Learning Outcomes
- Describe the structure and function of nails and glands
Nails
The nail bed is a specialized structure of the epidermis that is found at the tips of our fingers and toes. The nail body is formed on the nail bed, and protects the tips of our fingers and toes as they are the farthest extremities and the parts of the body that experience the maximum mechanical stress (Figure 1).

Figure 1. The nail is an accessory structure of the integumentary system.
In addition, the nail body forms a back-support for picking up small objects with the fingers. The nail body is composed of densely packed dead keratinocytes. The epidermis in this part of the body has evolved a specialized structure upon which nails can form. The nail body forms at the nail root, which has a matrix of proliferating cells from the stratum basale that enables the nail to grow continuously. The lateral nail fold overlaps the nail on the sides, helping to anchor the nail body. The nail fold that meets the proximal end of the nail body forms the nail cuticle, also called the eponychium. The nail bed is rich in blood vessels, making it appear pink, except at the base, where a thick layer of epithelium over the nail matrix forms a crescent-shaped region called the lunula (the “little moon”). The area beneath the free edge of the nail, furthest from the cuticle, is called the hyponychium. It consists of a thickened layer of stratum corneum.
Nails are accessory structures of the integumentary system. Watch this video to learn more about the origin and growth of fingernails.
Practice Question
Describe the structure and composition of nails.
Glands
Sweat Glands
When the body becomes warm, sudoriferous glands produce sweat to cool the body. Sweat glands develop from epidermal projections into the dermis and are classified as merocrine glands; that is, the secretions are excreted by exocytosis through a duct without affecting the cells of the gland. There are two types of sweat glands, each secreting slightly different products.
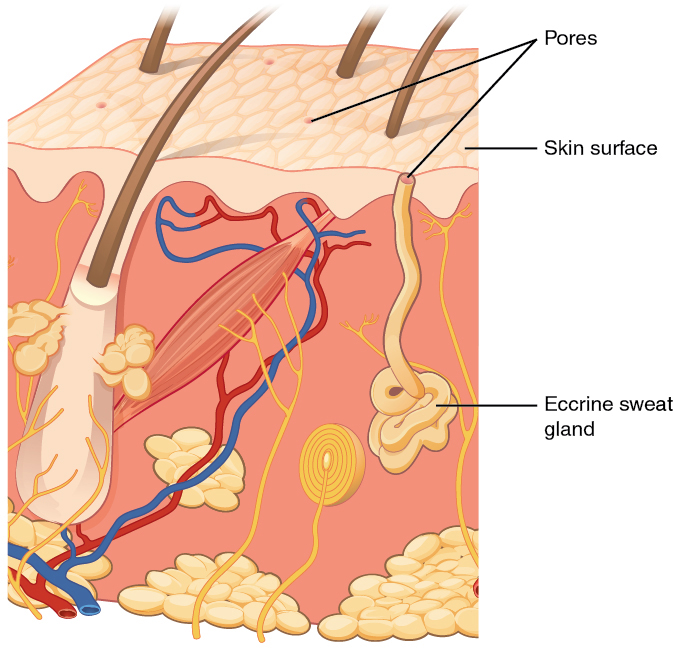
Figure 1. Eccrine glands are coiled glands in the dermis that release sweat that is mostly water.
An eccrine sweat gland is type of gland that produces a hypotonic sweat for thermoregulation. These glands are found all over the skin’s surface, but are especially abundant on the palms of the hand, the soles of the feet, and the forehead (Figure 1). They are coiled glands lying deep in the dermis, with the duct rising up to a pore on the skin surface, where the sweat is released. This type of sweat, released by exocytosis, is hypotonic and composed mostly of water, with some salt, antibodies, traces of metabolic waste, and dermicidin, an antimicrobial peptide. Eccrine glands are a primary component of thermoregulation in humans and thus help to maintain homeostasis.
An apocrine sweat gland is usually associated with hair follicles in densely hairy areas, such as armpits and genital regions. Apocrine sweat glands are larger than eccrine sweat glands and lie deeper in the dermis, sometimes even reaching the hypodermis, with the duct normally emptying into the hair follicle. In addition to water and salts, apocrine sweat includes organic compounds that make the sweat thicker and subject to bacterial decomposition and subsequent smell. The release of this sweat is under both nervous and hormonal control, and plays a role in the poorly understood human pheromone response. Most commercial antiperspirants use an aluminum-based compound as their primary active ingredient to stop sweat. When the antiperspirant enters the sweat gland duct, the aluminum-based compounds precipitate due to a change in pH and form a physical block in the duct, which prevents sweat from coming out of the pore.
Practice Question
Explain the differences between eccrine and apocrine sweat glands.
Sebaceous Glands
A sebaceous gland is a type of oil gland that is found all over the body and helps to lubricate and waterproof the skin and hair. Most sebaceous glands are associated with hair follicles. They generate and excrete sebum, a mixture of lipids, onto the skin surface, thereby naturally lubricating the dry and dead layer of keratinized cells of the stratum corneum, keeping it pliable. The fatty acids of sebum also have antibacterial properties, and prevent water loss from the skin in low-humidity environments. The secretion of sebum is stimulated by hormones, many of which do not become active until puberty. Thus, sebaceous glands are relatively inactive during childhood.
Try It
Candela Citations
- Anatomy & Physiology. Provided by: OpenStax. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/14fb4ad7-39a1-4eee-ab6e-3ef2482e3e22@8.79. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/14fb4ad7-39a1-4eee-ab6e-3ef2482e3e22@8.79
