Learning Outcomes
- Multiply and divide real numbers
- Multiply two or more real numbers.
- Divide real numbers
- Simplify expressions with both multiplication and division
Multiplication and division are inverse operations, just as addition and subtraction are. You may recall that when you divide fractions, you multiply by the reciprocal. Inverse operations “undo” each other.
Multiply Real Numbers
Multiplying real numbers is not that different from multiplying whole numbers and positive fractions. However, you haven’t learned what effect a negative sign has on the product.
With whole numbers, you can think of multiplication as repeated addition. Using the number line, you can make multiple jumps of a given size. For example, the following picture shows the product [latex]3\cdot4[/latex] as [latex]3[/latex] jumps of [latex]4[/latex] units each.
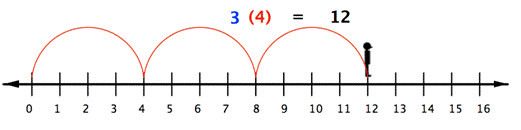
So to multiply [latex]3(−4)[/latex], you can face left (toward the negative side) and make three “jumps” forward (in a negative direction).
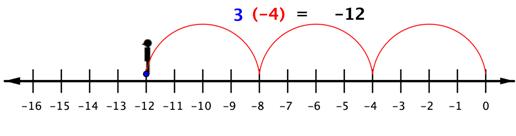
The product of a positive number and a negative number (or a negative and a positive) is negative.
The Product of a Positive Number and a Negative Number
To multiply a positive number and a negative number, multiply their absolute values. The product is negative.
Example
Find [latex]−3.8(0.6)[/latex].
Try It
The following video contains examples of how to multiply decimal numbers with different signs.
The Product of Two Numbers with the Same Sign (both positive or both negative)
To multiply two positive numbers, multiply their absolute values. The product is positive.
To multiply two negative numbers, multiply their absolute values. The product is positive.
Example
Find [latex]~\left( -\frac{3}{4} \right)\left( -\frac{2}{5} \right)[/latex]
The following video shows examples of multiplying two signed fractions, including simplification of the answer.
To summarize:
- positive [latex]\cdot[/latex] positive: The product is positive.
- negative [latex]\cdot[/latex] negative: The product is positive.
- negative [latex]\cdot[/latex] positive: The product is negative.
- positive [latex]\cdot[/latex] negative: The product is negative.
You can see that the product of two negative numbers is a positive number. So, if you are multiplying more than two numbers, you can count the number of negative factors.
Multiplying More Than Two Negative Numbers
If there are an even number ([latex]0, 2, 4[/latex], …) of negative factors to multiply, the product is positive.
If there are an odd number ([latex]1, 3, 5[/latex], …) of negative factors, the product is negative.
Example
Find [latex]3(−6)(2)(−3)(−1)[/latex].
The following video contains examples of multiplying more than two signed integers.
Divide Real Numbers
You may remember that when you divided fractions, you multiplied by the reciprocal. Reciprocal is another name for the multiplicative inverse (just as opposite is another name for additive inverse).
An easy way to find the multiplicative inverse is to just “flip” the numerator and denominator as you did to find the reciprocal. Here are some examples:
- The reciprocal of [latex]\frac{4}{9}[/latex] is [latex]\frac{9}{4}[/latex]because [latex]\frac{4}{9}\left(\frac{9}{4}\right)=\frac{36}{36}=1[/latex].
- The reciprocal of [latex]3[/latex] is [latex]\frac{1}{3}[/latex] because [latex]\frac{3}{1}\left(\frac{1}{3}\right)=\frac{3}{3}=1[/latex].
- The reciprocal of [latex]-\frac{5}{6}[/latex] is [latex]\frac{-6}{5}[/latex] because [latex]-\frac{5}{6}\left( -\frac{6}{5} \right)=\frac{30}{30}=1[/latex].
- The reciprocal of [latex]1[/latex] is [latex]1[/latex] as [latex]1(1)=1[/latex].
When you divided by positive fractions, you learned to multiply by the reciprocal. You also do this to divide real numbers.
Think about dividing a bag of [latex]26[/latex] marbles into two smaller bags with the same number of marbles in each. You can also say each smaller bag has one half of the marbles.
[latex]26\div 2=26\left( \frac{1}{2} \right)=13[/latex]
Notice that [latex]2[/latex] and [latex]\frac{1}{2}[/latex] are reciprocals.
Try again, dividing a bag of [latex]36[/latex] marbles into smaller bags.
| Number of bags | Dividing by number of bags | Multiplying by reciprocal |
|---|---|---|
| [latex]3[/latex] | [latex]\frac{36}{3}=12[/latex] | [latex]36\left( \frac{1}{3} \right)=\frac{36}{3}=\frac{12(3)}{3}=12[/latex] |
| [latex]4[/latex] | [latex]\frac{36}{4}=9[/latex] | [latex]36\left(\frac{1}{4}\right)=\frac{36}{4}=\frac{9\left(4\right)}{4}=9[/latex] |
| [latex]6[/latex] | [latex]\frac{36}{6}=6[/latex] | [latex]36\left(\frac{1}{6}\right)=\frac{36}{6}=\frac{6\left(6\right)}{6}=6[/latex] |
Dividing by a number is the same as multiplying by its reciprocal. (That is, you use the reciprocal of the divisor, the second number in the division problem.)
Example
Find [latex]28\div \frac{4}{3}[/latex]
Now let’s see what this means when one or more of the numbers is negative. A number and its reciprocal have the same sign. Since division is rewritten as multiplication using the reciprocal of the divisor, and taking the reciprocal doesn’t change any of the signs, division follows the same rules as multiplication.
Rules of Division
When dividing, rewrite the problem as multiplication using the reciprocal of the divisor as the second factor.
When one number is positive and the other is negative, the quotient is negative.
When both numbers are negative, the quotient is positive.
When both numbers are positive, the quotient is positive.
Example
Find [latex]24\div\left(-\frac{5}{6}\right)[/latex].
Example
Find [latex]4\,\left( -\frac{2}{3} \right)\,\div \left( -6 \right)[/latex]
Try It
The following video explains how to divide signed fractions.

Remember that a fraction bar also indicates division, so a negative sign in front of a fraction goes with the numerator, the denominator, or the whole fraction: [latex]-\frac{3}{4}=\frac{-3}{4}=\frac{3}{-4}[/latex].
In each case, the overall fraction is negative because there’s only one negative in the division.
The following video explains how to divide signed fractions.
Candela Citations
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Ex: Multiplying Signed Decimals. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) for Lumen Learning. Located at: https://youtu.be/7gY0S3LUUyQ. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Ex: Multiplying Three or More Integers. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) for Lumen Learning. Located at: https://youtu.be/rx8F9SPd0HE. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Authored by: Ex: Multiplying Signed Fractions Mathispower4u . Provided by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) for Lumen Learning. Located at: https://youtu.be/yUdJ46pTblo. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Ex 1: Dividing Signed Fractions. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) for Lumen Learning. Located at: https://youtu.be/OPHdadhDJoI. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Unit 9: Real Numbers, from Developmental Math: An Open Program. Provided by: Monterey Institute of Technology and Education. Located at: http://nrocnetwork.org/resources/downloads/nroc-math-open-textbook-units-1-12-pdf-and-word-formats/. License: CC BY: Attribution
