Learning Objective
- Recognize molecules that are likely to have multiple covalent bonds.
In many molecules, the octet rule would not be satisfied if each pair of bonded atoms shares two electrons. Consider carbon dioxide (CO2). If each oxygen atom shares one electron with the carbon atom, we get the following:

This does not give the carbon atom a complete octet; you will find only six electrons in its valence shell. In addition, each oxygen atom has only seven electrons in its valence shell. Finally, no atom makes the number of bonds it typically forms (Figure 4.2 “How Many Covalent Bonds Are Formed?”). This arrangement of shared electrons is far from satisfactory.
Sometimes more than one pair of electrons must be shared between two atoms for both atoms to have an octet. In carbon dioxide, a second electron from each oxygen atom is also shared with the central carbon atom, and the carbon atom shares one more electron with each oxygen atom:

In this arrangement, the carbon atom shares four electrons (two pairs) with the oxygen atom on the left and four electrons with the oxygen atom on the right. There are now eight electrons around each atom. Two pairs of electrons shared between two atoms make a double bond between the atoms, which is represented by a double dash:

Some molecules contain triple bonds, covalent bonds in which three pairs of electrons are shared by two atoms. A simple compound that has a triple bond is acetylene (C2H2), whose Lewis diagram is as follows:

Example 5
Draw the Lewis diagram for each molecule.
- N2
- CH2O (The carbon atom is the central atom.)
Solution
Notes
One application of CH2O, also called formaldehyde, is the preservation of biological specimens. Aqueous solutions of CH2O are called formalin and have a sharp, characteristic (pungent) odor.
Skill-Building Exercise
-
O2
-
C2H4
Concept Review Exercise
-
What is one clue that a molecule has a multiple bond?
Answer
Key Takeaway
- Some molecules must have multiple covalent bonds between atoms to satisfy the octet rule.
Exercises
-
Each molecule contains multiple bonds. Draw the Lewis diagram for each. The first element is the central atom.
- CS2
- C2F4
- COCl2
-
Each molecule contains double bonds. Draw the Lewis diagram for each. Assume that the first element is the central atom, unless otherwise noted.
- N2
- HCN (The carbon atom is the central atom.)
- POCl (The phosphorus atom is the central atom.)
-
Explain why hydrogen atoms do not form double bonds.
-
Why is it incorrect to draw a double bond in the Lewis diagram for MgO?
Answers

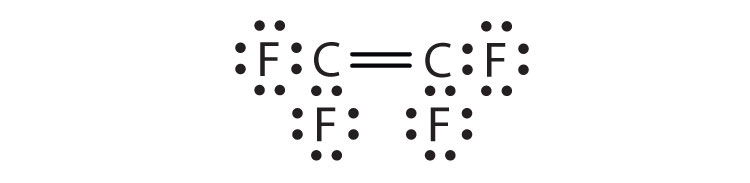

3. Hydrogen can accept only one more electron; multiple bonds require more than one electron pair to be shared.
Candela Citations
- The Basics of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry v. 1.0. Provided by: Saylor Academy. Located at: https://saylordotorg.github.io/text_the-basics-of-general-organic-and-biological-chemistry/. License: CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial. License Terms: This text was adapted by Saylor Academy under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License without attribution as requested by the work's original creator or licensor.


