Learning Objectives
- Identify the general structure for an amine.
- Identify the functional group for amines.
- Determine the structural feature that classifies amines as primary, secondary, or tertiary.
- Use nomenclature systems to name amines.
Amines are classified according to the number of carbon atoms bonded directly to the nitrogen atom. A primary (1°) amineA compound that has only one alkyl or aryl group on the nitrogen atom. has one alkyl (or aryl) group on the nitrogen atom, a secondary (2°) amineA compound that has two alkyl or aryl groups on the nitrogen atom. has two, and a tertiary (3°) amineA compound that has three alkyl or aryl groups on the nitrogen atom. has three (Figure 15.5 “The Structure of Amines Compared to Water, an Alcohol, and an Ether”).

Figure 15.5 The Structure of Amines Compared to Water, an Alcohol, and an Ether.
Note
To classify alcohols, we look at the number of carbon atoms bonded to the carbon atom bearing the OH group, not the oxygen atom itself. Thus, although isopropylamine looks similar to isopropyl alcohol, the former is a primary amine, while the latter is a secondary alcohol.

The common names for simple aliphatic amines consist of an alphabetic list of alkyl groups attached to the nitrogen atom, followed by the suffix –amine. (Systematic names are often used by some chemists.) The amino groupAn NH2 unit. (NH2) is named as a substituent in more complicated amines, such as those that incorporate other functional groups or in which the alkyl groups cannot be simply named.
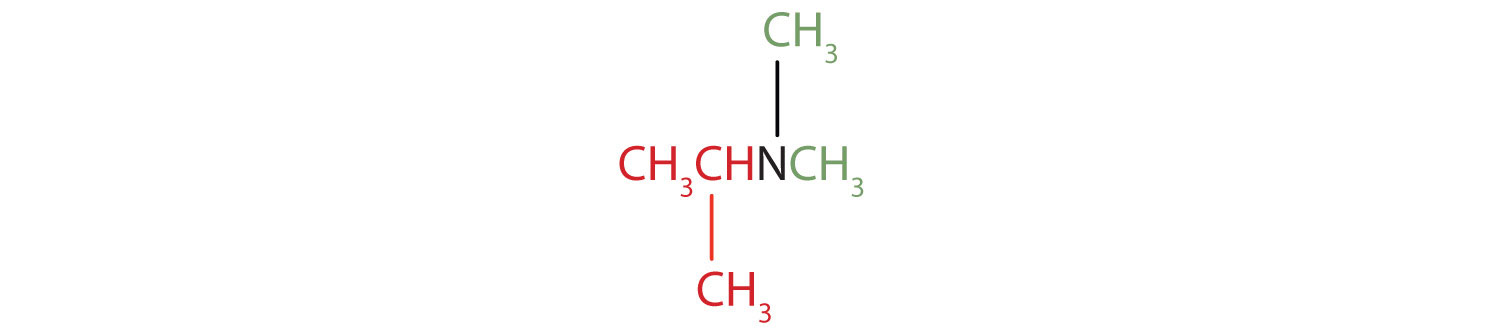
Example 9
Name and classify each compound.
- CH3CH2CH2NH2
-

- CH3CH2NHCH2CH3
- CH3CH2CH2NHCH3
Skill-Building Exercise
Name and classify each compound.
-
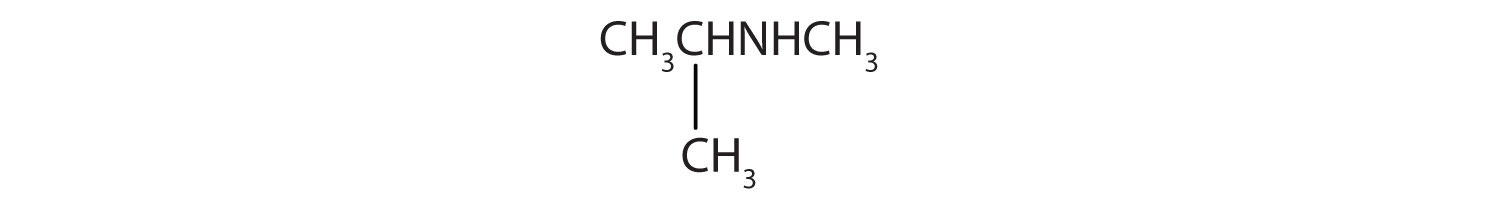
-

-
CH3CH2CH2CH2NH2
-
CH3CH2CH2NHCH2CH2 CH3
Example 10
Draw the structure for each compound and classify.
- isopropyldimethylamine
- dipropylamine
Skill-Building Exercise
Draw the structure for each compound and classify.
-
ethylisopropylamine
-
diethylpropylamine
The primary amine in which the nitrogen atom is attached directly to a benzene ring has a special name—aniline. Aryl amines are named as derivatives of aniline.

Example 11
Name this compound.

Skill-Building Exercise
-
Name this compound.

Example 12
Draw the structure for p-ethylaniline and classify.
Skill-Building Exercise
-
Draw the structure for p-isopropylaniline and classify.
Example 13
Draw the structure for 2-amino-3-methylpentane.
Skill-Building Exercise
-
Draw the structure for 2-amino-3-ethyl-1-chloroheptane.
Ammonium (NH4+) ions, in which one or more hydrogen atoms are replaced with alkyl groups, are named in a manner analogous to that used for simple amines. The alkyl groups are named as substituents, and the parent species is regarded as the NH4+ ion. For example, CH3NH3+ is the methylammonium ion. The ion formed from aniline (C6H5NH3+) is called the anilinium ion.
Example 14
Name each ion.
- CH3NH3+
- (CH3)2NH2+
- (CH3)3NH+
- (CH3)4N+
Skill-Building Exercise
Name each ion.
-
CH3CH2NH3+
-
(CH3CH2)3NH+
-
(CH3CH2CH2)2NH2+
-
(CH3CH2CH2CH2)4N+
Concept Review Exercises
-
To what inorganic compound are the amines related?
-
How are amines classified?
Key Takeaways
- An amine is a derivative of ammonia in which one, two, or all three hydrogen atoms are replaced by hydrocarbon groups.
-
The amine functional group is as follows:

- Amines are classified as primary, secondary, or tertiary by the number of hydrocarbon groups attached to the nitrogen atom.
- Amines are named by naming the alkyl groups attached to the nitrogen atom, followed by the suffix –amine.
Exercises
-
Draw the structure for each compound and classify the amine as primary, secondary, or tertiary.
- dimethylamine
- diethylmethylamine
- 2-aminoethanol
-
Draw the structure for each compound and classify the amine as primary, secondary, or tertiary.
- 3-aminopentane
- 1,6-diaminohexane
- ethylphenylamine
-
Draw the structure for each compound.
- aniline
- m-bromoaniline
-
Draw the structure for each compound.
- 2-chloroaniline
- 3,5-dichloroaniline
-
Name each compound.
- CH3CH2CH2NH2
-

-

-
Name each compound.
- (CH3CH2)3N
- (CH3CH2)2NCH3
-
Draw the structure for each compound.
- dimethylammonium chloride
- anilinium chloride
-
Draw the structure for each compound.
- ethylmethylammonium chloride
- anilinium nitrate
-
Name each compound.
- [CH3CH2NH2CH2CH3]+Br−
- [(CH3CH2)3NH]+I−
-
Name each compound.
- [(CH3)3NH]+NO3−
- [(CH3CH2)2NH2]+Cl−
Candela Citations
- The Basics of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry v. 1.0. Provided by: Saylor Academy. Located at: https://saylordotorg.github.io/text_the-basics-of-general-organic-and-biological-chemistry/. License: CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial. License Terms: This text was adapted by Saylor Academy under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License without attribution as requested by the work's original creator or licensor.