Learning Objectives
- Graph the inverse function of an exponential function
- Determine the equation of the inverse function of an exponential function
In chapter 3, we discussed that every function has an inverse, but only a one-to-one function has an inverse function. Since an exponential function is a one-to-one function, its inverse is also a one-to-one function. Therefore, the inverse of an exponential function is also a function.
Graphing the Inverse Function of an Exponential Function
We can graph the inverse of an exponential function by creating and using a table of values. For example, given the function [latex]f(x)=2^x[/latex], we may graph the function by creating a table of values by choosing [latex]x[/latex]-values then determining the corresponding function values (table 1).
| [latex]x[/latex] | [latex]y=f(x)=2^x[/latex] |
|---|---|
| [latex]-3[/latex] | [latex]\dfrac{1}{8}[/latex] |
| [latex]-2[/latex] | [latex]\dfrac{1}{4}[/latex] |
| [latex]-1[/latex] | [latex]\dfrac{1}{2}[/latex] |
| [latex]0[/latex] | [latex]1[/latex] |
| [latex]1[/latex] | [latex]2[/latex] |
| [latex]2[/latex] | [latex]4[/latex] |
| [latex]3[/latex] | [latex]8[/latex] |
| Table 1. Table of values | |
The inverse of the function is found by switching the values of the [latex]x[/latex] and [latex]y[/latex] columns so that the inputs are the values of [latex]y[/latex] and the outputs are the values of [latex]x[/latex]. Table 2 shows the values after switching the [latex]x[/latex] and [latex]y[/latex] columns, and is called the inverse table.
| [latex]x[/latex] | [latex]y=f^{-1}(x)[/latex] |
|---|---|
| [latex]\dfrac{1}{8}[/latex] | [latex]-3[/latex] |
| [latex]\dfrac{1}{4}[/latex] | [latex]-2[/latex] |
| [latex]\dfrac{1}{2}[/latex] | [latex]-1[/latex] |
| [latex]1[/latex] | [latex]0[/latex] |
| [latex]2[/latex] | [latex]1[/latex] |
| [latex]4[/latex] | [latex]2[/latex] |
| [latex]8[/latex] | [latex]3[/latex] |
| Table 2. Inverse table | |
Figure 1 shows the graphs of the function [latex]f(x)=2^x[/latex] (blue curve) and its inverse function (green curve) based on the values in table 1 of the function and its inverse table (table 2). Notice that the graph of the inverse function is a reflection of the graph of the original function with respect to the line of symmetry [latex]y=x[/latex] (red line).

Figure 1. The graphs of the function f(x)=2^x and its inverse function [latex]x=2^y[/latex]
Notice that any point [latex](x, y)[/latex] on the original function becomes the point [latex](y, x)[/latex] on the inverse function. The domain of the original function becomes the range of the inverse function, and vice versa. Domain of [latex]f(x)=(-\infty, +\infty)=[/latex] range of [latex]f^{-1}(x)[/latex]. Range of [latex]f(x)=(0, +\infty)=[/latex] domain of [latex]f^{-1}(x)[/latex].
Example 1
Use Desmos to graph the function [latex]f(x)=2^{x-3}[/latex] then use reflection about the line [latex]y=x[/latex] to graph the inverse function [latex]y=f^{-1}(x)[/latex].
Solution
Putting the function [latex]f(x)=2^{x-3}[/latex] into Desmos gives the graph:
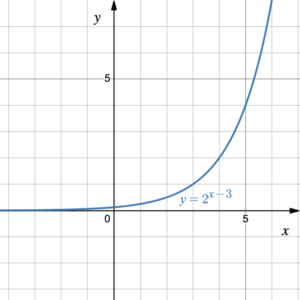
Draw the line [latex]y=x[/latex] then reflect the curve across the line so that any point [latex](x, y)[/latex] reflects to [latex](y, x)[/latex].

Try It 1
Use Desmos to graph the function [latex]f(x)=3^{x+4}+2[/latex] then use reflection about the line [latex]y=x[/latex] to graph the inverse function [latex]y=f^{-1}(x)[/latex].
Example 2
An exponential function has domain [latex](-\infty, +\infty)[/latex] and range [latex](2, +\infty)[/latex]. What is the domain and range of its inverse function?
Solution
The range of the original function becomes the domain of the inverse function and vice versa.
So, the domain of the inverse function is [latex](2, +\infty)[/latex] and the range of the inverse function is [latex](-\infty, +\infty)[/latex].
Try It 2
An exponential function has domain [latex](-\infty, +\infty)[/latex] and range [latex](-3, +\infty)[/latex]. What is the domain and range of its inverse function?
Determining the Equation of the Inverse Function
The inverse function of an exponential function [latex]f(x)=r^x[/latex], is found by switching the input [latex]x[/latex] and output [latex]y[/latex]. We start by writing [latex]y[/latex] for [latex]f(x)[/latex] then switch [latex]x[/latex] and [latex]y[/latex] to get the inverse function:
Original function: [latex]y=r^x[/latex]
Inverse function: [latex]x=r^y[/latex]
The minute we switch [latex]x[/latex] and [latex]y[/latex], we have the inverse function. Now all we have to do is solve for [latex]y[/latex] so we can write the inverse function using function notation.
To solve the equation [latex]x=r^y[/latex], we need to solve for the exponent. To do this we introduce logarithms. Logarithms were invented by John Napier, a Scottish mathematician, in 1614 as a means of simplifying calculations.
logarithms
A logarithm is a quantity representing the power to which a fixed number (the base) must be raised to produce a given number.
For all real numbers [latex]x[/latex] and positive real numbers [latex]a[/latex] and [latex]b, b\neq1[/latex],
if [latex]a=b^x[/latex], then [latex]x=log_b{a}[/latex]
[latex]x=log_b{a}[/latex] is read ‘[latex]x[/latex] equals the logarithm base [latex]b[/latex] of [latex]a[/latex].
The base of the exponential expression becomes the base of the logarithm.
INVERSE FUNCTION OF AN EXPONENTIAL FUNCTION
The exponential function [latex]f(x)=r^x[/latex] has an inverse function [latex]f^{-1}(x)=log_r{x}[/latex].
Example 3
Determine the inverse function of [latex]f(x)=5^{x-1}[/latex].
Solution
The inverse function is found by switching [latex]x[/latex] and [latex]y[/latex] in the function [latex]y=5^{x-1}[/latex]:
[latex]x=5^{y-1}[/latex]
Now we need to solve for [latex]y[/latex]. By definition, if [latex]a=b^x[/latex], then [latex]x=log_b{a}[/latex].
[latex]\begin{aligned}x&=5^{y-1}\\y-1&=log_5{x}\\y&=log_5{x}+1\end{aligned}[/latex]
Finish by writing the inverse in function notation. Replace [latex]y[/latex] with [latex]f^{-1}(x)[/latex]:
[latex]f^{-1}(x)=log_5(x)+1[/latex]
Example 4
Determine the inverse function of [latex]g(x)=5^x-1[/latex].
Solution
The inverse function is found by switching [latex]x[/latex]and [latex]y[/latex] in the function [latex]y=5^x-1[/latex]:
[latex]x=5^y-1[/latex]
Now we need to solve for [latex]y[/latex]. By definition, if [latex]a=b^x[/latex], then [latex]x=log_b{a}[/latex].
We start by isolating the exponential term in the equation by adding 1 to both sides:
[latex]x+1=5^y[/latex]
Use the definition of logarithms:
[latex]y=log_5{(x+1)}[/latex]
Finish by writing the equation in function notation:
[latex]g^{-1}(x)=log_5{(x+1)}[/latex]
Example 5
Determine the inverse function of [latex]h(x)=(3)2^x+5[/latex].
Solution
Switch [latex]x[/latex] and [latex]y[/latex] in [latex]y=(3)2^x+5[/latex]:
[latex]x=(3)2^y+5[/latex]
Isolate the exponential term by subtracting 5 from both sides:
[latex]x-5=(3)2^y[/latex]
Isolate the exponential by dividing both sides by 3:
[latex]\dfrac{x-5}{3}=2^y[/latex]
Use the definition of logarithms to solve for [latex]y[/latex]:
[latex]y=log_2{\left(\dfrac{x-5}{3}\right)}[/latex]
Write in function notation:
[latex]h^{-1}(x)=log_2{\left(\dfrac{x-5}{3}\right)}[/latex]
Try It 3
Determine the inverse function of [latex]f(x)=4^{x+3}[/latex].
Try It 4
Determine the inverse function of [latex]g(x)=7^x-4[/latex].
Try It 5
Determine the inverse function of [latex]h(x)=(5)6^x-4[/latex].
Candela Citations
- The Inverse of an Exponential Function . Authored by: Leo Chang and Hazel McKenna. Provided by: Utah Valley University. License: CC BY: Attribution
- All graphs created using desmos graphing calculator. Authored by: Hazel McKenna. Provided by: www.desmos.com/calculator. License: CC BY: Attribution

