
Figure 1. Plato, Aristotle, and other ancient Greek philosophers examined a wide range of topics relating to what we now consider psychology.
Many cultures throughout history have speculated on the nature of the mind, heart, soul, spirit, and brain. Philosophical interest in behavior and the mind dates back to the ancient civilizations of Egypt, Greece, China, and India, but psychology as a discipline didn’t develop until the mid-1800s, when it evolved from the study of philosophy and began in German and American labs. This section will teach you more about the major founding psychologists and their contributions to the development of psychology.
What is Psychology?
In Greek mythology, Psyche was a mortal woman whose beauty was so great that it rivaled that of the goddess Aphrodite. Aphrodite became so jealous of Psyche that she sent her son, Eros, to make Psyche fall in love with the ugliest man in the world. However, Eros accidentally pricked himself with the tip of his arrow and fell madly in love with Psyche himself. He took Psyche to his palace and showered her with gifts, yet she could never see his face. While visiting Psyche, her sisters roused suspicion in Psyche about her mysterious lover, and eventually, Psyche betrayed Eros’ wishes to remain unseen to her. Because of this betrayal, Eros abandoned Psyche. When Psyche appealed to Aphrodite to reunite her with Eros, Aphrodite gave her a series of impossible tasks to complete. Psyche managed to complete all of these trials; ultimately, her perseverance paid off as she was reunited with Eros and was ultimately transformed into a goddess herself (Ashliman, 2001; Greek Myths & Greek Mythology, 2014).

Figure 2. Antonio Canova’s sculpture depicts Eros and Psyche.
Psyche comes to represent the human soul’s triumph over the misfortunes of life in the pursuit of true happiness (Bulfinch, 1855); in fact, the Greek word psyche means soul, and it is often represented as a butterfly. The word psychology was coined at a time when the concepts of soul and mind were not as clearly distinguished (Green, 2001). The root –ology denotes scientific study of, and psychology refers to the scientific study of the mind. Since science studies only observable phenomena and the mind is not directly observable, we expand this definition to the scientific study of mind and behavior.
The scientific study of any aspect of the world uses the scientific method to acquire knowledge. To apply the scientific method, a researcher with a question about how or why something happens will propose a tentative explanation, called a hypothesis, to explain the phenomenon. A hypothesis is not just any explanation; it should fit into the context of a scientific theory. A scientific theory is a broad explanation or group of explanations for some aspect of the natural world that is consistently supported by evidence over time. A theory is the best understanding that we have of that part of the natural world. Armed with the hypothesis, the researcher then makes observations or, better still, carries out an experiment to test the validity of the hypothesis. That test and its results are then published so that others can check the results or build on them. It is necessary that any explanation in science be testable, which means that the phenomenon must be perceivable and measurable. For example, that a bird sings because it is happy is not a testable hypothesis, since we have no way to measure the happiness of a bird. We must ask a different question, perhaps about the brain state of the bird, since this can be measured.
In general, science deals only with matter and energy, that is, those things that can be measured, and it cannot arrive at knowledge about values and morality. This is one reason why our scientific understanding of the mind is so limited, since thoughts, at least as we experience them, are neither matter nor energy. The scientific method is also a form of empiricism. An empirical method for acquiring knowledge is one based on observation, including experimentation, rather than a method based only on forms of logical argument or previous authorities.
It was not until the late 1800s that psychology became accepted as its own academic discipline. Before this time, the workings of the mind were considered under the auspices of philosophy. Given that any behavior is, at its roots, biological, some areas of psychology take on aspects of a natural science like biology. No biological organism exists in isolation, and our behavior is influenced by our interactions with others. Therefore, psychology is also a social science.
Psychology is a relatively young science with its experimental roots in the 19th century, compared, for example, to human physiology, which dates much earlier. As mentioned, anyone interested in exploring issues related to the mind generally did so in a philosophical context prior to the 19th century. Two men, working in the 19th century, are generally credited as being the founders of psychology as a science and academic discipline that was distinct from philosophy. Their names were Wilhelm Wundt and William James.
Video 1. What does Psychology mean? Where does it come from? This video gives you an introduction to one of the more tricky sciences and talks about some of the big names in the development of the field.
Wundt and Structuralism
Wilhelm Wundt (1832–1920) was a German scientist who was the first person to be referred to as a psychologist. His famous book entitled Principles of Physiological Psychology was published in 1873. Wundt viewed psychology as a scientific study of conscious experience, and he believed that the goal of psychology was to identify components of consciousness and how those components combined to result in our conscious experience. Wundt used introspection (he called it “internal perception”), a process by which someone examines their own conscious experience as objectively as possible, making the human mind like any other aspect of nature that a scientist observed. Wundt’s version of introspection used only very specific experimental conditions in which an external stimulus was designed to produce a scientifically observable (repeatable) experience of the mind (Danziger, 1980). The first stringent requirement was the use of “trained” or practiced observers, who could immediately observe and report a reaction. The second requirement was the use of repeatable stimuli that always produced the same experience in the subject and allowed the subject to expect and thus be fully attentive to the inner reaction. These experimental requirements were put in place to eliminate “interpretation” in the reporting of internal experiences and to counter the argument that there is no way to know that an individual is observing their mind or consciousness accurately, since it cannot be seen by any other person. This attempt to understand the structure or characteristics of the mind was known as structuralism. Wundt established his psychology laboratory at the University at Leipzig in 1879. In this laboratory, Wundt and his students conducted experiments on, for example, reaction times. A subject, sometimes in a room isolated from the scientist, would receive a stimulus such as a light, image, or sound. The subject’s reaction to the stimulus would be to push a button, and an apparatus would record the time to reaction. Wundt could measure reaction time to one-thousandth of a second (Nicolas & Ferrand, 1999).
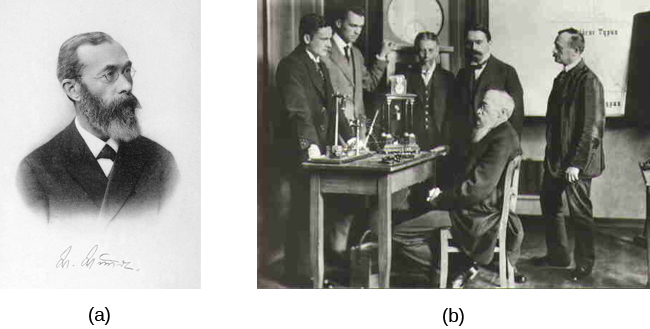
Figure 3. (a) Wilhelm Wundt is credited as one of the founders of psychology. He created the first laboratory for psychological research. (b) This photo shows him seated and surrounded by fellow researchers and equipment in his laboratory in Germany.
However, despite his efforts to train individuals in the process of introspection, this process remained highly subjective, and there was very little agreement between individuals. As a result, structuralism fell out of favor with the passing of Wundt’s student, Edward Titchener, in 1927 (Gordon, 1995).

Figure 4. William James, shown here in a self-portrait, was the first American psychologist.
James and Functionalism
William James (1842–1910) was the first American psychologist who espoused a different perspective on how psychology should operate. James was introduced to Darwin’s theory of evolution by natural selection and accepted it as an explanation of an organism’s characteristics. Key to that theory is the idea that natural selection leads to organisms that are adapted to their environment, including their behavior. Adaptation means that a trait of an organism has a function for the survival and reproduction of the individual, because it has been naturally selected. As James saw it, psychology’s purpose was to study the function of behavior in the world, and as such, his perspective was known as functionalism.
Functionalism focused on how mental activities helped an organism fit into its environment. Functionalism has a second, more subtle meaning in that functionalists were more interested in the operation of the whole mind rather than of its individual parts, which were the focus of structuralism. Like Wundt, James believed that introspection could serve as one means by which someone might study mental activities, but James also relied on more objective measures, including the use of various recording devices, and examinations of concrete products of mental activities and of anatomy and physiology (Gordon, 1995).
| The Early Schools of Psychology (No Longer Active) | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adapted from Early Schools of Psychology from the Open Learning Initiative’s Introduction to Psychology. CC-BY-NC-SA. | |||||||||
|

Figure 5. (a) Sigmund Freud was a highly influential figure in the history of psychology. (b) One of his many books, A General Introduction to Psychoanalysis, shared his ideas about psychoanalytical therapy; it was published in 1922
Psychoanalytic Theory

Figure 6. Freud’s theory of the unconscious Freud believed that we are only aware of a small amount of our mind’s activity, and that most of it remains hidden from us in our unconscious. The information in our unconscious affects our behavior, although we are unaware of it.
The Id, Ego, and Superego
Freud’s structural model of personality divides the personality into three parts—the id, the ego, and the superego. The id is the unconscious part that is the cauldron of raw drives, such as for sex or aggression. The ego, which has conscious and unconscious elements, is the rational and reasonable part of personality. Its role is to maintain contact with the outside world to keep the individual in touch with society, and to do this it mediates between the conflicting tendencies of the id and the superego. The superego is a person’s conscience, which develops early in life and is learned from parents, teachers, and others. Like the ego, the superego has conscious and unconscious elements. When all three parts of the personality are in dynamic equilibrium, the individual is thought to be mentally healthy. However, if the ego is unable to mediate between the id and the superego, an imbalance is believed to occur in the form of psychological distress.
Psychosexual Theory of Development
Freud’s theories also placed a great deal of emphasis on sexual development. Freud believed that each of us must pass through a series of stages during childhood and that if we lack proper nurturing during a particular stage, we may become stuck or fixated in that stage. Freud’s psychosexual model of development includes five stages: oral, anal, phallic, latency, and genital. According to Freud, children’s pleasure-seeking urges are focused on a different area of the body, called an erogenous zone, at each of these five stages. Psychologists today dispute that Freud’s psychosexual stages provide a legitimate explanation for how personality develops, but what we can take away from Freud’s theory is that personality is shaped, in some part, by experiences we have in childhood.
Freud’s ideas were influential, and you will learn more about them when you study lifespan development, personality, and therapy. For instance, many therapists believe strongly in the unconscious and the impact of early childhood experiences on the rest of a person’s life. The method of psychoanalysis, which involves the patient talking about their experiences and selves, while not invented by Freud, was certainly popularized by him and is still used today. Many of Freud’s other ideas, however, are controversial.
Evolutionary Psychology
 Evolutionary psychology stems from Charles Darwin’s theories of evolution, adaptation, and natural selection. Evolutionary biology emerged as an academic discipline in the 1930s and 1940s, along with the study of animal behavior (ethology), both of which heavily influence the development of evolutionary psychology. The field also draws on cognitive psychology, behavioral ecology, artificial intelligence, genetics, anthropology, archaeology, biology, and zoology. Though the term “evolutionary psychology” was most likely coined by American biologist Michael Ghiselin in 1973, it wasn’t until 1992 that the term was popularized by Jerome Barkow, Leda Cosmides, and John Tooby in their highly influential book The Adapted Mind: Evolutionary Psychology and The Generation of Culture.
Evolutionary psychology stems from Charles Darwin’s theories of evolution, adaptation, and natural selection. Evolutionary biology emerged as an academic discipline in the 1930s and 1940s, along with the study of animal behavior (ethology), both of which heavily influence the development of evolutionary psychology. The field also draws on cognitive psychology, behavioral ecology, artificial intelligence, genetics, anthropology, archaeology, biology, and zoology. Though the term “evolutionary psychology” was most likely coined by American biologist Michael Ghiselin in 1973, it wasn’t until 1992 that the term was popularized by Jerome Barkow, Leda Cosmides, and John Tooby in their highly influential book The Adapted Mind: Evolutionary Psychology and The Generation of Culture.
Evolutionary psychology is founded on several core premises:
- The brain produces behavior in response to external and internal inputs.
- The brain’s adaptive mechanisms have been shaped over time by natural and sexual selection.
- Different neural mechanisms in the brain were developed to solve problems in humanity’s evolutionary past; in many regards, humans can be considered to have Stone Age minds.
- Most processes of the brain are unconscious; most mental problems that seem easy to solve are actually extremely difficult problems that are solved unconsciously through complicated actions within the brain.
- Human psychology consists of many specialized mechanisms, each sensitive to different information or inputs. These mechanisms combine to produce observable behavior.
Evolutionary psychologists hypothesize, for example, that humans have inherited special mental capacities for learning language, making this process nearly automatic. Other adaptations might include the abilities to infer others’ emotions, to discern kin from non-kin, to identify and prefer healthier mates, to cooperate with others, and so on. Consistent with the theory of natural selection, evolutionary psychology sees organisms as often in conflict with others of their species, including mates and relatives. For example, mother mammals and their young offspring sometimes struggle over weaning, which benefits the mother more than the child. Evolutionary psychology is still a prominent approach to psychology today.
Glossary
Candela Citations
- Modification and adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Modification, adaptation, and original content. Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Early Roots of Psychology; The Id, Ego, and Superego and Psychosexual Theory. Provided by: Boundless. Located at: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-psychology/. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Iceberg. Authored by: Uwe Kils. Provided by: Wikimedia. Located at: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Iceberg.jpg. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Evolutionary Psychology. Provided by: Boundless Psychology. Located at: http://oer2go.org/mods/en-boundless/www.boundless.com/psychology/textbooks/boundless-psychology-textbook/introduction-to-psychology-1/theoretical-perspectives-in-modern-psychology-23/evolutionary-psychology-118-12655/index.html. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Psychology 101 - Wundt & James: Structuralism & Functionalism - Vook. Provided by: VookInc's channel. Located at: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SW6nm69Z_IE. License: Other. License Terms: Standard YouTube License
