Express the rational function as a sum or difference of two simpler rational expressions.
1. [latex]\frac{1}{\left(x - 3\right)\left(x - 2\right)}[/latex]
2. [latex]\frac{{x}^{2}+1}{x\left(x+1\right)\left(x+2\right)}[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]-\frac{2}{x+1}+\frac{5}{2\left(x+2\right)}+\frac{1}{2x}[/latex]
3. [latex]\frac{1}{{x}^{3}-x}[/latex]
4. [latex]\frac{3x+1}{{x}^{2}}[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\frac{1}{{x}^{2}}+\frac{3}{x}[/latex]
5. [latex]\frac{3{x}^{2}}{{x}^{2}+1}[/latex] (Hint: Use long division first.)
6. [latex]\frac{2{x}^{4}}{{x}^{2}-2x}[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]2{x}^{2}+4x+8+\frac{16}{x - 2}[/latex]
7. [latex]\frac{1}{\left(x - 1\right)\left({x}^{2}+1\right)}[/latex]
8. [latex]\frac{1}{{x}^{2}\left(x - 1\right)}[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]-\frac{1}{{x}^{2}}-\frac{1}{x}+\frac{1}{x - 1}[/latex]
9. [latex]\frac{x}{{x}^{2}-4}[/latex]
10. [latex]\frac{1}{x\left(x - 1\right)\left(x - 2\right)\left(x - 3\right)}[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]-\frac{1}{2\left(x - 2\right)}+\frac{1}{2\left(x - 1\right)}-\frac{1}{6x}+\frac{1}{6\left(x - 3\right)}[/latex]
11. [latex]\frac{1}{{x}^{4}-1}=\frac{1}{\left(x+1\right)\left(x - 1\right)\left({x}^{2}+1\right)}[/latex]
12. [latex]\frac{3{x}^{2}}{{x}^{3}-1}=\frac{3{x}^{2}}{\left(x - 1\right)\left({x}^{2}+x+1\right)}[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\frac{1}{x - 1}+\frac{2x+1}{{x}^{2}+x+1}[/latex]
13. [latex]\frac{2x}{{\left(x+2\right)}^{2}}[/latex]
14. [latex]\frac{3{x}^{4}+{x}^{3}+20{x}^{2}+3x+31}{\left(x+1\right){\left({x}^{2}+4\right)}^{2}}[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\frac{2}{x+1}+\frac{x}{{x}^{2}+4}-\frac{1}{{\left({x}^{2}+4\right)}^{2}}[/latex]
Use the method of partial fractions to evaluate each of the following integrals.
15. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{dx}{\left(x - 3\right)\left(x - 2\right)}[/latex]
16. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{3x}{{x}^{2}+2x - 8}dx[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\text{-}\text{ln}|2-x|+2\text{ln}|4+x|+C[/latex]
17. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{dx}{{x}^{3}-x}[/latex]
18. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{x}{{x}^{2}-4}dx[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\frac{1}{2}\text{ln}|4-{x}^{2}|+C[/latex]
19. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{dx}{x\left(x - 1\right)\left(x - 2\right)\left(x - 3\right)}[/latex]
20. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{2{x}^{2}+4x+22}{{x}^{2}+2x+10}dx[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]2\left(x+\frac{1}{3}\text{arctan}\left(\frac{1+x}{3}\right)\right)+C[/latex]
21. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{dx}{{x}^{2}-5x+6}[/latex]
22. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{2-x}{{x}^{2}+x}dx[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]2\text{ln}|x|-3\text{ln}|1+x|+C[/latex]
23. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{2}{{x}^{2}-x - 6}dx[/latex]
24. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{dx}{{x}^{3}-2{x}^{2}-4x+8}[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\frac{1}{16}\left(\text{-}\frac{4}{-2+x}-\text{ln}|-2+x|+\text{ln}|2+x|\right)+C[/latex]
25. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{dx}{{x}^{4}-10{x}^{2}+9}[/latex]
Evaluate the following integrals, which have irreducible quadratic factors.
26. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{2}{\left(x - 4\right)\left({x}^{2}+2x+6\right)}dx[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\frac{1}{30}\left(-2\sqrt{5}\text{arctan}\left[\frac{1+x}{\sqrt{5}}\right]+2\text{ln}|-4+x|-\text{ln}|6+2x+{x}^{2}|\right)+C[/latex]
27. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{{x}^{2}}{{x}^{3}-{x}^{2}+4x - 4}dx[/latex]
28. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{{x}^{3}+6{x}^{2}+3x+6}{{x}^{3}+2{x}^{2}}dx[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]-\frac{3}{x}+4\text{ln}|x+2|+x+C[/latex]
29. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{x}{\left(x - 1\right){\left({x}^{2}+2x+2\right)}^{2}}dx[/latex]
Use the method of partial fractions to evaluate the following integrals.
30. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{3x+4}{\left({x}^{2}+4\right)\left(3-x\right)}dx[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\text{-}\text{ln}|3-x|+\frac{1}{2}\text{ln}|{x}^{2}+4|+C[/latex]
31. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{2}{{\left(x+2\right)}^{2}\left(2-x\right)}dx[/latex]
32. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{3x+4}{{x}^{3}-2x - 4}dx[/latex] (Hint: Use the rational root theorem.)
Show Solution
[latex]\text{ln}|x - 2|-\frac{1}{2}\text{ln}|{x}^{2}+2x+2|+C[/latex]
Use substitution to convert the integrals to integrals of rational functions. Then use partial fractions to evaluate the integrals.
33. [latex]{\displaystyle\int }_{0}^{1}\frac{{e}^{x}}{36-{e}^{2x}}dx[/latex] (Give the exact answer and the decimal equivalent. Round to five decimal places.)
34. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{{e}^{x}dx}{{e}^{2x}-{e}^{x}}dx[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\text{-}x+\text{ln}|1-{e}^{x}|+C[/latex]
35. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{\sin{x}dx}{1-{\cos}^{2}x}[/latex]
36. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{\sin{x}}{{\cos}^{2}x+\cos{x} - 6}dx[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\frac{1}{5}\text{ln}|\frac{\cos{x}+3}{\cos{x} - 2}|+C[/latex]
37. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{1-\sqrt{x}}{1+\sqrt{x}}dx[/latex]
38. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{dt}{{\left({e}^{t}-{e}^{\text{-}t}\right)}^{2}}[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\frac{1}{2 - 2{e}^{2t}}+C[/latex]
39. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{1+{e}^{x}}{1-{e}^{x}}dx[/latex]
40. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{dx}{1+\sqrt{x+1}}[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]2\sqrt{1+x}-2\text{ln}|1+\sqrt{1+x}|+C[/latex]
41. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{dx}{\sqrt{x}+\sqrt[4]{x}}[/latex]
42. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{\cos{x}}{\sin{x}\left(1-\sin{x}\right)}dx[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\text{ln}|\frac{\sin{x}}{1-\sin{x}}|+C[/latex]
43. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{{e}^{x}}{{\left({e}^{2x}-4\right)}^{2}}dx[/latex]
44. [latex]\underset{1}{\overset{2}{\displaystyle\int }}\frac{1}{{x}^{2}\sqrt{4-{x}^{2}}}dx[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]\frac{\sqrt{3}}{4}[/latex]
45. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{1}{2+{e}^{\text{-}x}}dx[/latex]
46. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{1}{1+{e}^{x}}dx[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]x-\text{ln}\left(1+{e}^{x}\right)+C[/latex]
Use the given substitution to convert the integral to an integral of a rational function, then evaluate.
47. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{1}{t-\sqrt[3]{t}}dtt={x}^{3}[/latex]
48. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{1}{\sqrt{x}+\sqrt[3]{x}}dx;x={u}^{6}[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]6{x}^{\frac{1}{6}}-3{x}^{\frac{1}{3}}+2\sqrt{x}-6\text{ln}\left(1+{x}^{\frac{1}{6}}\right)+C[/latex]
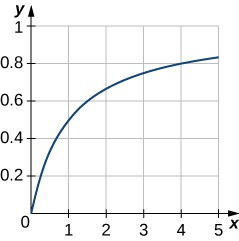
49. Graph the curve [latex]y=\frac{x}{1+x}[/latex] over the interval [latex]\left[0,5\right][/latex]. Then, find the area of the region bounded by the curve, the x-axis, and the line [latex]x=4[/latex].
50. Find the volume of the solid generated when the region bounded by [latex]y=\frac{1}{\sqrt{x\left(3-x\right)}}[/latex], [latex]y=0[/latex], [latex]x=1[/latex], and [latex]x=2[/latex] is revolved about the x-axis.
Show Solution
[latex]\frac{4}{3}\pi \text{arctanh}\left[\frac{1}{3}\right]=\frac{1}{3}\pi \text{ln}4[/latex]
51. The velocity of a particle moving along a line is a function of time given by [latex]v\left(t\right)=\frac{88{t}^{2}}{{t}^{2}+1}[/latex]. Find the distance that the particle has traveled after [latex]t=5[/latex] sec.
Solve the initial-value problem for x as a function of t.
52. [latex]\left({t}^{2}-7t+12\right)\frac{dx}{dt}=1,\left(t>4,x\left(5\right)=0\right)[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]x=\text{-}\text{ln}|t - 3|+\text{ln}|t - 4|+\text{ln}2[/latex]
53. [latex]\left(t+5\right)\frac{dx}{dt}={x}^{2}+1,t>\text{-}5,x\left(1\right)=\tan1[/latex]
54. [latex]\left(2{t}^{3}-2{t}^{2}+t - 1\right)\frac{dx}{dt}=3,x\left(2\right)=0[/latex]
Show Solution
[latex]x=\text{ln}|t - 1|-\sqrt{2}\text{arctan}\left(\sqrt{2}t\right)-\frac{1}{2}\text{ln}\left({t}^{2}+\frac{1}{2}\right)+\sqrt{2}\text{arctan}\left(2\sqrt{2}\right)+\frac{1}{2}\text{ln}4.5[/latex]
55. Find the x-coordinate of the centroid of the area bounded by [latex]y\left({x}^{2}-9\right)=1[/latex], [latex]y=0,x=4,\text{and }x=5[/latex]. (Round the answer to two decimal places.)
56. Find the volume generated by revolving the area bounded by [latex]y=\frac{1}{{x}^{3}+7{x}^{2}+6x}x=1,x=7,\text{and }y=0[/latex] about the y-axis.
Show Solution
[latex]\frac{2}{5}\pi \text{ln}\frac{28}{13}[/latex]
57. Find the area bounded by [latex]y=\frac{x - 12}{{x}^{2}-8x - 20}[/latex], [latex]y=0,x=2,\text{and }x=4[/latex]. (Round the answer to the nearest hundredth.)
58. Evaluate the integral [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{dx}{{x}^{3}+1}[/latex].
Show Solution
[latex]\frac{\text{arctan}\left[\frac{-1+2x}{\sqrt{3}}\right]}{\sqrt{3}}+\frac{1}{3}\text{ln}|1+x|-\frac{1}{6}\text{ln}|1-x+{x}^{2}|+C[/latex]
For the following problems, use the substitutions [latex]\tan\left(\frac{x}{2}\right)=t[/latex], [latex]dx=\frac{2}{1+{t}^{2}}dt[/latex], [latex]\sin{x}=\frac{2t}{1+{t}^{2}}[/latex], and [latex]\cos{x}=\frac{1-{t}^{2}}{1+{t}^{2}}[/latex].
59. [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{dx}{3 - 5\sin{x}}[/latex]
60. Find the area under the curve [latex]y=\frac{1}{1+\sin{x}}[/latex] between [latex]x=0[/latex] and [latex]x=\pi[/latex]. (Assume the dimensions are in inches.)
61. Given [latex]\tan\left(\frac{x}{2}\right)=t[/latex], derive the formulas [latex]dx=\frac{2}{1+{t}^{2}}dt[/latex], [latex]\sin{x}=\frac{2t}{1+{t}^{2}}[/latex], and [latex]\cos{x}=\frac{1-{t}^{2}}{1+{t}^{2}}[/latex].
62. Evaluate [latex]\displaystyle\int \frac{\sqrt[3]{x - 8}}{x}dx[/latex].
Show Solution
[latex]3{\left(-8+x\right)}^{\frac{1}{3}}[/latex] [latex]-2\sqrt{3}\text{arctan}\left[\frac{-1+{\left(-8+x\right)}^{\frac{1}{3}}}{\sqrt{3}}\right][/latex] [latex]-2\text{ln}\left[2+{\left(-8+x\right)}^{\frac{1}{3}}\right][/latex] [latex]+\text{ln}\left[4 - 2{\left(-8+x\right)}^{\frac{1}{3}}+{\left(-8+x\right)}^{\frac{2}{3}}\right]+C[/latex]
Candela Citations
CC licensed content, Shared previously

