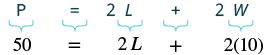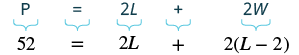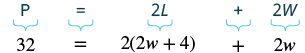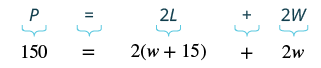Learning Outcomes
- Use properties of rectangles
A rectangle has four sides and four right angles. The opposite sides of a rectangle are the same length. We refer to one side of the rectangle as the length, [latex]L[/latex], and the adjacent side as the width, [latex]W[/latex]. See the image below.
A rectangle has four sides, and four right angles. The sides are labeled L for length and W for width.
![A rectangle is shown. Each angle is marked with a square. The top and bottom are labeled [latex]L[/latex], the sides are labeled [latex]W[/latex].](https://s3-us-west-2.amazonaws.com/courses-images/wp-content/uploads/sites/277/2017/04/24223837/CNX_BMath_Figure_09_04_012.png)
The perimeter, [latex]P[/latex], of the rectangle is the distance around the rectangle. If you started at one corner and walked around the rectangle, you would walk [latex]L+W+L+W[/latex] units, or two lengths and two widths. The perimeter then is
[latex]\begin{array}{c}P=L+W+L+W\hfill \\ \hfill \text{or}\hfill \\ P=2L+2W\hfill \end{array}[/latex]
What about the area of a rectangle? Remember the rectangular rug from the beginning of this section. It was [latex]2[/latex] feet long by [latex]3[/latex] feet wide, and its area was [latex]6[/latex] square feet. See the image below. Since [latex]A=2\cdot 3[/latex], we see that the area, [latex]A[/latex], is the length, [latex]L[/latex], times the width, [latex]W[/latex], so the area of a rectangle is [latex]A=L\cdot W[/latex].
The area of this rectangular rug is [latex]6[/latex] square feet, its length times its width.

Properties of Rectangles
- Rectangles have four sides and four right [latex]\left(\text{90}^ \circ\right)[/latex] angles.
- The lengths of opposite sides are equal.
- The perimeter, [latex]P[/latex], of a rectangle is the sum of twice the length and twice the width. See the first image. [latex]P=2L+2W[/latex]
- The area, [latex]A[/latex], of a rectangle is the length times the width. [latex]A=L\cdot W[/latex]
For easy reference as we work the examples in this section, we will restate the Problem Solving Strategy for Geometry Applications here.
Use a Problem Solving Strategy for Geometry Applications
- Read the problem and make sure you understand all the words and ideas. Draw the figure and label it with the given information.
- Identify what you are looking for.
- Name what you are looking for. Choose a variable to represent that quantity.
- Translate into an equation by writing the appropriate formula or model for the situation. Substitute in the given information.
- Solve the equation using good algebra techniques.
- Check the answer in the problem and make sure it makes sense.
- Answer the question with a complete sentence.
example
The length of a rectangle is [latex]32[/latex] meters and the width is [latex]20[/latex] meters.
1. Find the perimeter
2. Find the area
Solution
| 1. | |
| Step 1. Read the problem. Draw the figure and label it with the given information. |  |
| Step 2. Identify what you are looking for. | the perimeter of a rectangle |
| Step 3. Name. Choose a variable to represent it. | Let [latex]P[/latex] = the perimeter |
| Step 4. Translate.
Write the appropriate formula. Substitute. |
 |
| Step 5. Solve the equation. | [latex]P=64m+40m[/latex]
[latex]P=104m[/latex] |
| Step 6. Check:
[latex]p\stackrel{?}{=}104m[/latex] [latex]20m+32m+20m+32m\stackrel{?}{=}104m[/latex] [latex]104m=104m\checkmark[/latex] |
|
| Step 7. Answer the question. | The perimeter of the rectangle is [latex]104[/latex] meters. |
| 2. | |
| Step 1. Read the problem. Draw the figure and label it with the given information. |  |
| Step 2. Identify what you are looking for. | the area of a rectangle |
| Step 3. Name. Choose a variable to represent it. | Let A = the area |
| Step 4. Translate.
Write the appropriate formula. Substitute. |
 |
| Step 5. Solve the equation. | [latex]A=640m^2[/latex] |
| Step 6. Check:
[latex]A\stackrel{?}{=}640m^2[/latex] [latex]32m\cdot 20m\stackrel{?}{=}640m^2[/latex] [latex]640m^2=640m^2\checkmark[/latex] |
|
| Step 7. Answer the question. | The area of the rectangle is [latex]640[/latex] square meters. |
try it
example
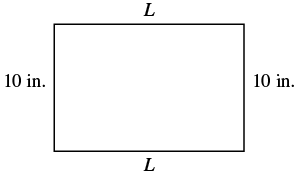
Find the length of a rectangle with perimeter [latex]50[/latex] inches and width [latex]10[/latex] inches.
try it
In the next example, the width is defined in terms of the length. We’ll wait to draw the figure until we write an expression for the width so that we can label one side with that expression.
example
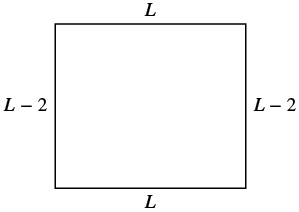
The width of a rectangle is two inches less than the length. The perimeter is [latex]52[/latex] inches. Find the length and width.
try it
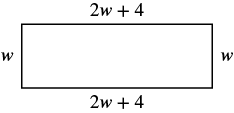
example
The length of a rectangle is four centimeters more than twice the width. The perimeter is [latex]32[/latex] centimeters. Find the length and width.
try it
Watch this video to see another similar example of finding area given the relationship between the length and width of a rectangle.
example
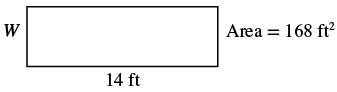
The area of a rectangular room is [latex]168[/latex] square feet. The length is [latex]14[/latex] feet. What is the width?
try it
In the next example you will see a similar application involving perimeter, length, and width.
example
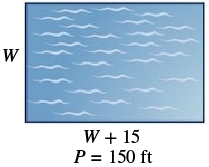
The perimeter of a rectangular swimming pool is [latex]150[/latex] feet. The length is [latex]15[/latex] feet more than the width. Find the length and width.
try it
Candela Citations
- Question ID 146524, 146522, 146518, 146504. Authored by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Ex: Find the Area of a Rectangle Given the Perimeter. Authored by: James Sousa (amthispower4u.com). Located at: https://youtu.be/zUlU64Umnq4. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Find the Width of a Rectangle Given the Perimeter / Literal Equation. Authored by: James Sousa (mathispower4u.com). Located at: https://youtu.be/jlxPgKQfhQs. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Prealgebra. Provided by: OpenStax. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/caa57dab-41c7-455e-bd6f-f443cda5519c@9.757