Learning Objectives
- Graph the inverse of a rational function
- Find the equation of the inverse function of a one-to-one rational function
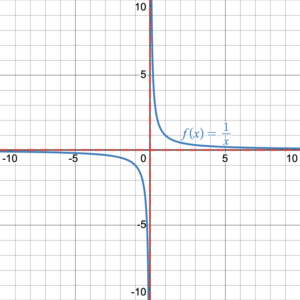
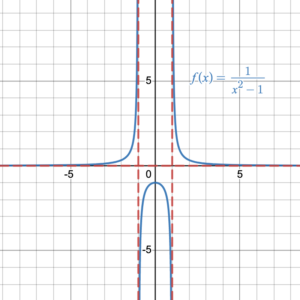
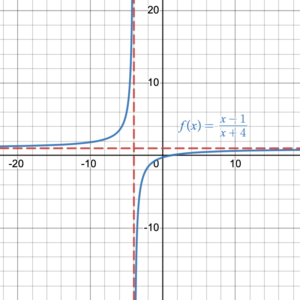
In chapter 3, we discussed that every function has an inverse, but only a one-to-one function has an inverse function. Some rational functions are one-to-one functions such as [latex]f(x)=\dfrac{1}{x}[/latex] or [latex]f(x)=\dfrac{x-1}{x+4}[/latex]. Therefore, their inverse is a function. Some rational functions are many-to-one functions such as [latex]f(x)=\dfrac{1}{x^2-1}[/latex] or [latex]f(x)=\dfrac{x^3-4x^2+2}{x^2-1}[/latex]. Therefore, their inverse is not a function (Figure 1).
| One-to-one rational functions that have an inverse function | Many-to-one rational functions that do not have an inverse function |
|---|---|
 |
 |
 |
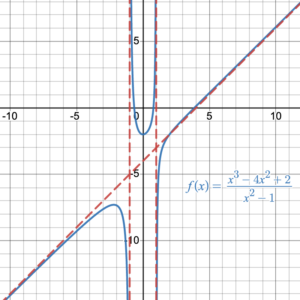 |
| Figure 1. Graphs of rational functions | |
Notice that three of the graphs in figure 1 have horizontal and vertical asymptotes but the 4th graph has two vertical asymptotes and a slant asymptote. A slant asymptote is a line of the form [latex]y=mx+b[/latex] that is neither vertical nor horizontal but that the graph gets closer and closer to as [latex]x[/latex] approaches positive and negative infinity. Slant asymptotes occur in the graph of a rational function [latex]f(x)=\dfrac{P(x)}{Q(x)}[/latex] when the degree of [latex]P(x)[/latex] is one more than the degree of [latex]Q(x)[/latex]. For example, in the function [latex]f(x)=\dfrac{x^3-4x^2+2}{x^2-1}[/latex] (Figure 1), [latex]P(x)=x^3-4x^2+2[/latex] and has degree 3, while [latex]Q(x)=x^2-1[/latex] which has degree 2. Since 3 is one more than 2, there is a slant asymptote.
Graphing the Inverse Function of a Rational Function
We may graph the inverse of a rational function by creating and using its inverse table. For example, given the function [latex]f(x)=\dfrac{1}{x}[/latex], we may graph the function by creating a table of values (Table 1).
| [latex]x[/latex] | [latex]y=\dfrac{1}{x}[/latex] |
|---|---|
| [latex]–2[/latex] | [latex]-\dfrac{1}{2}[/latex] |
| [latex]–1[/latex] | [latex]–1[/latex] |
| [latex]-\dfrac{1}{2}[/latex] | [latex]–2[/latex] |
| [latex]\dfrac{1}{2}[/latex] | [latex]2[/latex] |
| [latex]1[/latex] | [latex]1[/latex] |
| [latex]2[/latex] | [latex]\dfrac{1}{2}[/latex] |
| [latex]3[/latex] | [latex]\dfrac{1}{3}[/latex] |
| Table 1. Table of values for [latex]f(x)=\dfrac{1}{x}[/latex] | |
The inverse of the function is found by switching the values of the [latex]x[/latex] and [latex]y[/latex] columns so that the inputs become the values of [latex]y[/latex] and the outputs become the values of [latex]x[/latex]. The table after switching the values of the [latex]x[/latex] and [latex]y[/latex] columns is the inverse table (Table 2).
| [latex]x[/latex] | [latex]y=\dfrac{1}{x}[/latex] |
|---|---|
| [latex]-\dfrac{1}{2}[/latex] | [latex]-2[/latex] |
| [latex]-1[/latex] | [latex]-1[/latex] |
| [latex]-2[/latex] | [latex]-\dfrac{1}{2}[/latex] |
| [latex]2[/latex] | [latex]\dfrac{1}{2}[/latex] |
| [latex]1[/latex] | [latex]1[/latex] |
| [latex]\dfrac{1}{2}[/latex] | [latex]2[/latex] |
| [latex]\dfrac{1}{3}[/latex] | [latex]3[/latex] |
| Table 2. The inverse table for [latex]f^{-1}(x)=\dfrac{1}{x}[/latex] | |
Figure 2 shows the graph of the inverse of the function [latex]f(x)=\dfrac{1}{x}[/latex] drawn from its inverse table. Notice that the graph of the inverse is exactly the same as the graph of the original function [latex]f(x)=\dfrac{1}{x}[/latex]. In other words, the function [latex]f(x)=\dfrac{1}{x}[/latex] is the inverse of the function itself. The inverse function is a reflection of the original function with respect to the line of symmetry [latex]y=x[/latex].

Figure 2. The inverse of the function [latex]f(x)=\dfrac{1}{x}[/latex] is [latex]f^{-1}(x)=\dfrac{1}{x}[/latex].
Since the graph of the function [latex]f(x)=\dfrac{1}{x}[/latex] is symmetric across the line [latex]y=x[/latex], the inverse function is identical to the original function.
Determining the Inverse Function of an One-to-One Rational Function
To determine the equation of the inverse function of a one-to-one rational function, we use the same idea of switching the input and output. We start by writing [latex]y=f(x)[/latex], switch [latex]x[/latex] and [latex]y[/latex], and then solve for [latex]y[/latex].
For example, to determine the inverse function of the one-to-one rational function [latex]g(x)=\dfrac{1}{x}[/latex], we write [latex]y=g(x)[/latex] then switch [latex]x[/latex] and [latex]y[/latex]:
[latex]\begin{aligned}g(x)&=\dfrac{1}{x}\\\\y&=\dfrac{1}{x}\\\\x&=\dfrac{1}{y}\end{aligned}[/latex]
At this point, we have the inverse. We now need to solve for [latex]y[/latex] so we can write the inverse using function notation by replacing [latex]y[/latex] with [latex]g^{-1}(x)[/latex]:
[latex]\begin{aligned}x&=\dfrac{1}{y}\\\\x\color{blue}{\cdot y}&=\dfrac{1}{y}\color{blue}{\cdot y}&&\text{Multiply both sides by }y\text{ to clear the fractions}\\\\xy&=1\\\\y&=\dfrac{1}{x}\\\\g^{-1}(x)&=\dfrac{1}{x}\end{aligned}[/latex]
Therefore, the equation of the inverse function is [latex]g^{-1}(x)=\dfrac{1}{x}[/latex].
Example 1
Determine the inverse function of the one-to-one rational function [latex]h(x)=\dfrac{x-1}{x+4}[/latex].
Solution
We start by writing [latex]y=h(x)[/latex] then switch[latex]x[/latex] and [latex]y[/latex] to get the inverse:
[latex]\begin{aligned}y&=\dfrac{x-1}{x+4}&&\text{Write }y\text{ for }h(x)\\\\x&=\dfrac{y-1}{y+4}&&\text{Switch }x\text{ and }y\\\\x\color{blue}{(y+4)}&=\dfrac{y-1}{y+4}\color{blue}{\cdot (y+4)}&&\text{Multiply both sides by }y+4\text{ to clear the fractions}\\\\x(y+4)&=y-1\\\\xy+4x &=y-1&&\text{Multiply the left side using the distributive property}\\\\xy-y &=-4x-1&&\text{Collect }y\text{ terms on the left side}\\\\y(x-1)&=-4x-1&&\text{Pull }y\text{ out as a common factor on the left side}\\\\y&=\dfrac{-4x-1}{x-1}&&\text{Divide both sides by }x-1\end{aligned}[/latex]
Now write the inverse in function notation, [latex]h^{-1}(x)=\dfrac{-4x-1}{x-1}[/latex] or by pulling out [latex]-1[/latex] as a common factor on the numerator, [latex]h^{-1}(x)=-\dfrac{4x+1}{x-1}[/latex].
Example 2
Determine the inverse function of the one-to-one rational function [latex]h(x)=\dfrac{x+5}{x-1}[/latex].
Solution
We start by writing [latex]y=h(x)[/latex] then switch [latex]x[/latex] and [latex]y[/latex] to get the inverse:
[latex]\begin{aligned}y&=\dfrac{x+5}{x-1}&&\text{Write }y\text{ for }h(x)\\\\x&=\dfrac{y+5}{y-1}&&\text{Switch }x\text{ and }y\\\\x\color{blue}{(y-1)}&=\dfrac{y+5}{y-1}\color{blue}{\cdot (y-1)}&&\text{Multiply both sides by }y-1\text{ to clear the fractions}\\\\x(y-1)&=y+5\\\\xy-x &=y+5&&\text{Multiply the left side using the distributive property}\\\\xy-y &=x+5&&\text{Collect }y\text{ terms on the left side}\\\\y(x-1)&=x+5&&\text{Pull }y\text{ out as a common factor on the left side}\\\\y&=\dfrac{x+5}{x-1}&&\text{Divide both sides by }x-1\end{aligned}[/latex]
Now write the inverse in function notation, [latex]h^{-1}(x)=\dfrac{x+5}{x-1}[/latex].
Try It 1
Determine the inverse function of the one-to-one rational function:
- [latex]h(x)=\dfrac{x+4}{x-6}[/latex]
- [latex]g(x)=\dfrac{x+7}{x+4}[/latex]
- [latex]f(x)=\dfrac{2x+3}{5x+4}[/latex]
Candela Citations
- The Inverse of a Rational Function. Authored by: Leo Chang and Hazel McKenna. Provided by: Utah Valley University. License: CC BY: Attribution
- All graphs created using desmos graphing calculator. Authored by: Leo Chang. Provided by: Utah Valley University. Located at: http://www.desmos.com/calculator. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Examples and Try Its: hjm547. Authored by: Hazel McKenna. Provided by: Utah Valley University. License: CC BY: Attribution
