Esters of pyrophosphoric acid and triphosphoric acid are also important in biochemistry.

Esters of these acids are present in every plant and animal cell. They are biochemical intermediates in the transformation of food into usable energy. The bonds between phosphate units in adenosine triphosphate (ATP) are called phosphoanhydride bonds. These are high-energy bonds that store energy from the metabolism of foods. Hydrolysis of ATP releases energy as it is needed for biochemical processes (for instance, for muscle contraction). Phosphate esters are also important structural constituents of phospholipids and nucleic acids. (For more information about phospholipids and nucleic acids, see Chapter 17 “Lipids”, Section 17.3 “Membranes and Membrane Lipids”, and Chapter 19 “Nucleic Acids”, respectively.)
Note
The explosive nitroglycerin (glyceryl trinitrate) is an ester formed from glycerol and nitric acid. It is used in medicine to relieve chest pain in heart disease.
Concept Review Exercise
-
What compounds combine to form phosphate esters?
Key Takeaways
- Inorganic acids such as H3PO4 form esters.
- The esters of phosphoric acid are especially important in biochemistry.
Exercises
-
Draw the structure for each compound.
- diethyl hydrogen phosphate
- methyl dihydrogen phosphate
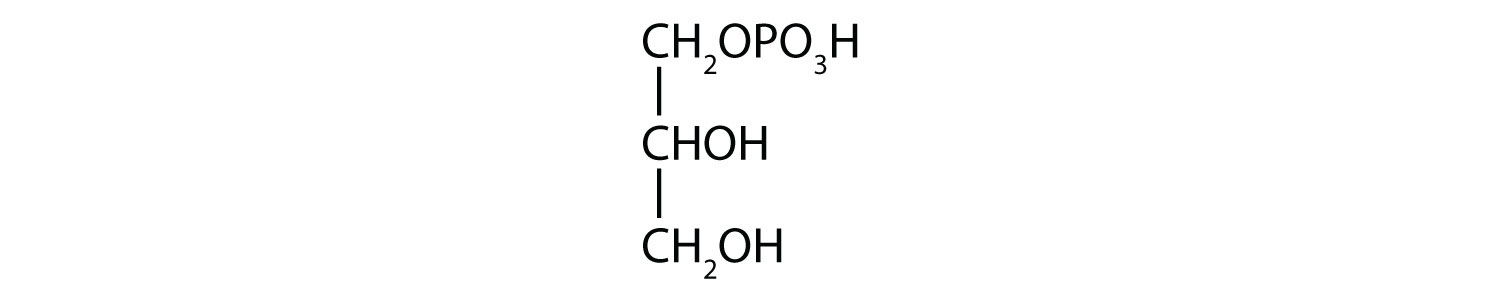
- 1-glycerol phosphate
-
Name each compound.



Candela Citations
- The Basics of General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry v. 1.0. Provided by: Saylor Academy. Located at: https://saylordotorg.github.io/text_the-basics-of-general-organic-and-biological-chemistry/. License: CC BY-NC: Attribution-NonCommercial. License Terms: This text was adapted by Saylor Academy under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 3.0 License without attribution as requested by the work's original creator or licensor.

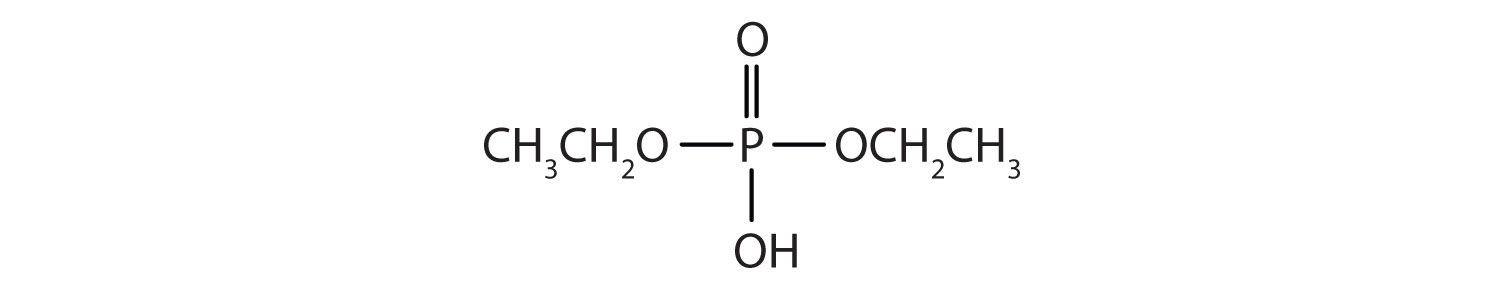 b.
b.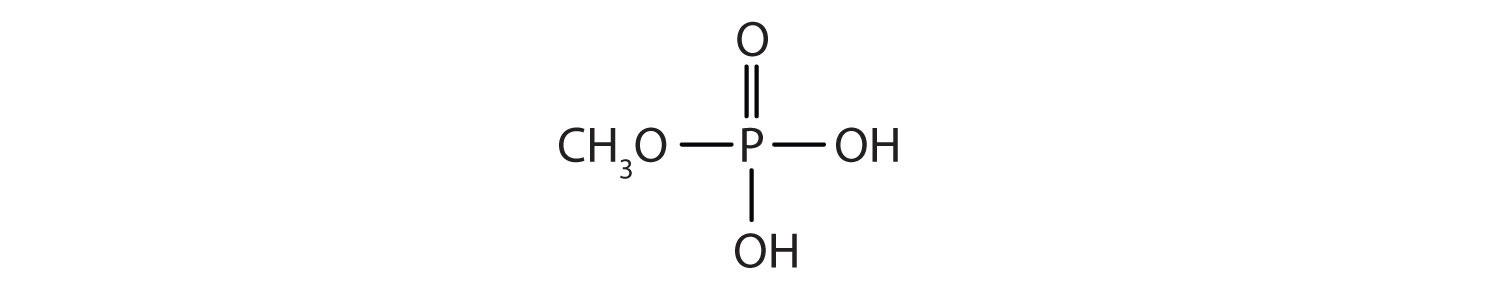 c.
c.