Genes specify functional products (such as proteins)
A DNA molecule is divided up into functional units called genes. Each gene provides instructions for a functional product, that is, a molecule needed to perform a job in the cell. In many cases, the functional product of a gene is a protein. For example, Mendel’s flower color gene provides instructions for a protein that helps make colored molecules (pigments) in flower petals.
The functional products of most known genes are proteins, or, more accurately, polypeptides. Polypeptide is just another word for a chain of amino acids. Although many proteins consist of a single polypeptide, some are made up of multiple polypeptides. Genes that specify polypeptides are called protein-coding genes. Not all genes specify polypeptides. Instead, some provide instructions to build functional RNA molecules, such as the transfer RNAs and ribosomal RNAs that play roles in translation.
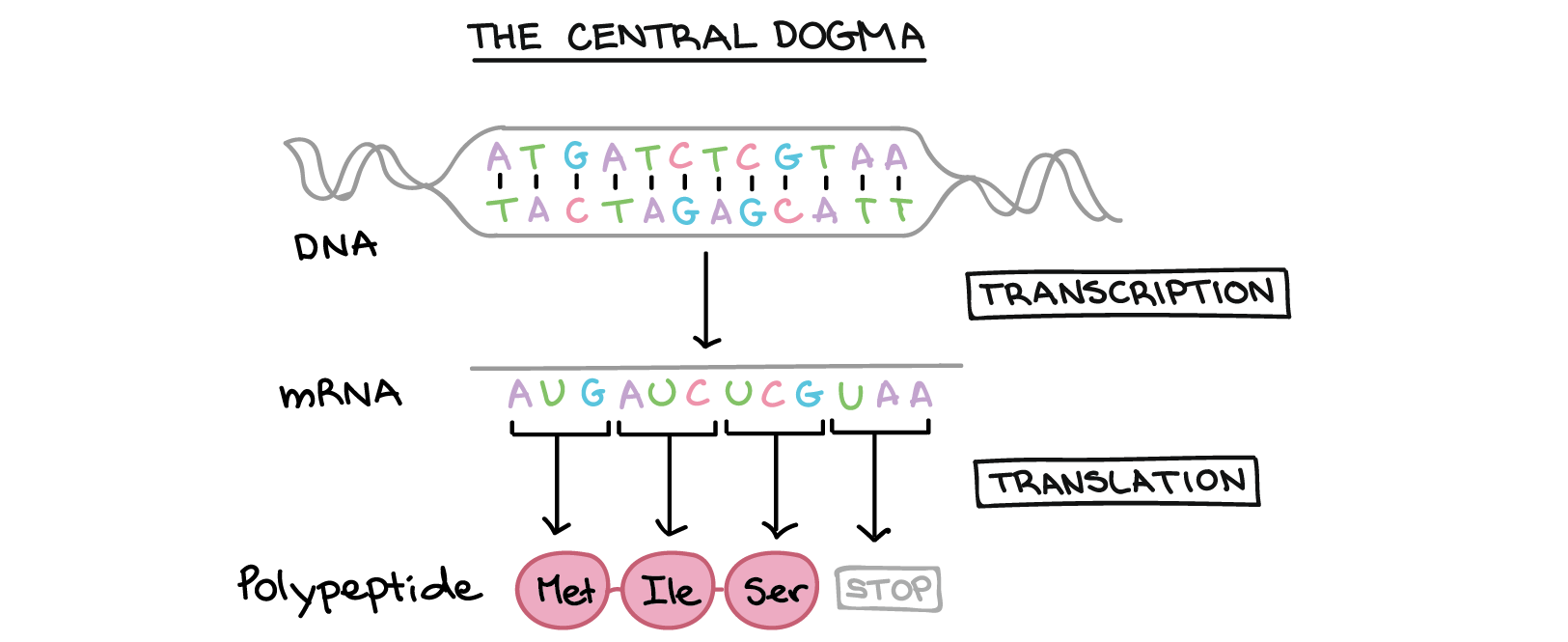
Many genes provide instructions for building polypeptides. How, exactly, does DNA direct the construction of a polypeptide? This process involves two major steps: transcription and translation.
- In transcription, the DNA sequence of a gene is copied to make an RNA molecule. This step is called transcription because it involves rewriting, or transcribing, the DNA sequence in a similar RNA “alphabet.” In eukaryotes, the RNA molecule must undergo processing to become a mature messenger RNA (mRNA).
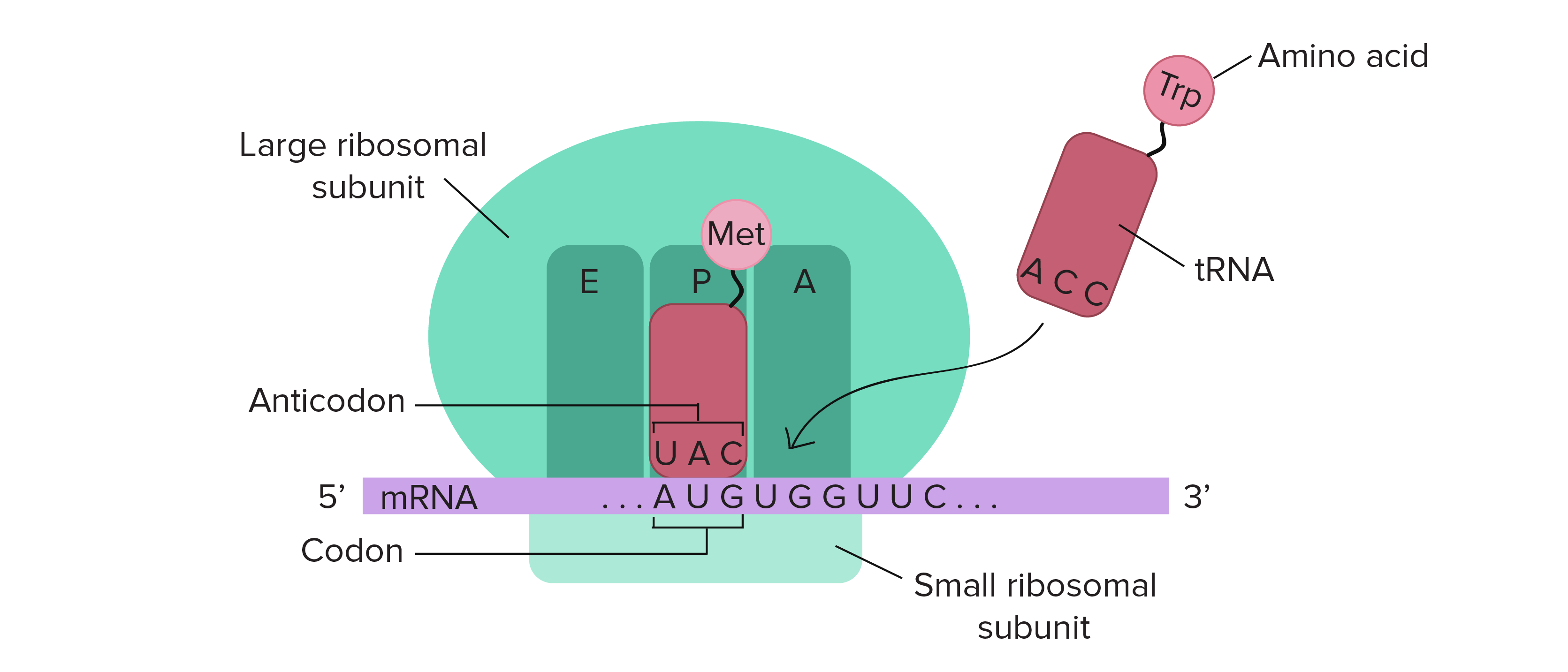
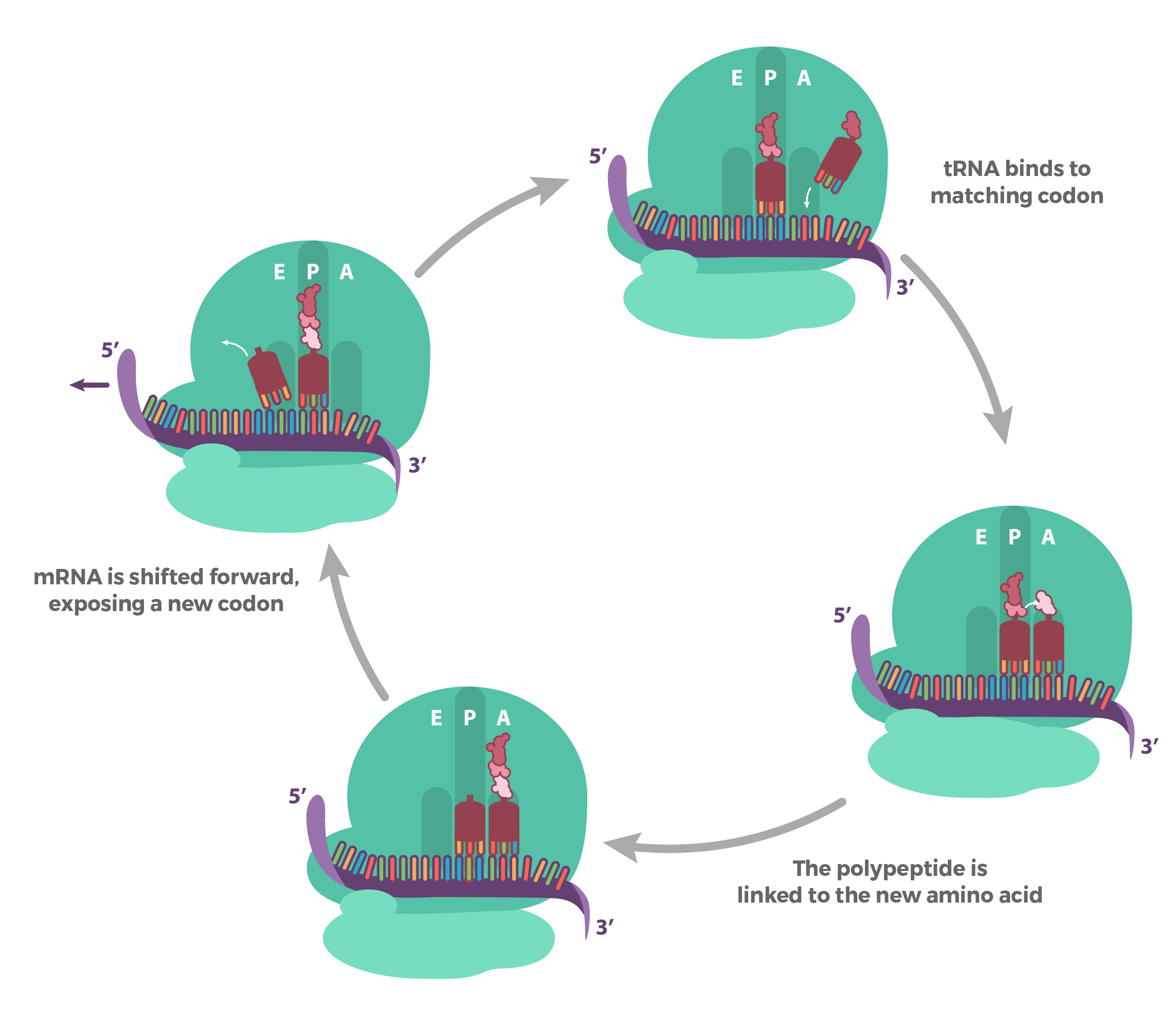
- In translation, the sequence of the mRNA is decoded to specify the amino acid sequence of a polypeptide. The name translation reflects that the nucleotide sequence of the mRNA sequence must be translated into the completely different “language” of amino acids.
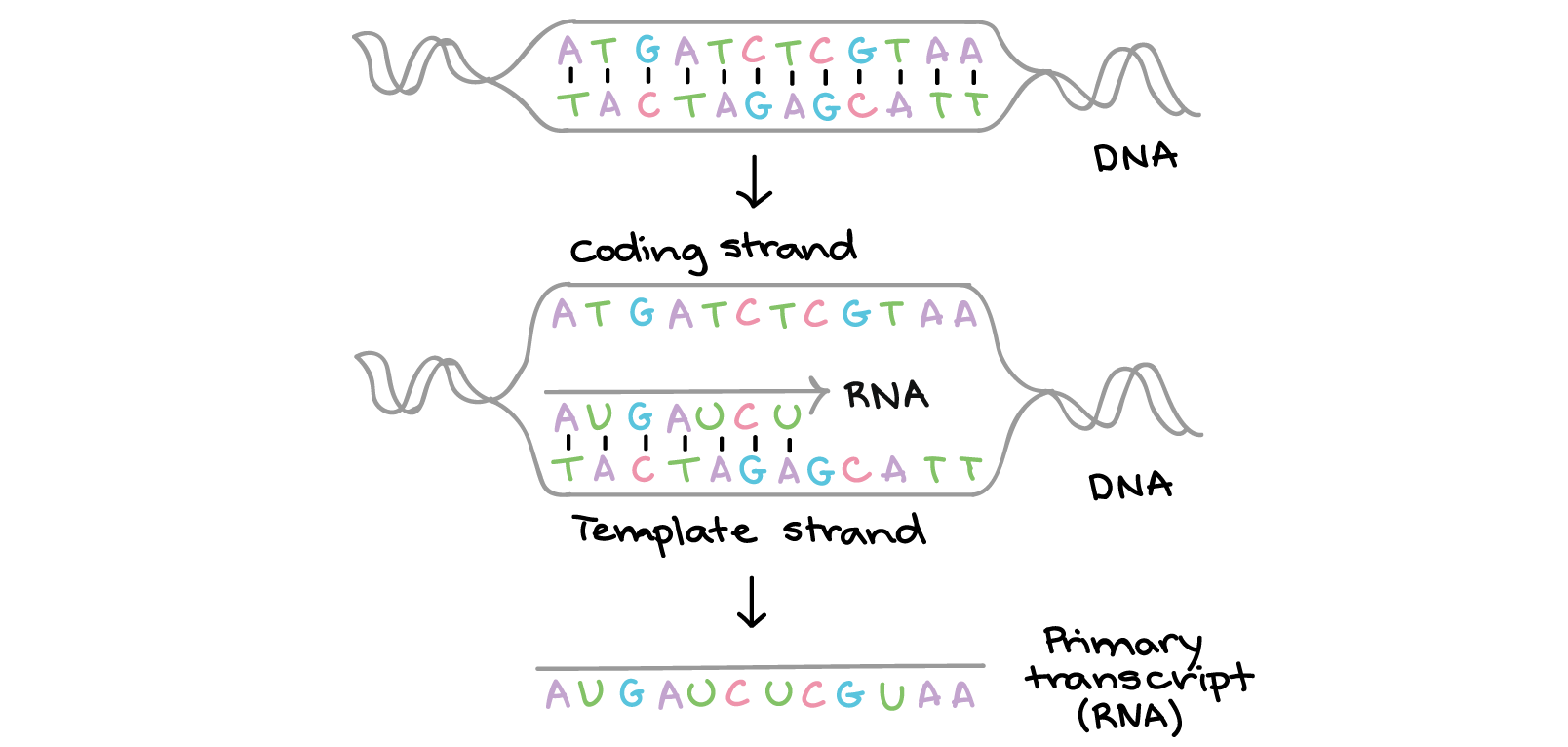
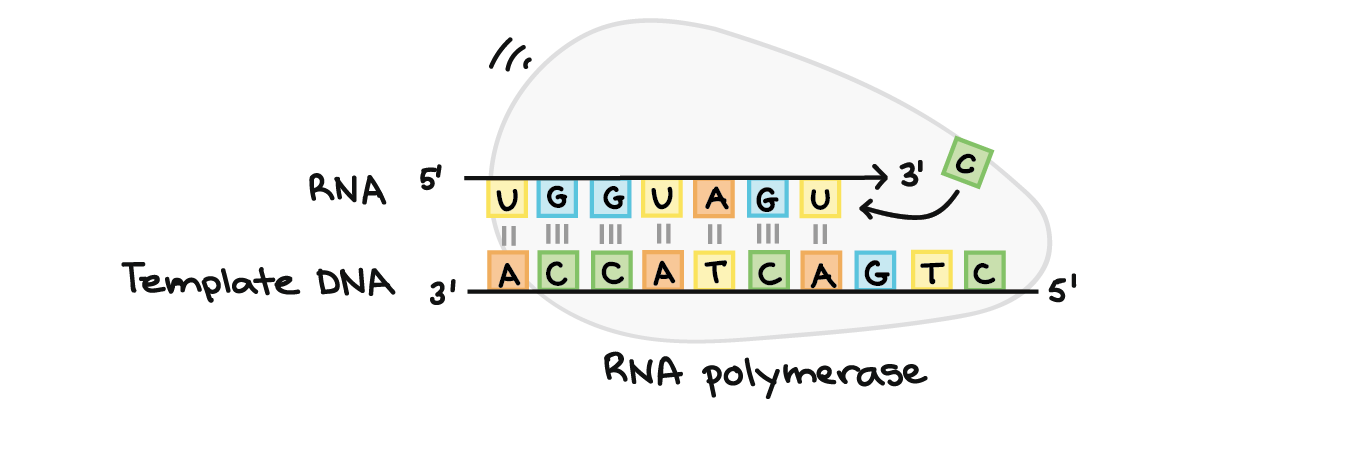
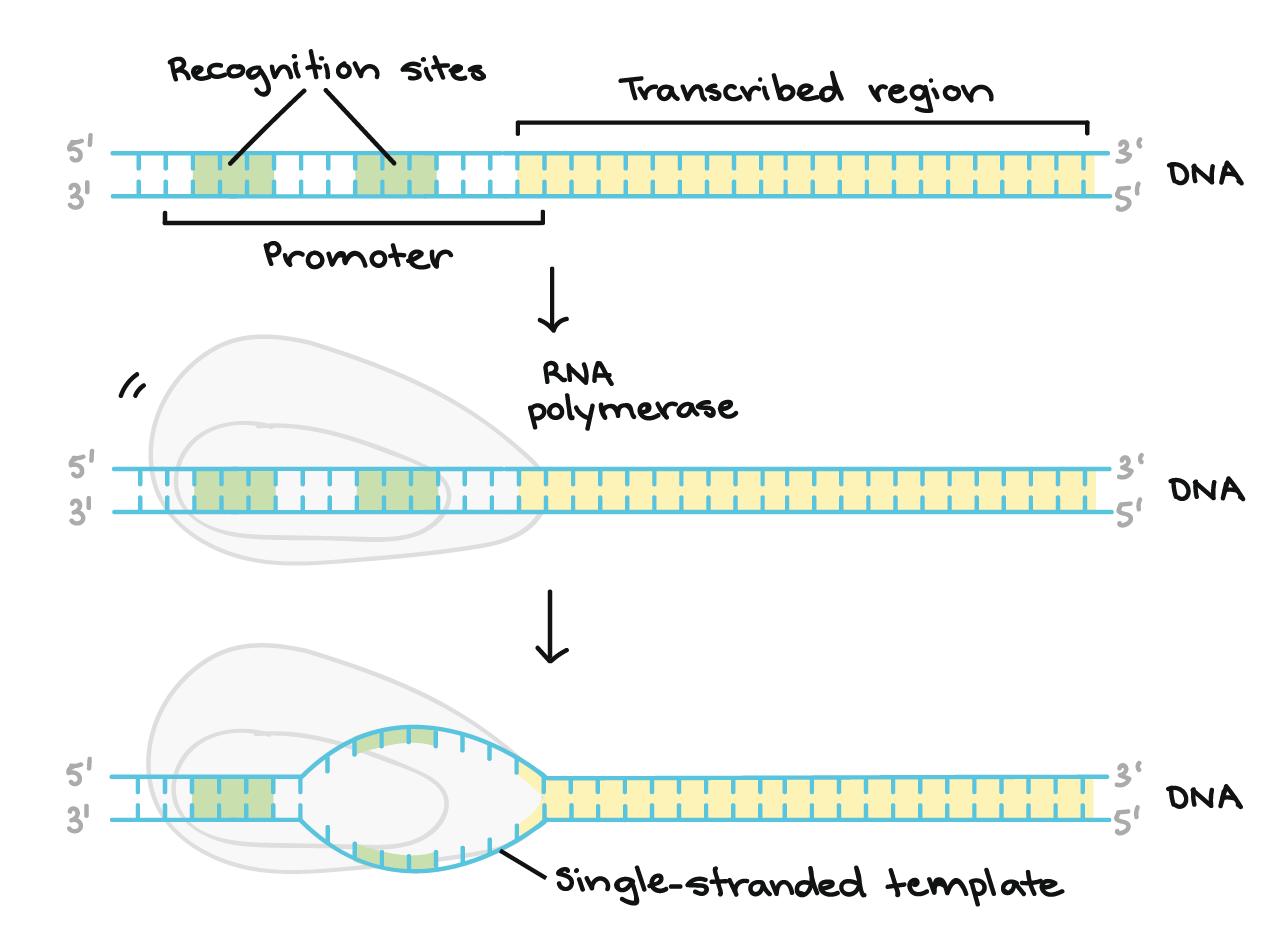
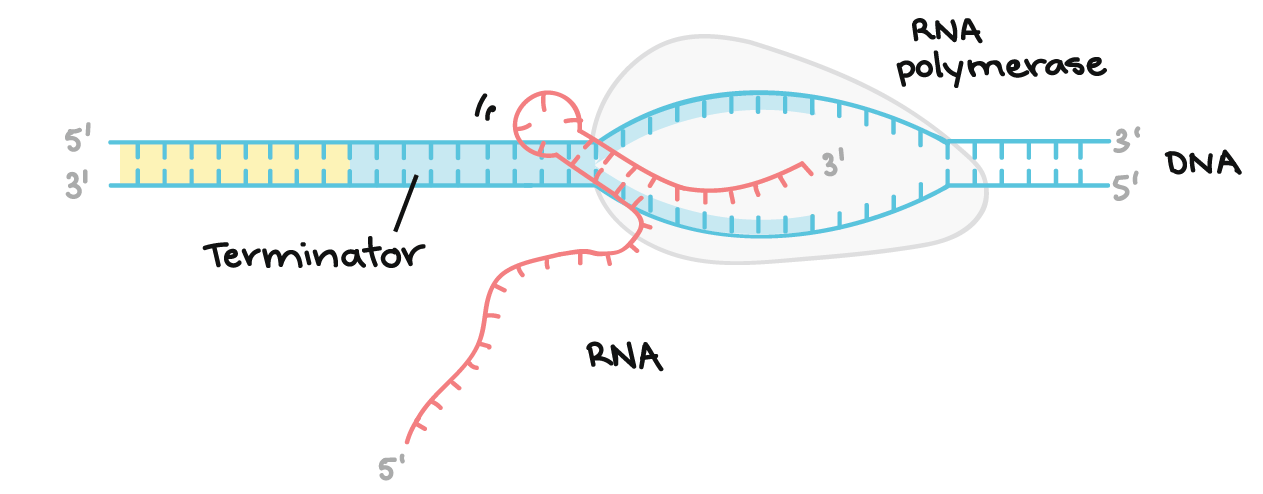
In transcription, one strand of the DNA that makes up a gene, called the non-coding strand, acts as a template for the synthesis of a matching (complementary) RNA strand by an enzyme called RNA polymerase. This RNA strand is the primary transcript.
Candela Citations
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- Provided by: Khan Academy. Located at: https://www.khanacademy.org/science/biology/gene-expression-central-dogma/translation-polypeptides/a/translation-overview. License: CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike