Learning Objectives
- Find the derivative of exponential functions.
- Find the derivative of logarithmic functions.
- Use logarithmic differentiation to determine the derivative of a function.
So far, we have learned how to differentiate a variety of functions, including trigonometric, inverse, and implicit functions. In this section, we explore derivatives of exponential and logarithmic functions. As we discussed in Introduction to Functions and Graphs, exponential functions play an important role in modeling population growth and the decay of radioactive materials. Logarithmic functions can help rescale large quantities and are particularly helpful for rewriting complicated expressions.
Derivative of the Exponential Function
Just as when we found the derivatives of other functions, we can find the derivatives of exponential and logarithmic functions using formulas. As we develop these formulas, we need to make certain basic assumptions. The proofs that these assumptions hold are beyond the scope of this course.
First of all, we begin with the assumption that the function [latex]B(x)={b}^{x},b>0,[/latex] is defined for every real number and is continuous. In previous courses, the values of exponential functions for all rational numbers were defined—beginning with the definition of [latex]{b}^{n},[/latex] where [latex]n[/latex] is a positive integer—as the product of [latex]b[/latex] multiplied by itself [latex]n[/latex] times. Later, we defined [latex]{b}^{0}=1,{b}^{\text{−}n}=\frac{1}{{b}^{n}},[/latex] for a positive integer [latex]n,[/latex] and [latex]{b}^{s\text{/}t}=(\sqrt[t]{b}{)}^{s}[/latex] for positive integers [latex]s[/latex] and [latex]t.[/latex] These definitions leave open the question of the value of [latex]{b}^{r}[/latex] where [latex]r[/latex] is an arbitrary real number. By assuming the continuity of [latex]B(x)={b}^{x},b>0,[/latex] we may interpret [latex]{b}^{r}[/latex] as [latex]\underset{x\to r}{\text{lim}}{b}^{x}[/latex] where the values of [latex]x[/latex] as we take the limit are rational. For example, we may view [latex]{4}^{\pi }[/latex] as the number satisfying
As we see in the following table, [latex]{4}^{\pi }\approx 77.88.[/latex]
| [latex]x[/latex] | [latex]{4}^{x}[/latex] | [latex]x[/latex] | [latex]{4}^{x}[/latex] |
|---|---|---|---|
| [latex]{4}^{3}[/latex] | 64 | [latex]{4}^{3.141593}[/latex] | 77.8802710486 |
| [latex]{4}^{3.1}[/latex] | 73.5166947198 | [latex]{4}^{3.1416}[/latex] | 77.8810268071 |
| [latex]{4}^{3.14}[/latex] | 77.7084726013 | [latex]{4}^{3.142}[/latex] | 77.9242251944 |
| [latex]{4}^{3.141}[/latex] | 77.8162741237 | [latex]{4}^{3.15}[/latex] | 78.7932424541 |
| [latex]{4}^{3.1415}[/latex] | 77.8702309526 | [latex]{4}^{3.2}[/latex] | 84.4485062895 |
| [latex]{4}^{3.14159}[/latex] | 77.8799471543 | [latex]{4}^{4}[/latex] | 256 |
We also assume that for [latex]B(x)={b}^{x},b>0,[/latex] the value [latex]{B}^{\prime }(0)[/latex] of the derivative exists. In this section, we show that by making this one additional assumption, it is possible to prove that the function [latex]B(x)[/latex] is differentiable everywhere.
We make one final assumption: that there is a unique value of [latex]b>0[/latex] for which [latex]{B}^{\prime }(0)=1.[/latex] We define [latex]e[/latex] to be this unique value, as we did in Introduction to Functions and Graphs. (Figure) provides graphs of the functions [latex]y={2}^{x},y={3}^{x},y={2.7}^{x},[/latex] and [latex]y={2.8}^{x}.[/latex] A visual estimate of the slopes of the tangent lines to these functions at 0 provides evidence that the value of [latex]e[/latex] lies somewhere between 2.7 and 2.8. The function [latex]E(x)={e}^{x}[/latex] is called the natural exponential function. Its inverse, [latex]L(x)={\text{log}}_{e}x=\text{ln}x[/latex] is called the natural logarithmic function.
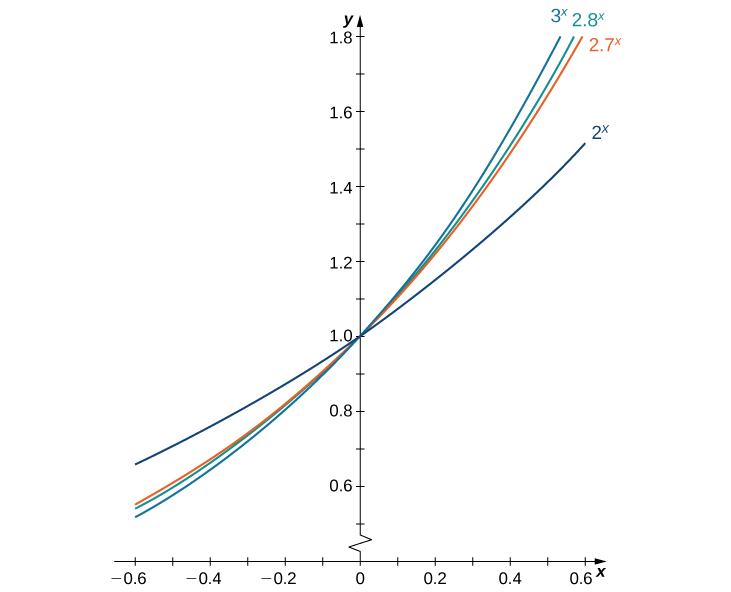
Figure 1. The graph of [latex]E(x)={e}^{x}[/latex] is between [latex]y={2}^{x}[/latex] and [latex]y={3}^{x}.[/latex]
For a better estimate of [latex]e,[/latex] we may construct a table of estimates of [latex]{B}^{\prime }(0)[/latex] for functions of the form [latex]B(x)={b}^{x}.[/latex] Before doing this, recall that
for values of [latex]x[/latex] very close to zero. For our estimates, we choose [latex]x=0.00001[/latex] and [latex]x=-0.00001[/latex] to obtain the estimate
See the following table.
| [latex]b[/latex] | [latex]\frac{{b}^{-0.00001}-1}{-0.00001}<{B}^{\prime }(0)<\frac{{b}^{0.00001}-1}{0.00001}[/latex] | [latex]b[/latex] | [latex]\frac{{b}^{-0.00001}-1}{-0.00001}<{B}^{\prime }(0)<\frac{{b}^{0.00001}-1}{0.00001}[/latex] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | [latex]0.693145<{B}^{\prime }(0)<0.69315[/latex] | 2.7183 | [latex]1.000002<{B}^{\prime }(0)<1.000012[/latex] |
| 2.7 | [latex]0.993247<{B}^{\prime }(0)<0.993257[/latex] | 2.719 | [latex]1.000259<{B}^{\prime }(0)<1.000269[/latex] |
| 2.71 | [latex]0.996944<{B}^{\prime }(0)<0.996954[/latex] | 2.72 | [latex]1.000627<{B}^{\prime }(0)<1.000637[/latex] |
| 2.718 | [latex]0.999891<{B}^{\prime }(0)<0.999901[/latex] | 2.8 | [latex]1.029614<{B}^{\prime }(0)<1.029625[/latex] |
| 2.7182 | [latex]0.999965<{B}^{\prime }(0)<0.999975[/latex] | 3 | [latex]1.098606<{B}^{\prime }(0)<1.098618[/latex] |
The evidence from the table suggests that [latex]2.7182 The graph of [latex]E(x)={e}^{x}[/latex] together with the line [latex]y=x+1[/latex] are shown in (Figure). This line is tangent to the graph of [latex]E(x)={e}^{x}[/latex] at [latex]x=0.[/latex] Figure 2. The tangent line to [latex]E(x)={e}^{x}[/latex] at [latex]x=0[/latex] has slope 1. Now that we have laid out our basic assumptions, we begin our investigation by exploring the derivative of [latex]B(x)={b}^{x},b>0.[/latex] Recall that we have assumed that [latex]{B}^{\prime }(0)[/latex] exists. By applying the limit definition to the derivative we conclude that Turning to [latex]{B}^{\prime }(x),[/latex] we obtain the following. We see that on the basis of the assumption that [latex]B(x)={b}^{x}[/latex] is differentiable at [latex]0,B(x)[/latex] is not only differentiable everywhere, but its derivative is For [latex]E(x)={e}^{x},{E}^{\prime }(0)=1.[/latex] Thus, we have [latex]{E}^{\prime }(x)={e}^{x}.[/latex] (The value of [latex]{B}^{\prime }(0)[/latex] for an arbitrary function of the form [latex]B(x)={b}^{x},b>0,[/latex] will be derived later.) Let [latex]E(x)={e}^{x}[/latex] be the natural exponential function. Then In general, Find the derivative of [latex]f(x)={e}^{ \tan (2x)}.[/latex] Find the derivative of [latex]y=\frac{{e}^{{x}^{2}}}{x}.[/latex] Find the derivative of [latex]h(x)=x{e}^{2x}.[/latex] A colony of mosquitoes has an initial population of 1000. After [latex]t[/latex] days, the population is given by [latex]A(t)=1000{e}^{0.3t}.[/latex] Show that the ratio of the rate of change of the population, [latex]{A}^{\prime }(t),[/latex] to the population, [latex]A(t)[/latex] is constant. If [latex]A(t)=1000{e}^{0.3t}[/latex] describes the mosquito population after [latex]t[/latex] days, as in the preceding example, what is the rate of change of [latex]A(t)[/latex] after 4 days? Find [latex]{A}^{\prime }(4).[/latex]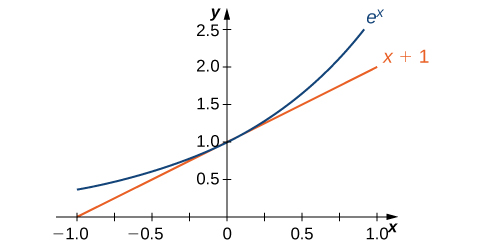
Derivative of the Natural Exponential Function
Derivative of an Exponential Function
Combining Differentiation Rules
Applying the Natural Exponential Function
Hint
Derivative of the Logarithmic Function
Now that we have the derivative of the natural exponential function, we can use implicit differentiation to find the derivative of its inverse, the natural logarithmic function.
The Derivative of the Natural Logarithmic Function
If [latex]x>0[/latex] and [latex]y=\text{ln}x,[/latex] then
More generally, let [latex]g(x)[/latex] be a differentiable function. For all values of [latex]x[/latex] for which [latex]{g}^{\prime }(x)>0,[/latex] the derivative of [latex]h(x)=\text{ln}(g(x))[/latex] is given by
Proof
If [latex]x>0[/latex] and [latex]y=\text{ln}x,[/latex] then [latex]{e}^{y}=x.[/latex] Differentiating both sides of this equation results in the equation
Solving for [latex]\frac{dy}{dx}[/latex] yields
Finally, we substitute [latex]x={e}^{y}[/latex] to obtain
We may also derive this result by applying the inverse function theorem, as follows. Since [latex]y=g(x)=\text{ln}x[/latex] is the inverse of [latex]f(x)={e}^{x},[/latex] by applying the inverse function theorem we have
Using this result and applying the chain rule to [latex]h(x)=\text{ln}(g(x))[/latex] yields
□
The graph of [latex]y=\text{ln}x[/latex] and its derivative [latex]\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{1}{x}[/latex] are shown in (Figure).
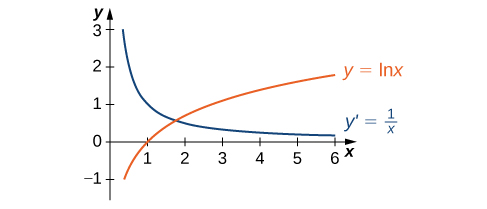
Figure 3. [latex]\text{The function}y=\text{ln}x[/latex] is increasing on [latex](0,\text{+}\infty ).[/latex] Its derivative [latex]y\prime =\frac{1}{x}[/latex] is greater than zero on [latex](0,\text{+}\infty ).[/latex]
Taking a Derivative of a Natural Logarithm
Find the derivative of [latex]f(x)=\text{ln}({x}^{3}+3x-4).[/latex]
Using Properties of Logarithms in a Derivative
Find the derivative of [latex]f(x)=\text{ln}(\frac{{x}^{2} \sin x}{2x+1}).[/latex]
Differentiate: [latex]f(x)=\text{ln}{(3x+2)}^{5}.[/latex]
Hint
Use a property of logarithms to simplify before taking the derivative.
Now that we can differentiate the natural logarithmic function, we can use this result to find the derivatives of [latex]y=lo{g}_{b}x[/latex] and [latex]y={b}^{x}[/latex] for [latex]b>0,b\ne 1.[/latex]
Derivatives of General Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
Let [latex]b>0,b\ne 1,[/latex] and let [latex]g(x)[/latex] be a differentiable function.
- If, [latex]y={\text{log}}_{b}x,[/latex] then
[latex]\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{1}{x\text{ln}b}.[/latex]
More generally, if [latex]h(x)={\text{log}}_{b}(g(x)),[/latex] then for all values of [latex]x[/latex] for which [latex]g(x)>0,[/latex]
[latex]{h}^{\prime }(x)=\frac{{g}^{\prime }(x)}{g(x)\text{ln}b}.[/latex] - If [latex]y={b}^{x},[/latex] then
[latex]\frac{dy}{dx}={b}^{x}\text{ln}b.[/latex]
More generally, if [latex]h(x)={b}^{g(x)},[/latex] then
[latex]{h}^{\prime }(x)={b}^{g(x)}g\text{″}(x)\text{ln}b.[/latex]
Proof
If [latex]y={\text{log}}_{b}x,[/latex] then [latex]{b}^{y}=x.[/latex] It follows that [latex]\text{ln}({b}^{y})=\text{ln}x.[/latex] Thus [latex]y\text{ln}b=\text{ln}x.[/latex] Solving for [latex]y,[/latex] we have [latex]y=\frac{\text{ln}x}{\text{ln}b}.[/latex] Differentiating and keeping in mind that [latex]\text{ln}b[/latex] is a constant, we see that
The derivative in (Figure) now follows from the chain rule.
If [latex]y={b}^{x},[/latex] then [latex]\text{ln}y=x\text{ln}b.[/latex] Using implicit differentiation, again keeping in mind that [latex]\text{ln}b[/latex] is constant, it follows that [latex]\frac{1}{y}\frac{dy}{dx}=\text{ln}b.[/latex] Solving for [latex]\frac{dy}{dx}[/latex] and substituting [latex]y={b}^{x},[/latex] we see that
The more general derivative ((Figure)) follows from the chain rule.
□
Applying Derivative Formulas
Find the derivative of [latex]h(x)=\frac{{3}^{x}}{{3}^{x}+2}.[/latex]
Finding the Slope of a Tangent Line
Find the slope of the line tangent to the graph of [latex]y={\text{log}}_{2}(3x+1)[/latex] at [latex]x=1.[/latex]
Find the slope for the line tangent to [latex]y={3}^{x}[/latex] at [latex]x=2.[/latex]
Hint
Evaluate the derivative at [latex]x=2.[/latex]
Logarithmic Differentiation
At this point, we can take derivatives of functions of the form [latex]y={(g(x))}^{n}[/latex] for certain values of [latex]n,[/latex] as well as functions of the form [latex]y={b}^{g(x)},[/latex] where [latex]b>0[/latex] and [latex]b\ne 1.[/latex] Unfortunately, we still do not know the derivatives of functions such as [latex]y={x}^{x}[/latex] or [latex]y={x}^{\pi }.[/latex] These functions require a technique called logarithmic differentiation, which allows us to differentiate any function of the form [latex]h(x)=g{(x)}^{f(x)}.[/latex] It can also be used to convert a very complex differentiation problem into a simpler one, such as finding the derivative of [latex]y=\frac{x\sqrt{2x+1}}{{e}^{x}{ \sin }^{3}x}.[/latex] We outline this technique in the following problem-solving strategy.
Problem-Solving Strategy: Using Logarithmic Differentiation
- To differentiate [latex]y=h(x)[/latex] using logarithmic differentiation, take the natural logarithm of both sides of the equation to obtain [latex]\text{ln}y=\text{ln}(h(x)).[/latex]
- Use properties of logarithms to expand [latex]\text{ln}(h(x))[/latex] as much as possible.
- Differentiate both sides of the equation. On the left we will have [latex]\frac{1}{y}\frac{dy}{dx}.[/latex]
- Multiply both sides of the equation by [latex]y[/latex] to solve for [latex]\frac{dy}{dx}.[/latex]
- Replace [latex]y[/latex] by [latex]h(x).[/latex]
Using Logarithmic Differentiation
Find the derivative of [latex]y={(2{x}^{4}+1)}^{ \tan x}.[/latex]
Using Logarithmic Differentiation
Find the derivative of [latex]y=\frac{x\sqrt{2x+1}}{{e}^{x}{ \sin }^{3}x}.[/latex]
Extending the Power Rule
Find the derivative of [latex]y={x}^{r}[/latex] where [latex]r[/latex] is an arbitrary real number.
Use logarithmic differentiation to find the derivative of [latex]y={x}^{x}.[/latex]
Hint
Follow the problem solving strategy.
Find the derivative of [latex]y={( \tan x)}^{\pi }.[/latex]
Hint
Use the result from (Figure).
Key Concepts
- On the basis of the assumption that the exponential function [latex]y={b}^{x},b>0[/latex] is continuous everywhere and differentiable at 0, this function is differentiable everywhere and there is a formula for its derivative.
- We can use a formula to find the derivative of [latex]y=\text{ln}x,[/latex] and the relationship [latex]{\text{log}}_{b}x=\frac{\text{ln}x}{\text{ln}b}[/latex] allows us to extend our differentiation formulas to include logarithms with arbitrary bases.
- Logarithmic differentiation allows us to differentiate functions of the form [latex]y=g{(x)}^{f(x)}[/latex] or very complex functions by taking the natural logarithm of both sides and exploiting the properties of logarithms before differentiating.
Key Equations
- Derivative of the natural exponential function
[latex]\frac{d}{dx}({e}^{g(x)})={e}^{g(x)}{g}^{\prime }(x)[/latex] - Derivative of the natural logarithmic function
[latex]\frac{d}{dx}(\text{ln}g(x))=\frac{1}{g(x)}{g}^{\prime }(x)[/latex] - Derivative of the general exponential function
[latex]\frac{d}{dx}({b}^{g(x)})={b}^{g(x)}{g}^{\prime }(x)\text{ln}b[/latex] - Derivative of the general logarithmic function
[latex]\frac{d}{dx}({\text{log}}_{b}g(x))=\frac{{g}^{\prime }(x)}{g(x)\text{ln}b}[/latex]
For the following exercises, find [latex]{f}^{\prime }(x)[/latex] for each function.
[latex]f(x)={x}^{2}{e}^{x}[/latex]
[latex]f(x)=\frac{{e}^{\text{−}x}}{x}[/latex]
[latex]f(x)={e}^{{x}^{3}\text{ln}x}[/latex]
[latex]f(x)=\sqrt{{e}^{2x}+2x}[/latex]
[latex]f(x)=\frac{{e}^{x}-{e}^{\text{−}x}}{{e}^{x}+{e}^{\text{−}x}}[/latex]
[latex]f(x)=\frac{{10}^{x}}{\text{ln}10}[/latex]
[latex]f(x)={2}^{4x}+4{x}^{2}[/latex]
[latex]f(x)={3}^{ \sin 3\text{x}}[/latex]
[latex]f(x)={x}^{\pi }·{\pi }^{x}[/latex]
[latex]f(x)=\text{ln}(4{x}^{3}+x)[/latex]
[latex]f(x)=\text{ln}\sqrt{5x-7}[/latex]
[latex]f(x)={x}^{2}\text{ln}9x[/latex]
[latex]f(x)=\text{log}( \sec x)[/latex]
[latex]f(x)={\text{log}}_{7}{(6{x}^{4}+3)}^{5}[/latex]
[latex]f(x)={2}^{x}·{\text{log}}_{3}{7}^{{x}^{2}-4}[/latex]
For the following exercises, use logarithmic differentiation to find [latex]\frac{dy}{dx}.[/latex]
[latex]y={x}^{\sqrt{x}}[/latex]
[latex]y={( \sin 2x)}^{4x}[/latex]
[latex]y={(\text{ln}x)}^{\text{ln}x}[/latex]
[latex]y={x}^{{\text{log}}_{2}x}[/latex]
[latex]y={({x}^{2}-1)}^{\text{ln}x}[/latex]
[latex]y={x}^{ \cot x}[/latex]
[latex]y=\frac{x+11}{\sqrt[3]{{x}^{2}-4}}[/latex]
[latex]y={x}^{-1\text{/}2}{({x}^{2}+3)}^{2\text{/}3}{(3x-4)}^{4}[/latex]
[T] Find an equation of the tangent line to the graph of [latex]f(x)=4x{e}^{({x}^{2}-1)}[/latex] at the point where
[latex]x=-1.[/latex] Graph both the function and the tangent line.
[T] Find the equation of the line that is normal to the graph of [latex]f(x)=x·{5}^{x}[/latex] at the point where [latex]x=1.[/latex] Graph both the function and the normal line.
[T] Find the equation of the tangent line to the graph of [latex]{x}^{3}-x\text{ln}y+{y}^{3}=2x+5[/latex] at the point where [latex]x=2.[/latex] (Hint: Use implicit differentiation to find [latex]\frac{dy}{dx}.[/latex]) Graph both the curve and the tangent line.
Consider the function [latex]y={x}^{1\text{/}x}[/latex] for [latex]x>0.[/latex]
- Determine the points on the graph where the tangent line is horizontal.
- Determine the points on the graph where [latex]{y}^{\prime }>0[/latex] and those where [latex]{y}^{\prime }<0.[/latex]
The formula [latex]I(t)=\frac{ \sin t}{{e}^{t}}[/latex] is the formula for a decaying alternating current.
- Complete the following table with the appropriate values.
[latex]t[/latex] [latex]\frac{ \sin t}{{e}^{t}}[/latex] 0 (i) [latex]\frac{\pi }{2}[/latex] (ii) [latex]\pi[/latex] (iii) [latex]\frac{3\pi }{2}[/latex] (iv) [latex]2\pi[/latex] (v) [latex]2\pi[/latex] (vi) [latex]3\pi[/latex] (vii) [latex]\frac{7\pi }{2}[/latex] (viii) [latex]4\pi[/latex] (ix) - Using only the values in the table, determine where the tangent line to the graph of [latex]I(t)[/latex] is horizontal.
[T] The population of Toledo, Ohio, in 2000 was approximately 500,000. Assume the population is increasing at a rate of 5% per year.
- Write the exponential function that relates the total population as a function of [latex]t.[/latex]
- Use a. to determine the rate at which the population is increasing in [latex]t[/latex] years.
- Use b. to determine the rate at which the population is increasing in 10 years.
[T] An isotope of the element erbium has a half-life of approximately 12 hours. Initially there are 9 grams of the isotope present.
- Write the exponential function that relates the amount of substance remaining as a function of [latex]t,[/latex] measured in hours.
- Use a. to determine the rate at which the substance is decaying in [latex]t[/latex] hours.
- Use b. to determine the rate of decay at [latex]t=4[/latex] hours.
[T] The number of cases of influenza in New York City from the beginning of 1960 to the beginning of 1961 is modeled by the function
[latex]N(t)=5.3{e}^{0.093{t}^{2}-0.87t},(0\le t\le 4),[/latex]
where [latex]N(t)[/latex] gives the number of cases (in thousands) and [latex]t[/latex] is measured in years, with [latex]t=0[/latex] corresponding to the beginning of 1960.
- Show work that evaluates [latex]N(0)[/latex] and [latex]N(4).[/latex] Briefly describe what these values indicate about the disease in New York City.
- Show work that evaluates [latex]{N}^{\prime }(0)[/latex] and [latex]{N}^{\prime }(3).[/latex] Briefly describe what these values indicate about the disease in the United States.
[T] The relative rate of change of a differentiable function [latex]y=f(x)[/latex] is given by [latex]\frac{100·{f}^{\prime }(x)}{f(x)}\text{%}.[/latex] One model for population growth is a Gompertz growth function, given by [latex]P(x)=a{e}^{\text{−}b·{e}^{\text{−}cx}}[/latex] where [latex]a,b,[/latex] and [latex]c[/latex] are constants.
- Find the relative rate of change formula for the generic Gompertz function.
- Use a. to find the relative rate of change of a population in [latex]x=20[/latex] months when [latex]a=204,b=0.0198,[/latex] and [latex]c=0.15.[/latex]
- Briefly interpret what the result of b. means.
For the following exercises, use the population of New York City from 1790 to 1860, given in the following table.
_by_population_by_decade.Years since 1790Population033,1311060,5152096,37330123,70640202,30050312,71060515,54770813,669
[T] Using a computer program or a calculator, fit a growth curve to the data of the form [latex]p=a{b}^{t}.[/latex]
[T] Using the exponential best fit for the data, write a table containing the derivatives evaluated at each year.
[T] Using the exponential best fit for the data, write a table containing the second derivatives evaluated at each year.
[T] Using the tables of first and second derivatives and the best fit, answer the following questions:
- Will the model be accurate in predicting the future population of New York City? Why or why not?
- Estimate the population in 2010. Was the prediction correct from a.?
Glossary
- logarithmic differentiation
- is a technique that allows us to differentiate a function by first taking the natural logarithm of both sides of an equation, applying properties of logarithms to simplify the equation, and differentiating implicitly


Hint
Don’t forget to use the product rule.