Learning Outcomes
- Define the different layers of protein structure
As discussed earlier, the shape of a protein is critical to its function. To understand how the protein gets its final shape or conformation, we need to understand the four levels of protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary (Figure 2).
The unique sequence and number of amino acids in a polypeptide chain is its primary structure. The unique sequence for every protein is ultimately determined by the gene that encodes the protein. Any change in the gene sequence may lead to a different amino acid being added to the polypeptide chain, causing a change in protein structure and function. In sickle cell anemia, the hemoglobin β chain has a single amino acid substitution, causing a change in both the structure and function of the protein. What is most remarkable to consider is that a hemoglobin molecule is made up of two alpha chains and two beta chains that each consist of about 150 amino acids. The molecule, therefore, has about 600 amino acids. The structural difference between a normal hemoglobin molecule and a sickle cell molecule—that dramatically decreases life expectancy—is a single amino acid of the 600.
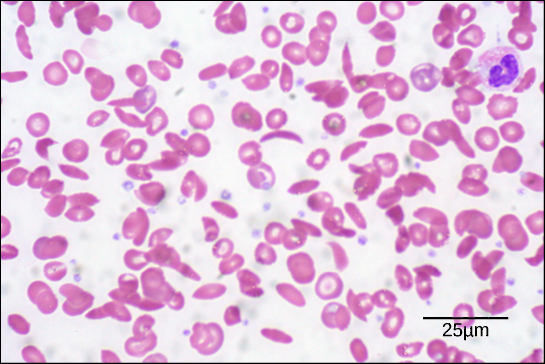
Figure 1. In this blood smear, visualized at 535x magnification using bright field microscopy, sickle cells are crescent shaped, while normal cells are disc-shaped. (credit: modification of work by Ed Uthman; scale-bar data from Matt Russell)
Because of this change of one amino acid in the chain, the normally biconcave, or disc-shaped, red blood cells assume a crescent or “sickle” shape, which clogs arteries. This can lead to a myriad of serious health problems, such as breathlessness, dizziness, headaches, and abdominal pain for those who have this disease.
Folding patterns resulting from interactions between the non-R group portions of amino acids give rise to the secondary structure of the protein. The most common are the alpha (α)-helix and beta (β)-pleated sheet structures. Both structures are held in shape by hydrogen bonds. In the alpha helix, the bonds form between every fourth amino acid and cause a twist in the amino acid chain.
In the β-pleated sheet, the “pleats” are formed by hydrogen bonding between atoms on the backbone of the polypeptide chain. The R groups are attached to the carbons, and extend above and below the folds of the pleat. The pleated segments align parallel to each other, and hydrogen bonds form between the same pairs of atoms on each of the aligned amino acids. The α-helix and β-pleated sheet structures are found in many globular and fibrous proteins.
The unique three-dimensional structure of a polypeptide is known as its tertiary structure. This structure is caused by chemical interactions between various amino acids and regions of the polypeptide. Primarily, the interactions among R groups create the complex three-dimensional tertiary structure of a protein. There may be ionic bonds formed between R groups on different amino acids, or hydrogen bonding beyond that involved in the secondary structure. When protein folding takes place, the hydrophobic R groups of nonpolar amino acids lay in the interior of the protein, whereas the hydrophilic R groups lay on the outside. The former types of interactions are also known as hydrophobic interactions.
In nature, some proteins are formed from several polypeptides, also known as subunits, and the interaction of these subunits forms the quaternary structure. Weak interactions between the subunits help to stabilize the overall structure. For example, hemoglobin is a combination of four polypeptide subunits.
Each protein has its own unique sequence and shape held together by chemical interactions. If the protein is subject to changes in temperature, pH, or exposure to chemicals, the protein structure may change, losing its shape in what is known as denaturation as discussed earlier. Denaturation is often reversible because the primary structure is preserved if the denaturing agent is removed, allowing the protein to resume its function. Sometimes denaturation is irreversible, leading to a loss of function. One example of protein denaturation can be seen when an egg is fried or boiled. The albumin protein in the liquid egg white is denatured when placed in a hot pan, changing from a clear substance to an opaque white substance. Not all proteins are denatured at high temperatures; for instance, bacteria that survive in hot springs have proteins that are adapted to function at those temperatures.
The four levels of protein structure (primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary) are illustrated in Figure 2.
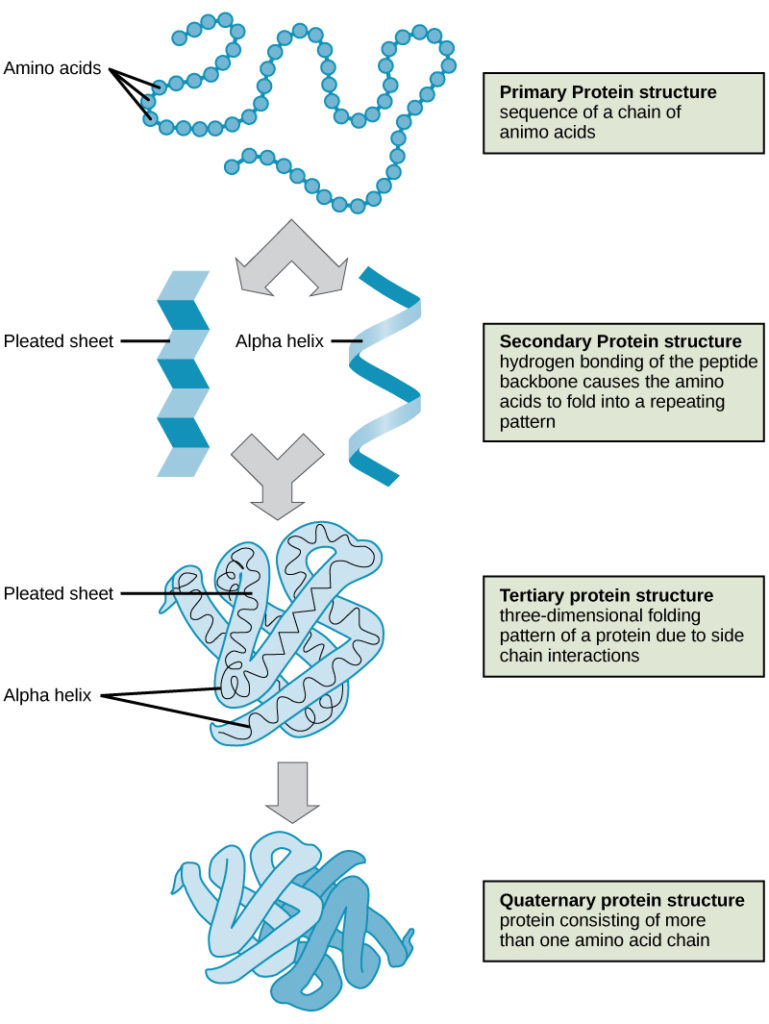
Figure 2. The four levels of protein structure can be observed in these illustrations. (credit: modification of work by National Human Genome Research Institute)
Try It
