The United States
In 1900, the most common causes of death were infectious diseases which brought death quickly. Today, the most common causes of death are chronic diseases in which a slow and steady decline in health ultimately results in death. How might this impact the way we think of death, how we grieve, and the amount of control a person has over his or her own dying process?
The leading causes of death and number of deaths per category in 2004 in the United States are listed below. (National Vital Statistics Reports, Center for Disease Control, 2006).
- Heart Disease (654,092)
- Malignant neoplasms (cancer) (550,270)
- Cerebrovascular disease (stroke) (150,147)
- Chronic lower respiratory disease (123,884)
- Accidents (123,884)
- Diabetes Mellitus (106.694)
- Alzheimer’s Disease (72,815)
- Influenza and Pneumonia (65,829)
- Nephritis (61,472)
- Septicemia (42,762)
- Suicide (33,464)
- Chronic Liver Disease (31,647)
- Hypertension and hypertensive renal disease (26,549)
- Parkinson’s disease (22,953)
- Pneumonitis (18,018)
These numbers reflect a change in Alzheimer’s disease which moved up from the 8th leading cause of death to the 7th and influenza and pneumonia moved down in rank from 7th to 8th.
Deadliest Diseases Worldwide
The top 12 deadliest diseases in the world are listed below along with the estimated number of deaths per cause. These figures are for 2002 and do not reflect deaths due to violence or suicide (World Health Organization, World Health Report, 2004). Notice the higher rates of death due to HIV/AIDS, perinatal conditions and diarrheal conditions than is found in the United States. Deaths of infants, young children, young mothers, and men and women in adolescence, young adulthood and midlife are more common. Many of these deaths are due to preventable causes. Ideas about the swiftness and unpredictable nature of death are certainly greater when living under such circumstances.
- Heart disease (7.2 million)
- Cerebrovascular disease (5.5 million)
- Lower respiratory infections (3.9 million)
- HIV/AIDS (2.8 million)
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary (2.7 million)
- Perinatal conditions (2.5 million)
- Diarrheal diseases (1.8 million)
- Tuberculosis (1.6 million)
- Malaria (1.3 million)
- Trachea, bronchus, lung cancers (1.2 million)
- Road traffic accidents (1.2 million)
- Diabetes mellitus (1 million)
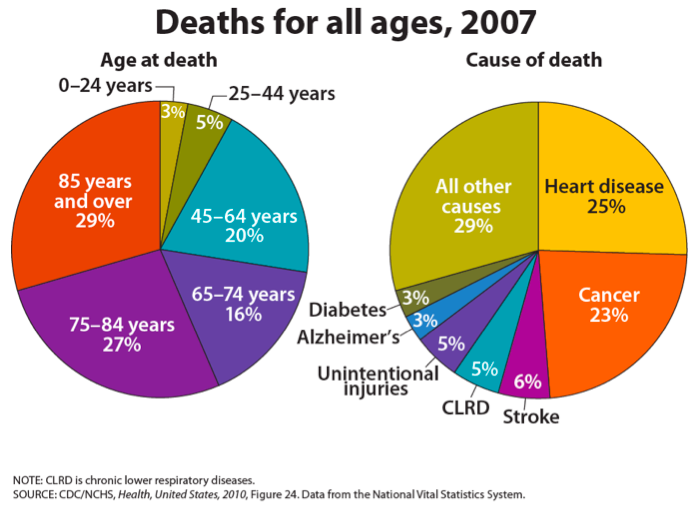
A Comparison of Death by Age in the United States:
A comparison of the causes of death in the United States in the year 2007 for people in late adulthood and among all ages is given below. Notice that 29 percent of all deaths were of people ages 85 and older and that rates of death due to heart disease had declined since 1997, although heart disease is still the leading cause of death.

Candela Citations
- Psyc 200 Lifespan Psychology. Authored by: Laura Overstreet. Located at: http://opencourselibrary.org/econ-201/. License: CC BY: Attribution
