Learning Outcomes
- Express square roots of negative numbers as multiples of [latex]i[/latex].
- Plot complex numbers on the complex plane.
- Add and subtract complex numbers.
- Multiply and divide complex numbers.
The study of mathematics continuously builds upon itself. Negative integers, for example, fill a void left by the set of positive integers. The set of rational numbers, in turn, fills a void left by the set of integers. The set of real numbers fills a void left by the set of rational numbers. The set of real numbers has voids as well. For example, we still have no solution to equations such as
[latex]{x}^{2}+4=0[/latex]
Our best guesses might be +2 or –2. But if we test +2 in this equation, it does not work. If we test –2, it does not work. If we want to have a solution for this equation, we will have to go farther than we have so far. After all, to this point we have described the square root of a negative number as undefined. Fortunately there is another system of numbers that provides solutions to problems such as these. In this section we will explore this number system and how to work within it.
Express and Plot Complex Numbers
We know how to find the square root of any positive real number. In a similar way we can find the square root of a negative number. The difference is that the root is not real. If the value in the radicand is negative, the root is said to be an imaginary number. The imaginary number [latex]i[/latex] is defined as the square root of negative 1.
[latex]\sqrt{-1}=i[/latex]
So, using properties of radicals,
[latex]{i}^{2}={\left(\sqrt{-1}\right)}^{2}=-1[/latex]
We can write the square root of any negative number as a multiple of [latex]i[/latex]. Consider the square root of –25.
[latex]\begin{align}\sqrt{-25}&=\sqrt{25\cdot \left(-1\right)}\\&=\sqrt{25}\cdot\sqrt{-1}\\ &=5i\end{align}[/latex]
We use [latex]5i[/latex] and not [latex]-\text{5}i[/latex] because the principal root of 25 is the positive root.
A complex number is the sum of a real number and an imaginary number. A complex number is expressed in standard form when written [latex]a+bi[/latex] where [latex]a[/latex] is the real part and [latex]bi[/latex] is the imaginary part. For example, [latex]5+2i[/latex] is a complex number. So, too, is [latex]3+4\sqrt{3}i[/latex].
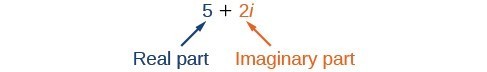
Imaginary numbers are distinguished from real numbers because a squared imaginary number produces a negative real number. Recall, when a positive real number is squared, the result is a positive real number and when a negative real number is squared, again, the result is a positive real number. Complex numbers are a combination of real and imaginary numbers.
A General Note: Imaginary and Complex Numbers
A complex number is a number of the form [latex]a+bi[/latex] where
- [latex]a[/latex] is the real part of the complex number.
- [latex]bi[/latex] is the imaginary part of the complex number.
If [latex]b=0[/latex], then [latex]a+bi[/latex] is a real number. If [latex]a=0[/latex] and [latex]b[/latex] is not equal to 0, the complex number is called an imaginary number. An imaginary number is an even root of a negative number.
How To: Given an imaginary number, express it in standard form.
- Write [latex]\sqrt{-a}[/latex] as [latex]\sqrt{a}\cdot\sqrt{-1}[/latex].
- Express [latex]\sqrt{-1}[/latex] as i.
- Write [latex]\sqrt{a}\cdot i[/latex] in simplest form.
Example: Expressing an Imaginary Number in Standard Form
Express [latex]\sqrt{-9}[/latex] in standard form.
Try It
Express [latex]\sqrt{-24}[/latex] in standard form.
Plot complex numbers on the complex plane
We cannot plot complex numbers on a number line as we might real numbers. However, we can still represent them graphically. To represent a complex number we need to address the two components of the number. We use the complex plane, which is a coordinate system in which the horizontal axis represents the real component and the vertical axis represents the imaginary component. Complex numbers are the points on the plane, expressed as ordered pairs [latex](a, b)[/latex], where [latex]a[/latex] represents the coordinate for the horizontal axis and [latex]b[/latex] represents the coordinate for the vertical axis.
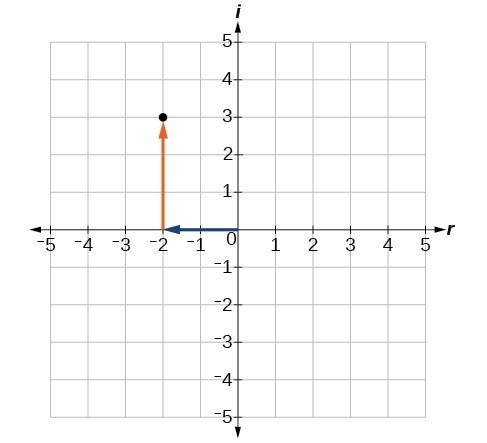
Let’s consider the number [latex]-2+3i[/latex]. The real part of the complex number is [latex]–2[/latex] and the imaginary part is [latex]3i[/latex]. We plot the ordered pair [latex]\left(-2,3\right)[/latex] to represent the complex number [latex]-2+3i[/latex].
A General Note: Complex Plane
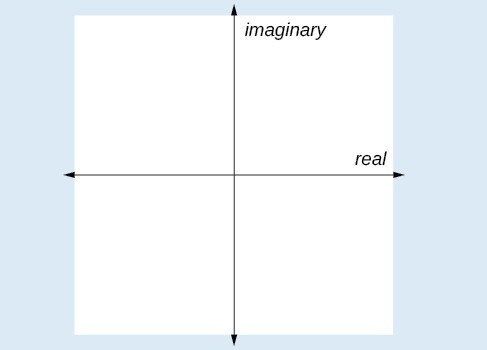
In the complex plane, the horizontal axis is the real axis, and the vertical axis is the imaginary axis.
How To: Given a complex number, represent its components on the complex plane.
- Determine the real part and the imaginary part of the complex number.
- Move along the horizontal axis to show the real part of the number.
- Move parallel to the vertical axis to show the imaginary part of the number.
- Plot the point.
Example: Plotting a Complex Number on the Complex Plane
Plot the complex number [latex]3 - 4i[/latex] on the complex plane.
Try It
Plot the complex number [latex]-4-i[/latex] on the complex plane.
Add, Subtract, and Multiply Complex Numbers
Just as with real numbers, we can perform arithmetic operations on complex numbers. To add or subtract complex numbers, we combine the real parts and combine the imaginary parts.
A General Note: Addition and Subtraction of Complex Numbers
Adding complex numbers:
[latex]\left(a+bi\right)+\left(c+di\right)=\left(a+c\right)+\left(b+d\right)i[/latex]
Subtracting complex numbers:
[latex]\left(a+bi\right)-\left(c+di\right)=\left(a-c\right)+\left(b-d\right)i[/latex]
How To: Given two complex numbers, find the sum or difference.
- Identify the real and imaginary parts of each number.
- Add or subtract the real parts.
- Add or subtract the imaginary parts.
Example: Adding Complex Numbers
Add [latex]3 - 4i[/latex] and [latex]2+5i[/latex].
Try It
Subtract [latex]2+5i[/latex] from [latex]3 - 4i[/latex].
Multiplying Complex Numbers
Multiplying complex numbers is much like multiplying binomials. The major difference is that we work with the real and imaginary parts separately.
Multiplying a Complex Number by a Real Number
Let’s begin by multiplying a complex number by a real number. We distribute the real number just as we would with a binomial. So, for example,
[latex]\begin{align}3(6+2i)&=(3\cdot6)+(3\cdot2i)&&\text{Distribute.}\\&=18+6i&&\text{Simplify.}\end{align}[/latex]
How To: Given a complex number and a real number, multiply to find the product.
- Use the distributive property.
- Simplify.
Example: Multiplying a Complex Number by a Real Number
Find the product [latex]4\left(2+5i\right)[/latex].
Try It
Find the product [latex]-4\left(2+6i\right)[/latex].
Multiplying Complex Numbers Together
Now, let’s multiply two complex numbers. We can use either the distributive property or the FOIL method. Recall that FOIL is an acronym for multiplying First, Outer, Inner, and Last terms together. Using either the distributive property or the FOIL method, we get
[latex]\left(a+bi\right)\left(c+di\right)=ac+adi+bci+bd{i}^{2}[/latex]
Because [latex]{i}^{2}=-1[/latex], we have
[latex]\left(a+bi\right)\left(c+di\right)=ac+adi+bci-bd[/latex]
To simplify, we combine the real parts, and we combine the imaginary parts.
[latex]\left(a+bi\right)\left(c+di\right)=\left(ac-bd\right)+\left(ad+bc\right)i[/latex]
How To: Given two complex numbers, multiply to find the product.
- Use the distributive property or the FOIL method.
- Simplify.
Example: Multiplying a Complex Number by a Complex Number
Multiply [latex]\left(4+3i\right)\left(2 - 5i\right)[/latex].
Try It
Multiply [latex]\left(3 - 4i\right)\left(2+3i\right)[/latex].
Divide Complex Numbers
Division of two complex numbers is more complicated than addition, subtraction, and multiplication because we cannot divide by an imaginary number, meaning that any fraction must have a real-number denominator. We need to find a term by which we can multiply the numerator and the denominator that will eliminate the imaginary portion of the denominator so that we end up with a real number as the denominator. This term is called the complex conjugate of the denominator, which is found by changing the sign of the imaginary part of the complex number. In other words, the complex conjugate of [latex]a+bi[/latex] is [latex]a-bi[/latex].
Note that complex conjugates have a reciprocal relationship: The complex conjugate of [latex]a+bi[/latex] is [latex]a-bi[/latex], and the complex conjugate of [latex]a-bi[/latex] is [latex]a+bi[/latex]. Importantly, complex conjugate pairs have a special property. Their product is always real.
[latex]\begin{align}(a+bi)(a-bi)&=a^2-abi+abi-b^2i^2\\[2mm]&=a^2-b^2(-1)\\[2mm]&=a^2+b^2\end{align}[/latex]
Suppose we want to divide [latex]c+di[/latex] by [latex]a+bi[/latex], where neither [latex]a[/latex] nor [latex]b[/latex] equals zero. We first write the division as a fraction, then find the complex conjugate of the denominator, and multiply.
[latex]\dfrac{c+di}{a+bi}[/latex] where [latex]a\ne 0[/latex] and [latex]b\ne 0[/latex].
Multiply the numerator and denominator by the complex conjugate of the denominator.
[latex]\dfrac{\left(c+di\right)}{\left(a+bi\right)}\cdot \dfrac{\left(a-bi\right)}{\left(a-bi\right)}=\dfrac{\left(c+di\right)\left(a-bi\right)}{\left(a+bi\right)\left(a-bi\right)}[/latex]
Apply the distributive property.
[latex]=\dfrac{ca-cbi+adi-bd{i}^{2}}{{a}^{2}-abi+abi-{b}^{2}{i}^{2}}[/latex]
Simplify, remembering that [latex]{i}^{2}=-1[/latex].
[latex]\begin{align}&=\dfrac{ca-cbi+adi-bd\left(-1\right)}{{a}^{2}-abi+abi-{b}^{2}\left(-1\right)} \\[2mm] &=\dfrac{\left(ca+bd\right)+\left(ad-cb\right)i}{{a}^{2}+{b}^{2}}\end{align}[/latex]
A General Note: The Complex Conjugate
The complex conjugate of a complex number [latex]a+bi[/latex] is [latex]a-bi[/latex]. It is found by changing the sign of the imaginary part of the complex number. The real part of the number is left unchanged.
- When a complex number is multiplied by its complex conjugate, the result is a real number.
- When a complex number is added to its complex conjugate, the result is a real number.
Example: Finding Complex Conjugates
Find the complex conjugate of each number.
- [latex]2+i\sqrt{5}[/latex]
- [latex]-\frac{1}{2}i[/latex]
How To: Given two complex numbers, divide one by the other.
- Write the division problem as a fraction.
- Determine the complex conjugate of the denominator.
- Multiply the numerator and denominator of the fraction by the complex conjugate of the denominator.
- Simplify.
Example: Dividing Complex Numbers
Divide [latex]\left(2+5i\right)[/latex] by [latex]\left(4-i\right)[/latex].
Try It
Example: Substituting a Complex Number into a Polynomial Function
Let [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{2}-5x+2[/latex]. Evaluate [latex]f\left(3+i\right)[/latex].
Try It
Let [latex]f\left(x\right)=2{x}^{2}-3x[/latex]. Evaluate [latex]f\left(8-i\right)[/latex].
Example: Substituting an Imaginary Number in a Rational Function
Let [latex]f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{2+x}{x+3}[/latex]. Evaluate [latex]f\left(10i\right)[/latex].
Try It
Let [latex]f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{x+1}{x - 4}[/latex]. Evaluate [latex]f\left(-i\right)[/latex].
Simplifying Powers of [latex]i[/latex]
The powers of [latex]i[/latex] are cyclic. Let’s look at what happens when we raise [latex]i[/latex] to increasing powers.
[latex]{i}^{1}=i[/latex]
[latex]{i}^{2}=-1[/latex]
[latex]{i}^{3}={i}^{2}\cdot i=-1\cdot i=-i[/latex]
[latex]{i}^{4}={i}^{3}\cdot i=-i\cdot i=-{i}^{2}=-\left(-1\right)=1[/latex]
[latex]{i}^{5}={i}^{4}\cdot i=1\cdot i=i[/latex]
We can see that when we get to the fifth power of [latex]i[/latex], it is equal to the first power. As we continue to multiply [latex]i[/latex] by itself for increasing powers, we will see a cycle of 4. Let’s examine the next 4 powers of [latex]i[/latex].
[latex]{i}^{6}={i}^{5}\cdot i=i\cdot i={i}^{2}=-1[/latex]
[latex]{i}^{7}={i}^{6}\cdot i={i}^{2}\cdot i={i}^{3}=-i[/latex]
[latex]{i}^{8}={i}^{7}\cdot i={i}^{3}\cdot i={i}^{4}=1[/latex]
[latex]{i}^{9}={i}^{8}\cdot i={i}^{4}\cdot i={i}^{5}=i[/latex]
Example: Simplifying Powers of [latex]i[/latex]
Evaluate [latex]{i}^{35}[/latex].
Q & A
Can we write [latex]{i}^{35}[/latex] in other helpful ways?
As we saw in Example: Simplifying Powers of [latex]i[/latex], we reduced [latex]{i}^{35}[/latex] to [latex]{i}^{3}[/latex] by dividing the exponent by 4 and using the remainder to find the simplified form. But perhaps another factorization of [latex]{i}^{35}[/latex] may be more useful. The table below shows some other possible factorizations.
| Factorization of [latex]{i}^{35}[/latex] | [latex]{i}^{34}\cdot i[/latex] | [latex]{i}^{33}\cdot {i}^{2}[/latex] | [latex]{i}^{31}\cdot {i}^{4}[/latex] | [latex]{i}^{19}\cdot {i}^{16}[/latex] |
| Reduced form | [latex]{\left({i}^{2}\right)}^{17}\cdot i[/latex] | [latex]{i}^{33}\cdot \left(-1\right)[/latex] | [latex]{i}^{31}\cdot 1[/latex] | [latex]{i}^{19}\cdot {\left({i}^{4}\right)}^{4}[/latex] |
| Simplified form | [latex]{\left(-1\right)}^{17}\cdot i[/latex] | [latex]-{i}^{33}[/latex] | [latex]{i}^{31}[/latex] | [latex]{i}^{19}[/latex] |
Each of these will eventually result in the answer we obtained above but may require several more steps than our earlier method.
Key Concepts
- The square root of any negative number can be written as a multiple of [latex]i[/latex].
- To plot a complex number, we use two number lines, crossed to form the complex plane. The horizontal axis is the real axis, and the vertical axis is the imaginary axis.
- Complex numbers can be added and subtracted by combining the real parts and combining the imaginary parts.
- Complex numbers can be multiplied and divided.
- To multiply complex numbers, distribute just as with polynomials.
- To divide complex numbers, multiply both the numerator and denominator by the complex conjugate of the denominator to eliminate the complex number from the denominator.
- The powers of [latex]i[/latex] are cyclic, repeating every fourth one.
Glossary
- complex conjugate
- the complex number in which the sign of the imaginary part is changed and the real part of the number is left unchanged; when added to or multiplied by the original complex number, the result is a real number
- complex number
- the sum of a real number and an imaginary number, written in the standard form [latex]a+bi[/latex], where [latex]a[/latex] is the real part, and [latex]bi[/latex] is the imaginary part
- complex plane
- a coordinate system in which the horizontal axis is used to represent the real part of a complex number and the vertical axis is used to represent the imaginary part of a complex number
- imaginary number
- a number in the form [latex]bi[/latex] where [latex]i=\sqrt{-1}\\[/latex]

STOP HERE and complete Homework 2.1 – Complex Numbers
Candela Citations
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Question ID 120193. Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: IMathAS Community License CC-BY + GPL
- College Algebra. Authored by: Abramson, Jay et al.. Provided by: OpenStax. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/9b08c294-057f-4201-9f48-5d6ad992740d@5.2. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/9b08c294-057f-4201-9f48-5d6ad992740d@5.2
- Introduction to Complex Numbers. Authored by: Sousa, James. Located at: https://youtu.be/NeTRNpBI17I. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Question ID 61706. Authored by: Day, Alyson. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: IMathAS Community License CC-BY + GPL
- Question ID 65709. Authored by: Kaslik, Pete, mb Lippman, David. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: IMathAS Community License CC-BY + GPL
- Ex: Dividing Complex Numbers. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) . Located at: https://youtu.be/XBJjbJAwM1c. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Ex 1: Adding and Subtracting Complex Numbers. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) . Located at: https://youtu.be/SGhTjioGqqA. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Question ID 61710, 61715. Authored by: Day, Alyson. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: IMathAS Community License CC-BY + GPL
- Question ID 40462. Authored by: Jenck, Michael. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: IMathAS Community License CC-BY + GPL
- Question ID 3903. Authored by: Lippman, David . License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: IMathAS Community License CC-BY + GPL
- Ex 2: Multiply Complex Numbers. Authored by: Sousa, James (Mathispower4u). Located at: https://youtu.be/O9xQaIi0NX0. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Ex: Dividing Complex Numbers . Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) . Located at: https://youtu.be/XBJjbJAwM1c. License: CC BY: Attribution
- College Algebra. Authored by: OpenStax College Algebra. Provided by: OpenStax. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/9b08c294-057f-4201-9f48-5d6ad992740d@3.278:1/Preface. License: CC BY: Attribution


