q[/latex] is associated with two different outputs.
Definition
A function is a relation in which each possible input value leads to exactly one output value. We say “the output is a function of the input.”
The input values make up the domain, and the output values make up the range.
How To
Given a relationship between two quantities, determine whether the relationship is a function.
- Identify the input values.
- Identify the output values.
- If each input value leads to only one output value, classify the relationship as a function. If any input value leads to two or more outputs, do not classify the relationship as a function.
Example 1: Determining If Menu Price Lists Are Functions
The coffee shop menu, shown in Figure 2 consists of items and their prices.
- Is price a function of the item?
- Is the item a function of the price?

Figure 2
Example 2: Determining If Class Grade Rules Are Functions
In a particular math class, the overall percent grade corresponds to a grade point average. Is grade point average a function of the percent grade? Is the percent grade a function of the grade point average? Table 1 shows a possible rule for assigning grade points.
| Percent grade | 0–56 | 57–61 | 62–66 | 67–71 | 72–77 | 78–86 | 87–91 | 92–100 |
| Grade point average | 0.0 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 3.5 | 4.0 |
Try it #1
Using Function Notation
Once we determine that a relationship is a function, we need to display and define the functional relationships so that we can understand and use them, and sometimes also so that we can program them into computers. There are various ways of representing functions. A standard function notation is one representation that facilitates working with functions.
To represent “height is a function of age,” we start by identifying the descriptive variables [latex]h[/latex] for height and [latex]a[/latex] for age. The letters [latex]f,\text{ }g,[/latex] and [latex]h[/latex] are often used to represent functions just as we use [latex]x,\text{ }y,[/latex] and [latex]z[/latex] to represent numbers and [latex]A,\text{ }B,[/latex] and [latex]C[/latex] to represent sets.
[latex]\begin{array}{lllll}h\text{ is }f\text{ of }a\hfill & \hfill & \hfill & \hfill & \text{We name the function }f;\text{ height is a function of age}.\hfill \\ h=f\left(a\right)\hfill & \hfill & \hfill & \hfill & \text{We use parentheses to indicate the function input}\text{. }\hfill \\ f\left(a\right)\hfill & \hfill & \hfill & \hfill & \text{We name the function }f;\text{ the expression is read as “}f\text{ of }a\text{.”}\hfill \end{array}[/latex]
Remember, we can use any letter to name the function; the notation [latex]f\left(a\right)[/latex] shows us that height, [latex]h,[/latex] depends on age, [latex]a.[/latex] The value [latex]a[/latex] must be put into the function [latex]f[/latex] to get the height. The parentheses indicate that age is input into the function; they do not indicate multiplication.
We can also give an algebraic expression as the input to a function. For example [latex]f\left(a+b\right)[/latex] means “first add a and b, and the result is the input for the function f.” The operations must be performed in this order to obtain the correct result.
Definition
function notation: The notation [latex]y=f\left(x\right)[/latex] defines a function named [latex]f.[/latex] This is read as [latex]“y[/latex] is a function of [latex]x.”[/latex] The letter [latex]x[/latex] represents the input value, or independent variable. The letter [latex]y\text{, }[/latex] or [latex]f\left(x\right),[/latex] represents the output value, or dependent variable.
Example 3: Using Function Notation for Days in a Month
Use function notation to represent a function whose input is the name of a month and output is the number of days in that month. Assume that the domain does not include leap years.
Example 4: Interpreting Function Notation
A function [latex]N=f\left(y\right)[/latex] gives the number of police officers, [latex]N,[/latex] in a town in year [latex]y.[/latex] What does [latex]f\left(2005\right)=300[/latex] represent?
Try it #2
Use function notation to express the weight of a pig in pounds as a function of its age in days [latex]d\text{.}[/latex]
Q&A
Instead of a notation such as [latex]y=f\left(x\right),[/latex] could we use the same symbol for the output as for the function, such as [latex]y=y\left(x\right),[/latex] meaning “y is a function of x?”
Yes, this is often done, especially in applied subjects that use higher math, such as physics and engineering. However, in exploring math itself we like to maintain a distinction between a function such as [latex]f,[/latex] which is a rule or procedure, and the output [latex]y[/latex] we get by applying [latex]f[/latex] to a particular input [latex]x.[/latex] This is why we usually use notation such as [latex]y=f\left(x\right),P=W\left(d\right),[/latex] and so on.
Representing Functions Using Tables
A common method of representing functions is in the form of a table. The table rows or columns display the corresponding input and output values. In some cases, these values represent all we know about the relationship; other times, the table provides a few select examples from a more complete relationship.
Table 3 lists the input number of each month (January = 1, February = 2, and so on) and the output value of the number of days in that month. This information represents all we know about the months and days for a given year (that is not a leap year). Note that, in this table, we define a days-in-a-month function [latex]f[/latex] where [latex]D=f\left(m\right)[/latex] identifies months by an integer rather than by name.
| Month number, [latex]m[/latex](input) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| Days in month, [latex]D[/latex](output) | 31 | 28 | 31 | 30 | 31 | 30 | 31 | 31 | 30 | 31 | 30 | 31 |
Table 4 defines a function [latex]Q=g\left(n\right).[/latex] Remember, this notation tells us that [latex]g[/latex] is the name of the function that takes the input [latex]n[/latex] and gives the output [latex]Q\text{ .}[/latex]
| [latex]n[/latex] | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| [latex]Q[/latex] | 8 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 8 |
Table 5 displays the age of children in years and their corresponding heights. This table displays just some of the data available for the heights and ages of children. We can see right away that this table does not represent a function because the same input value, 5 years, has two different output values, 40 in. and 42 in.
| Age in years, [latex]a[/latex] (input) | 5 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| Height in inches,[latex]h[/latex] (output) | 40 | 42 | 44 | 47 | 50 | 52 | 54 |
How To
Given a table of input and output values, determine whether the table represents a function.
- Identify the input and output values.
- Check to see if each input value is paired with only one output value. If so, the table represents a function.
When a table represents a function, corresponding input and output values can also be specified using function notation.
The function represented by Table 6 can be represented by writing
[latex]f\left(2\right)=1,\text{ }f\left(5\right)=3,[/latex] and [latex]f\left(8\right)=6.[/latex]
Similarly, the statements
[latex]g\left(-3\right)=5,\text{ }g\left(0\right)=1,[/latex] and [latex]g\left(4\right)=5[/latex]
represent the function in Table 7.
Table 8 cannot be expressed in a similar way because it does not represent a function.
Try it #3
Finding Input and Output Values of a Function
When we know an input value and want to determine the corresponding output value for a function, we evaluate the function. Evaluating will always produce one result because each input value of a function corresponds to exactly one output value.
When we know an output value and want to determine the input values that would produce that output value, we set the output equal to the function’s formula and solve for the input. Solving can produce more than one solution because different input values can produce the same output value.
Evaluation of Functions in Algebraic Forms
When we have a function in formula form, it is usually a simple matter to evaluate the function. For example, the function [latex]f\left(x\right)=5-3{x}^{2}[/latex] can be evaluated by squaring the input value, multiplying by 3, and then subtracting the product from 5.
How To
Given the formula for a function, evaluate.
- Replace the input variable in the formula with the value provided.
- Calculate the result.
Example 6: Evaluating Functions at Specific Values
Evaluate [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{2}+3x-4[/latex] at
- [latex]2[/latex]
- [latex]a[/latex]
- [latex]a+h[/latex]
- [latex]\frac{f\left(a+h\right)-f\left(a\right)}{h}[/latex]
In Example 6, you worked with the expression below:
[latex]\begin{align*}\frac{f(a+h)-f(a)}{h}\\\end{align*}[/latex]
This is called the difference quotient. In Calculus, we use the difference quotient to develop an important concept called the derivative. You should work to become very comfortable with the difference quotient. We will work with it more in later sections of this chapter.
Example 7: Evaluating Functions
Given the function [latex]h\left(p\right)={p}^{2}+2p,[/latex] evaluate [latex]h\left(4\right).[/latex]
Try it #4
Given the function [latex]g\left(m\right)=\sqrt[\leftroot{1}\uproot{2} ]{m-4},[/latex] evaluate [latex]g\left(5\right).[/latex]
Example 8: Solving Functions
Given the function [latex]h\left(p\right)={p}^{2}+2p,[/latex] solve for [latex]h\left(p\right)=3.[/latex]
Try it #5
Given the function [latex]g\left(m\right)=\sqrt[\leftroot{1}\uproot{2} ]{m-4},[/latex] solve [latex]g\left(m\right)=2.[/latex]
Evaluating Functions Expressed in Formulas
Some functions are defined by mathematical rules or procedures expressed in equation form. If it is possible to express the function output with a formula involving the input quantity, then we can define a function in algebraic form. For example, the equation [latex]2n+6p=12[/latex] expresses a functional relationship between [latex]n[/latex] and [latex]p.[/latex] We can rewrite it to decide if [latex]p[/latex] is a function of [latex]n.[/latex]
How To
Given a function in equation form, write its algebraic formula.
- Solve the equation to isolate the output variable on one side of the equal sign, with the other side as an expression that involves only the input variable.
- Use all the usual algebraic methods for solving equations, such as adding or subtracting the same quantity to or from both sides, or multiplying or dividing both sides of the equation by the same quantity.
Example 9: Finding an Equation of a Function
Express the relationship [latex]2n+6p=12[/latex] as a function [latex]p=f\left(n\right),[/latex] if possible.
Example 10: Expressing the Equation of a Circle as a Function
Does the equation [latex]{x}^{2}+{y}^{2}=1[/latex] represent a function with [latex]x[/latex] as input and [latex]y[/latex] as output? If so, express the relationship as a function [latex]y=f\left(x\right).[/latex]
Try it #6
If [latex]x-8{y}^{3}=0,[/latex] express [latex]y[/latex] as a function of [latex]x.[/latex]
Q&A
Are there relationships expressed by an equation that do represent a function but which still cannot be represented by an algebraic formula?
Yes, this can happen. For example, given the equation [latex]x=y+{2}^{y},[/latex] if we want to express [latex]y[/latex] as a function of [latex]x,[/latex] there is no simple algebraic formula involving only [latex]x[/latex] that equals [latex]y.[/latex] However, each [latex]x[/latex] does determine a unique value for [latex]y,[/latex] and there are mathematical procedures by which [latex]y[/latex] can be found to any desired accuracy. In this case, we say that the equation gives an implicit (implied) rule for [latex]y[/latex] as a function of [latex]x,[/latex] even though the formula cannot be written explicitly.
Evaluating a Function Given in Tabular Form
As we saw previously, we can represent functions in tables. Conversely, we can use information in tables to write functions, and we can evaluate functions using the tables. For example, how well do our pets recall the fond memories we share with them? There is an urban legend that a goldfish has a memory of 3 seconds, but this is just a myth. Goldfish can remember up to 3 months, while the beta fish has a memory of up to 5 months. And while a puppy’s memory span is no longer than 30 seconds, the adult dog can remember for 5 minutes. This is meager compared to a cat, whose memory span lasts for 16 hours.
The function that relates the type of pet to the duration of its memory span is more easily visualized with the use of a table. See Table 10.[2]
| Pet | Memory span in hours |
| Puppy | 0.008 |
| Adult dog | 0.083 |
| Cat | 16 |
| Goldfish | 2160 |
| Beta fish | 3600 |
At times, evaluating a function in table form may be more useful than using equations. Here let us call the function [latex]P.[/latex] The domain of the function is the type of pet and the range is a real number representing the number of hours the pet’s memory span lasts. We can evaluate the function [latex]P[/latex] at the input value of “goldfish.” We would write [latex]P\left(\text{goldfish}\right)=2160.[/latex] Notice that, to evaluate the function in table form, we identify the input value and the corresponding output value from the pertinent row of the table. The tabular form for function [latex]P[/latex] seems ideally suited to this function, more so than writing it in paragraph or function form.
How To
Given a function represented by a table, identify specific output and input values.
- Find the given input in the row (or column) of input values.
- Identify the corresponding output value paired with that input value.
- Find the given output values in the row (or column) of output values, noting every time that output value appears.
- Identify the input value(s) corresponding to the given output value.
Example 11: Evaluating and Solving a Tabular Function
Using Table 11,
- Evaluate [latex]g\left(3\right).[/latex]
- Solve [latex]g\left(n\right)=6.[/latex]
| [latex]n[/latex] | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| [latex]g\left(n\right)[/latex] | 8 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 8 |
Try it #7
Using Table 11, evaluate [latex]g\left(1\right).[/latex]
Finding Function Values from a Graph
Evaluating a function using a graph also requires finding the corresponding output value for a given input value, only in this case, we find the output value by looking at the graph. Solving a function equation using a graph requires finding all instances of the given output value on the graph and observing the corresponding input value(s).
Example 12: Reading Function Values from a Graph
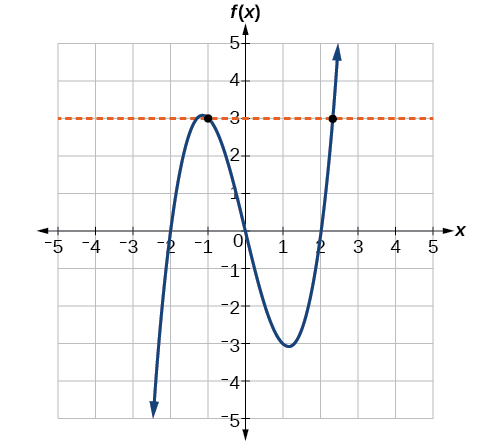
Given the graph in Figure 7,
- Evaluate [latex]f\left(2\right).[/latex]
- Solve [latex]f\left(x\right)=4.[/latex]

Figure 7
Try it #8
Using Figure 7, solve [latex]f\left(x\right)=1.[/latex]
Determining Whether a Function is One-to-One
Some functions have a given output value that corresponds to two or more input values. For example, in the stock chart shown in Figure 10, the stock price was $1000 on five different dates, meaning that there were five different input values that all resulted in the same output value of $1000.

Figure 10
However, some functions have only one input value for each output value, as well as having only one output for each input. We call these functions one-to-one functions. As an example, consider a school that uses only letter grades and decimal equivalents, as listed in Table 12.
| Letter grade | Grade point average |
| A | 4.0 |
| B | 3.0 |
| C | 2.0 |
| D | 1.0 |
This grading system represents a one-to-one function, because each letter input yields one particular grade point average output and each grade point average corresponds to one input letter.
To visualize this concept, let’s look again at the two simple functions sketched in Figure 1(a) and Figure 1(b). The function in part (a) shows a relationship that is not a one-to-one function because inputs [latex]q[/latex] and [latex]r[/latex] both give output [latex]n.[/latex] The function in part (b) shows a relationship that is a one-to-one function because each input is associated with a single output.
Definition
A one-to-one function is a function in which each output value corresponds to exactly one input value.
Example 13: Determining Whether a Relationship Is a One-to-One Function
Is the area of a circle a function of its radius? If yes, is the function one-to-one?
Try it #9
- Is a balance a function of the bank account number?
- Is a bank account number a function of the balance?
- Is a balance a one-to-one function of the bank account number?
Try it #10
Evaluate the following:
- If each percent grade earned in a course translates to one letter grade, is the letter grade a function of the percent grade? Explain.
- If so, is the function one-to-one? Explain.
Using the Vertical Line Test
As we have seen in some examples above, we can represent a function using a graph. Graphs display a great many input-output pairs in a small space. The visual information they provide often makes relationships easier to understand. By convention, graphs are typically constructed with the input values along the horizontal axis and the output values along the vertical axis.
Very often graphs name the input value [latex]x[/latex] and the output value [latex]y,[/latex] and we say [latex]y[/latex] is a function of [latex]x,[/latex] or [latex]y=f\left(x\right)[/latex] when the function is named [latex]f.[/latex] The graph of the function is the set of all points [latex]\left(x,y\right)[/latex] in the plane that satisfies the equation [latex]y=f\left(x\right).[/latex] If the function is defined for only a few input values, then the graph of the function is only a few points, where the x-coordinate of each point is an input value and the y-coordinate of each point is the corresponding output value. For example, the black dots on the graph in Figure 11 tell us that [latex]f\left(0\right)=2[/latex] and [latex]f\left(6\right)=1.[/latex] However, the set of all points [latex]\left(x,y\right)[/latex] satisfying [latex]y=f\left(x\right)[/latex] is a curve. The curve shown includes [latex]\left(0,2\right)[/latex] and [latex]\left(6,1\right)[/latex] because the curve passes through those points.

Figure 11
The vertical line test can be used to determine whether a graph represents a function. If we can draw any vertical line that intersects a graph more than once, then the graph does not define a function because a function can have only one output value for each input value. See Figure 12.

Figure 12
The second and third graphs in Figure 12 are not functions because the input value represented by the dotted line has two output values in each case. The two output values are the [latex]y[/latex] values where each dotted line intersects the solid line. This contradicts the definition of a function. Remember, a function is a rule where each input is mapped to exactly one output.
How To
Given a graph, use the vertical line test to determine if the graph represents a function.
- Inspect the graph to see if any vertical line drawn would intersect the curve more than once.
- If there is any such line, determine that the graph does not represent a function.
Example 14: Applying the Vertical Line Test
Which of the graphs in Figure 13 represent(s) a function [latex]y=f\left(x\right)?[/latex]

Figure 13
Using the Horizontal Line Test
Once we have determined that a graph defines a function, an easy way to determine if it is a one-to-one function is to use the horizontal line test. Draw horizontal lines through the graph. If any horizontal line intersects the graph more than once, then the graph does not represent a one-to-one function. Each intersection along the horizontal line represents an x-value with the same output which contradicts the definition of one-to-one which states that each output value must be unique for the function to be one-to-one.
How To
Given a graph of a function, use the horizontal line test to determine if the graph represents a one-to-one function.
- Inspect the graph to see if any horizontal line drawn would intersect the curve more than once.
- If there is any such line, determine that the function is not one-to-one.
Try it #12
Is the graph shown in Figure 13 (c) one-to-one?
Identifying Basic Toolkit Functions
In this text, we will be exploring functions including the shapes of their graphs, their unique characteristics, their algebraic formulas, and how to solve problems with them. When learning to read, we start with the alphabet. When learning to do arithmetic, we start with numbers. When working with functions, it is similarly helpful to have a base set of building-block elements. We call these our “toolkit functions,” which form a set of basic named functions for which we know the graph, formula, and special properties. Some of these functions are programmed to individual buttons on many calculators. For these definitions we will use [latex]x[/latex] as the input variable and [latex]y=f\left(x\right)[/latex] as the output variable.
We will see these toolkit functions, combinations of toolkit functions, their graphs, and their transformations frequently throughout this book. It will be very helpful if we can recognize these toolkit functions and their features quickly by name, formula, graph, and basic table properties. The graphs and sample table values are included with each function shown in Table 13.
Toolkit Functions |
||
| Name | Function | Graph |
| Constant | [latex]f\left(x\right)=c,[/latex] where [latex]c[/latex] is a constant |  |
| Identity | [latex]f\left(x\right)=x[/latex] |  |
| Absolute value | [latex]f\left(x\right)=|x|[/latex] |  |
| Quadratic | [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{2}[/latex] |  |
| Cubic | [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{3}[/latex] |  |
| Reciprocal | [latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{x}[/latex] |  |
| Reciprocal squared | [latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{{x}^{2}}[/latex] |  |
| Square root | [latex]f\left(x\right)=\sqrt{x}[/latex] |  |
| Cube root | [latex]f\left(x\right)=\sqrt[3]{x}[/latex] |  |
Access the following online resources for additional instruction and practice with functions.
Key Equations
| Constant function | [latex]f\left(x\right)=c,[/latex] where [latex]c[/latex] is a constant |
| Identity function | [latex]f\left(x\right)=x[/latex] |
| Absolute value function | [latex]f\left(x\right)=|x|[/latex] |
| Quadratic function | [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{2}[/latex] |
| Cubic function | [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{3}[/latex] |
| Reciprocal function | [latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{x}[/latex] |
| Reciprocal squared function | [latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{{x}^{2}}[/latex] |
| Square root function | [latex]f\left(x\right)=\sqrt[\leftroot{1}\uproot{2} ]{x}[/latex] |
| Cube root function | [latex]f\left(x\right)=\sqrt[\leftroot{1}\uproot{2}3]{x}[/latex] |
| Difference Quotient | [latex]\frac{f(a+h)-f(a)}{h}\\[/latex] |
Key Concepts
- A relation is a set of ordered pairs. A function is a specific type of relation in which each domain value, or input, leads to exactly one range value, or output.
- Function notation is a shorthand method for relating the input to the output in the form [latex]y=f\left(x\right).[/latex]
- In tabular form, a function can be represented by rows or columns that relate to input and output values.
- To evaluate a function, we determine an output value for a corresponding input value. Algebraic forms of a function can be evaluated by replacing the input variable with a given value.
- To solve for a specific function value, we determine the input values that yield the specific output value.
- An algebraic form of a function can be written from an equation.
- Input and output values of a function can be identified from a table.
- Relating input values to output values on a graph is another way to evaluate a function.
- A function is one-to-one if each output value corresponds to only one input value.
- A graph represents a function if any vertical line drawn on the graph intersects the graph at no more than one point.
- The graph of a one-to-one function passes the horizontal line test.
Glossary
- dependent variable
- an output variable
- domain
- the set of all possible input values for a relation
- function
- a relation in which each input value yields a unique output value
- horizontal line test
- a method of testing whether a function is one-to-one by determining whether any horizontal line intersects the graph more than once
- independent variable
- an input variable
- input
- each object or value in a domain that relates to another object or value by a relationship known as a function
- one-to-one function
- a function for which each value of the output is associated with a unique input value
- output
- each object or value in the range that is produced when an input value is entered into a function
- range
- the set of output values that result from the input values in a relation
- relation
- a set of ordered pairs
- vertical line test
- a method of testing whether a graph represents a function by determining whether a vertical line intersects the graph no more than once
Candela Citations
- Functions and Function Notation. Authored by: Douglas Hoffman. Provided by: Openstax. Located at: https://cnx.org/contents/l3_8ZlRi@1.94:EfTqzMNI@13/Functions-and-Function-Notation. Project: Essential Precalcus, Part 1. License: CC BY: Attribution
- http://www.baseball-almanac.com/legendary/lisn100.shtml. Accessed 3/24/2014 ↵
- http://www.kgbanswers.com/how-long-is-a-dogs-memory-span/4221590. Accessed 3/24/2014. ↵