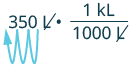Learning Outcomes
- Convert between Metric units of length, volume, and mass
- Use mixed units of measurement in the metric system
Make Unit Conversions in the Metric System
In the metric system, units are related by powers of [latex]10[/latex]. The root words of their names reflect this relation. For example, the basic unit for measuring length is a meter. One kilometer is [latex]1000[/latex] meters; the prefix kilo- means thousand. One centimeter is [latex]\Large\frac{1}{100}[/latex] of a meter, because the prefix centi- means one one-hundredth (just like one cent is [latex]\Large\frac{1}{100}[/latex] of one dollar).
The equivalencies of measurements in the metric system are shown in the reference table below. The common abbreviations for each measurement are given in parentheses.
| Metric Measurements | ||
|---|---|---|
| Length | Mass | Volume/Capacity |
| [latex]1[/latex] kilometer (km) = [latex]1000[/latex] m
[latex]1[/latex] hectometer (hm) = [latex]100[/latex] m [latex]1[/latex] dekameter (dam) = [latex]10[/latex] m [latex]1[/latex] meter (m) = [latex]1[/latex] m [latex]1[/latex] decimeter (dm) = [latex]0.1[/latex] m [latex]1[/latex] centimeter (cm) = [latex]0.01[/latex] m [latex]1[/latex] millimeter (mm) = [latex]0.001[/latex] m |
[latex]1[/latex] kilogram (kg) = [latex]1000[/latex] g
[latex]1[/latex] hectogram (hg) = [latex]100[/latex] g [latex]1[/latex] dekagram (dag) = [latex]10[/latex] g [latex]1[/latex] gram (g) = [latex]1[/latex] g [latex]1[/latex] decigram (dg) = [latex]0.1[/latex] g [latex]1[/latex] centigram (cg) = [latex]0.01[/latex] g [latex]1[/latex] milligram (mg) = [latex]0.001[/latex] g |
[latex]1[/latex] kiloliter (kL) = [latex]1000[/latex] L
[latex]1[/latex] hectoliter (hL) = [latex]100[/latex] L [latex]1[/latex] dekaliter (daL) = [latex]10[/latex] L [latex]1[/latex] liter (L) = [latex]1[/latex] L [latex]1[/latex] deciliter (dL) = [latex]0.1[/latex] L [latex]1[/latex] centiliter (cL) = [latex]0.01[/latex] L [latex]1[/latex] milliliter (mL) = [latex]0.001[/latex] L |
| [latex]1[/latex] meter = [latex]100[/latex] centimeters
[latex]1[/latex] meter = [latex]1000[/latex] millimeters |
[latex]1[/latex] gram = [latex]100[/latex] centigrams
[latex]1[/latex] gram = [latex]1000[/latex] milligrams |
[latex]1[/latex] liter = [latex]100[/latex] centiliters
[latex]1[/latex] liter = [latex]1000[/latex] milliliters |
To make conversions in the metric system, we will use the same technique we did in the U.S. system. Using the identity property of multiplication, we will multiply by a conversion factor of one to get to the correct units.
Have you ever run a [latex]\text{5 k}[/latex] or [latex]\text{10 k}[/latex] race? The lengths of those races are measured in kilometers. The metric system is commonly used in the United States when talking about the length of a race.
example
Nick ran a [latex]\text{10-kilometer}[/latex] race. How many meters did he run?
(credit: William Warby, Flickr)

Solution
We will convert kilometers to meters using the Identity Property of Multiplication and the equivalencies in the reference table from earlier.
| [latex]10[/latex] kilometers | |
| Multiply the measurement to be converted by [latex]1[/latex]. | [latex]10 \color{red}{km}\cdot 1[/latex] |
| Write [latex]1[/latex] as a fraction relating kilometers and meters. | [latex]10 \color{red}{km}\cdot\Large\frac{1000 m}{1\color{red}{km}}[/latex] |
| Simplify. | [latex]\Large\frac{10\color{red}{km}\cdot 1000 m}{1\color{red}{km}}[/latex] |
| Multiply. | [latex]10,000[/latex] m |
| Nick ran [latex]10,000[/latex] meters. |
try it
example
Eleanor’s newborn baby weighed [latex]3200[/latex] grams. How many kilograms did the baby weigh?
try it
Since the metric system is based on multiples of ten, conversions involve multiplying by multiples of ten. In Decimal Operations, we learned how to simplify these calculations by just moving the decimal.
To multiply by [latex]10,100,\text{or}1000[/latex], we move the decimal to the right [latex]1,2,\text{or}3[/latex] places, respectively. To multiply by [latex]0.1,0.01,\text{or}0.001[/latex] we move the decimal to the left [latex]1,2,\text{or}3[/latex] places respectively.
We can apply this pattern when we make measurement conversions in the metric system.
In the previous example, we changed [latex]3200[/latex] grams to kilograms by multiplying by [latex]\Large\frac{1}{1000}\normalsize\left(\text{or}0.001\right)[/latex]. This is the same as moving the decimal [latex]3[/latex] places to the left.

example
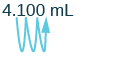
Convert: 1. [latex]350[/latex] liters to kiloliters 2. [latex]4.1[/latex] liters to milliliters.
try it
Use Mixed Units of Measurement in the Metric System
Performing arithmetic operations on measurements with mixed units of measures in the metric system requires the same care we used in the U.S. system. But it may be easier because of the relation of the units to the powers of [latex]10[/latex]. We still must make sure to add or subtract like units.
example
Ryland is [latex]1.6[/latex] meters tall. His younger brother is [latex]85[/latex] centimeters tall. How much taller is Ryland than his younger brother?
try it
example
Dena’s recipe for lentil soup calls for [latex]150[/latex] milliliters of olive oil. Dena wants to triple the recipe. How many liters of olive oil will she need?
try it
Candela Citations
- Question ID 146874, 146873, 146872, 146871, 146870, 146869, 146868. Authored by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Prealgebra. Provided by: OpenStax. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/caa57dab-41c7-455e-bd6f-f443cda5519c@9.757