Learning Objectives
- Identify and describe the substances from which most esters are prepared.
Esters can be prepared by esterification, a reaction in which a carboxylic acid and an alcohol, heated in the presence of an acid catalyst, form an ester and water:

The reaction is reversible. As a specific example of an esterification reaction, butyl acetate can be made from acetic acid and 1-butanol.

A Closer Look: Condensation Polymers
A commercially important esterification reaction is condensation polymerization, in which a reaction occurs between a dicarboxylic acid and a dihydric alcohol (diol), with the elimination of water. Such a reaction yields an ester that contains a free (unreacted) carboxyl group at one end and a free alcohol group at the other end. Further condensation reactions then occur, producing polyester polymers.
The most important polyester, polyethylene terephthalate (PET), is made from terephthalic acid and ethylene glycol monomers:

Polyester molecules make excellent fibers and are used in many fabrics. A knitted polyester tube, which is biologically inert, can be used in surgery to repair or replace diseased sections of blood vessels. PET is used to make bottles for beverages. It is also formed into films called Mylar. When magnetically coated, Mylar tape is used in audio- and videocassettes.
Concept Review Exercises
-
From what carboxylic acid and what alcohol can the ester isopropyl nonanoate be made?
-
From what carboxylic acid and what alcohol can the ester cyclobutyl butyrate be made?
Key Takeaway
- Esters are made by the reaction of a carboxylic acid with an alcohol, a process that is called esterification.
Exercises
-
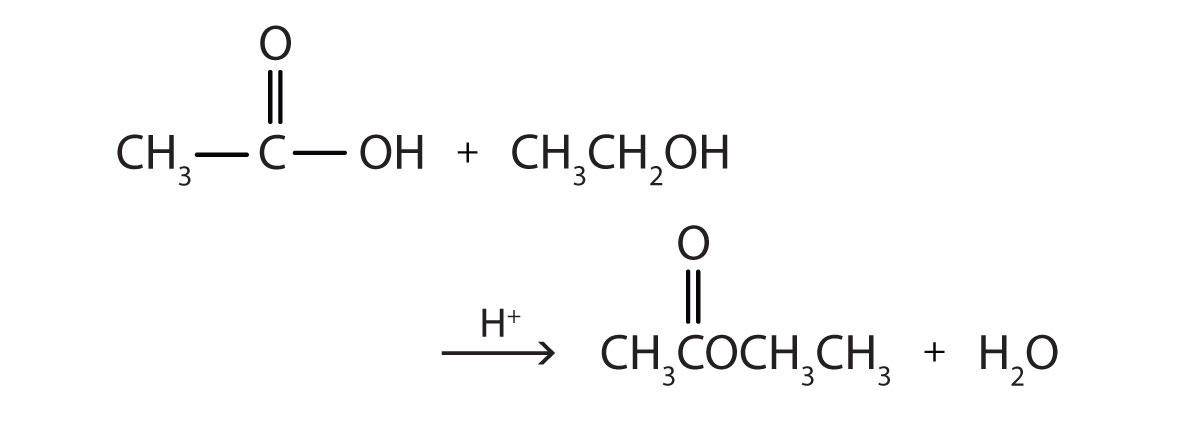
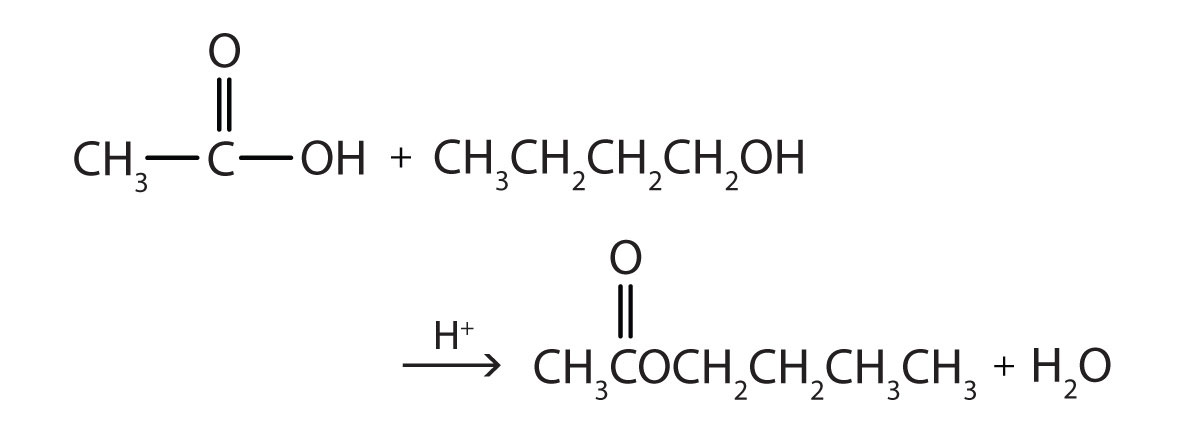
Write the equation for the reaction of acetic acid with each compound, in the presence of an acid catalyst.
- ethanol
- 1-butanol
-
Write the equation for the reaction of benzoic acid with each compound, in the presence of an acid catalyst.
- methanol
- 1-propanol
Candela Citations
- The Basics of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry v. 1.0. Provided by: Saylor Academy. Located at: https://saylordotorg.github.io/text_the-basics-of-general-organic-and-biological-chemistry/. License: CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial. License Terms: This text was adapted by Saylor Academy under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License without attribution as requested by the work's original creator or licensor.