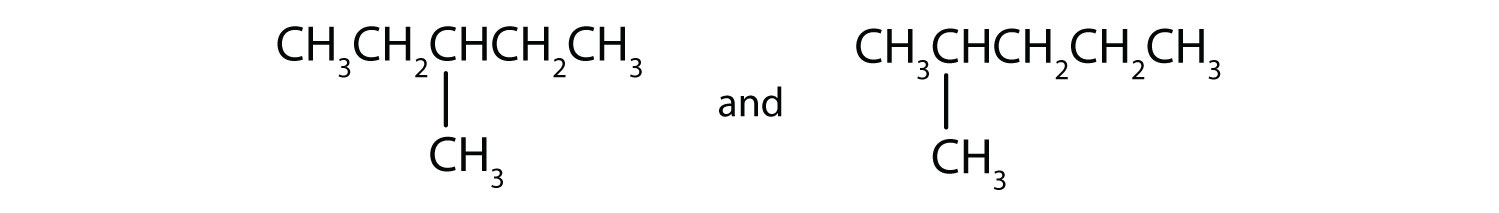Additional Exercises
-
You find an unlabeled jar containing a solid that melts at 48°C. It ignites readily and burns readily. The substance is insoluble in water and floats on the surface. Is the substance likely to be organic or inorganic?
-
Give the molecular formulas for methylcyclopentane, 2-methylpentane, and cyclohexane. Which are isomers?
-
What is wrong with each name? (Hint: first write the structure as if it were correct.) Give the correct name for each compound.
- 2-dimethylpropane
- 2,3,3-trimethylbutane
- 2,4-diethylpentane
- 3,4-dimethyl-5-propylhexane
-
What is the danger in swallowing a liquid alkane?
-
Distinguish between lighter and heavier liquid alkanes in terms of their effects on the skin.
-
Following is the line formula for an alkane. Draw its structure and give its name.

-
Write equations for the complete combustion of each compound.
- propane (a bottled gas fuel)
- octane (a typical hydrocarbon in gasoline).
-
The density of a gasoline sample is 0.690 g/mL. On the basis of the complete combustion of octane, calculate the amount in grams of carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) formed per gallon (3.78 L) of the gasoline when used in an automobile.
-
Draw the structures for the five isomeric hexanes (C6H14). Name each by the IUPAC system.
-
Indicate whether the structures in each set represent the same compound or isomers.
-
-
Consider the line-angle formulas shown here and answer the questions.

- Which pair of formulas represents isomers? Draw each structure.
- Which formula represents an alkyl halide? Name the compound and write its condensed structural formula.
- Which formula represents a cyclic alkane? Name the compound and draw its structure.
- What is the molecular formula of the compound represented by (i)?
Answers
Candela Citations
- The Basics of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry v. 1.0. Provided by: Saylor Academy. Located at: https://saylordotorg.github.io/text_the-basics-of-general-organic-and-biological-chemistry/. License: CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial. License Terms: This text was adapted by Saylor Academy under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License without attribution as requested by the work's original creator or licensor.