The peripheral nervous system (PNS) is the connection between the central nervous system and the rest of the body. The CNS is like the power plant of the nervous system. It creates the signals that control the functions of the body. The PNS is like the wires that go to individual houses. Without those “wires,” the signals produced by the CNS could not control the body (and the CNS would not be able to receive sensory information from the body either).
The PNS can be broken down into the autonomic nervous system, which controls bodily functions without conscious control, and the sensory-somatic nervous system, which transmits sensory information from the skin, muscles, and sensory organs to the CNS and sends motor commands from the CNS to the skeletal muscles.
Autonomic Nervous System
Art Connection
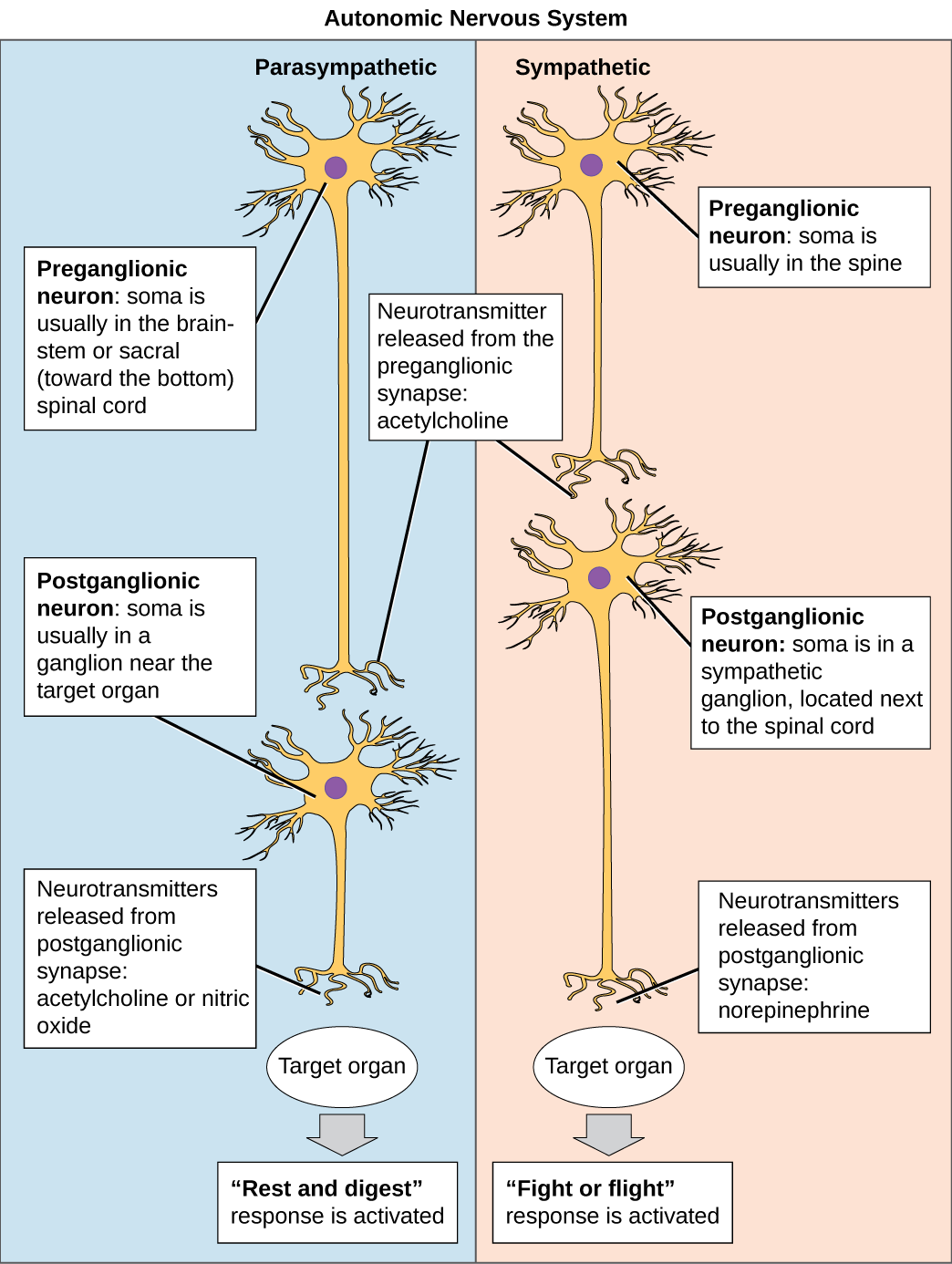
Figure 1. In the autonomic nervous system, a preganglionic neuron of the CNS synapses with a postganglionic neuron of the PNS. The postganglionic neuron, in turn, acts on a target organ. Autonomic responses are mediated by the sympathetic and the parasympathetic systems, which are antagonistic to one another. The sympathetic system activates the “fight or flight” response, while the parasympathetic system activates the “rest and digest” response.
The autonomic nervous system serves as the relay between the CNS and the internal organs. It controls the lungs, the heart, smooth muscle, and exocrine and endocrine glands. The autonomic nervous system controls these organs largely without conscious control; it can continuously monitor the conditions of these different systems and implement changes as needed. Signaling to the target tissue usually involves two synapses: a preganglionic neuron (originating in the CNS) synapses to a neuron in a ganglion that, in turn, synapses on the target organ, as illustrated in Figure 1. There are two divisions of the autonomic nervous system that often have opposing effects: the sympathetic nervous system and the parasympathetic nervous system.
Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system is responsible for the “fight or flight” response that occurs when an animal encounters a dangerous situation. One way to remember this is to think of the surprise a person feels when encountering a snake (“snake” and “sympathetic” both begin with “s”). Examples of functions controlled by the sympathetic nervous system include an accelerated heart rate and inhibited digestion. These functions help prepare an organism’s body for the physical strain required to escape a potentially dangerous situation or to fend off a predator.

Figure 2. The sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous systems often have opposing effects on target organs.
Most preganglionic neurons in the sympathetic nervous system originate in the spinal cord, as illustrated in Figure 2. The axons of these neurons release acetylcholine on postganglionic neurons within sympathetic ganglia (the sympathetic ganglia form a chain that extends alongside the spinal cord). The acetylcholine activates the postganglionic neurons. Postganglionic neurons then release norepinephrine onto target organs. As anyone who has ever felt a rush before a big test, speech, or athletic event can attest, the effects of the sympathetic nervous system are quite pervasive. This is both because one preganglionic neuron synapses on multiple postganglionic neurons, amplifying the effect of the original synapse, and because the adrenal gland also releases norepinephrine (and the closely related hormone epinephrine) into the bloodstream. The physiological effects of this norepinephrine release include dilating the trachea and bronchi (making it easier to breathe), increasing heart rate, and moving blood from the skin to the heart, muscles, and brain making it easier to process information and run). The strength and speed of the sympathetic response helps an organism avoid danger, and scientists have found evidence that it may also increase LTP—allowing the animal to remember the dangerous situation and avoid it in the future.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
While the sympathetic nervous system is activated in stressful situations, the parasympathetic nervous system allows an animal to “rest and digest.” One way to remember this is to think that during a restful situation like a picnic, the parasympathetic nervous system is in control (“picnic” and “parasympathetic” both start with “p”). Parasympathetic preganglionic neurons have cell bodies located in the brainstem and in the sacral (toward the bottom) spinal cord, as shown in Figure 2. The axons of the preganglionic neurons release acetylcholine on the postganglionic neurons, which are generally located very near the target organs. Most postganglionic neurons release acetylcholine onto target organs, although some release nitric oxide.
The parasympathetic nervous system resets organ function after the sympathetic nervous system is activated (the common adrenaline dump you feel after a ‘fight-or-flight’ event). Effects of acetylcholine release on target organs include slowing of the heart rate, lowered blood pressure, and stimulation of digestion.
Sensory-Somatic Nervous System
The sensory-somatic nervous system is made up of cranial and spinal nerves and contains both sensory and motor neurons. Sensory neurons transmit sensory information from the skin, skeletal muscle, and sensory organs to the CNS. Motor neurons transmit messages about desired movement from the CNS to the muscles to make them contract. Without its sensory-somatic nervous system, a person would be unable to process any information about their environment (what is seen, felt, heard, and so on) and could not control motor movements. Unlike the autonomic nervous system, which has two synapses between the CNS and the target organ, sensory and motor neurons have only one synapse—one ending of the neuron is at the organ and the other directly contacts a CNS neuron. Acetylcholine is the main neurotransmitter released at these synapses.
Humans have 12 cranial nerves, nerves that emerge from or enter the skull (cranium), as opposed to the spinal nerves, which emerge from the vertebral column. Each cranial nerve is accorded a name, which are detailed in Figure 3. Some cranial nerves transmit only sensory information. For example, the olfactory nerve transmits information about smells from the nose to the brainstem. Other cranial nerves transmit almost solely motor information. For example, the oculomotor nerve controls the opening and closing of the eyelid and some eye movements. Other cranial nerves contain a mix of sensory and motor fibers. For example, the glossopharyngeal nerve has a role in both taste (sensory) and swallowing (motor).

Figure 3. The human brain contains 12 cranial nerves that receive sensory input and control motor output for the head and neck.
Cranial nerves
- Olfactory: sensory for smell
- Optic: sensory, process visual information
- Oculomotor: motor, movement of eyes and smooth muscles controlling pupil and lens
- Trochlear: motor, eye movements
- Trigeminal: sensory of upper, and mid face and upper jaw; motor for muscles of chewing
- Abducens: motor, eye movements
- Facial: motor for facial expression, tears and salivary glands; sensory for taste
- Vestibulocochlear: sensory, hearing and equilibrium
- Glossopharyngeal: motor for mouth (swallowing) and for regulation of blood pressure; sensory for tongue and pharynx and outer ear
- Vagus: motor for swallowing, speech, cardivascular and digestive regulation; hunger and fullness; sensory from visceral organs and taste. Main parasympathetic nerve
- Accessory: swallowing, and head, neck, shoulder movement
- Hypoglossal: tongue movements
Spinal nerves transmit sensory and motor information between the spinal cord and the rest of the body. Each of the 31 spinal nerves contains both sensory and motor axons. The sensory neuron cell bodies are grouped in structures called dorsal root ganglia and are shown in Figure 4. Each sensory neuron has one projection—with a sensory receptor ending in skin, muscle, or sensory organs—and another that synapses with a neuron in the dorsal spinal cord. Motor neurons have cell bodies in the ventral gray matter of the spinal cord that project to muscle through the ventral root. These neurons are usually stimulated by interneurons within the spinal cord but are sometimes directly stimulated by sensory neurons.

Figure 4. Spinal nerves contain both sensory and motor axons. The somas of sensory neurons are located in dorsal root ganglia. The somas of motor neurons are found in the ventral portion of the gray matter of the spinal cord.
Candela Citations
- Biology 2e. Provided by: OpenStax. Located at: https://openstax.org/details/books/biology-2e. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/8d50a0af-948b-4204-a71d-4826cba765b8@8.19
- Unit 14: Nervous System (Module 54). Authored by: Open Learning Initiative. Provided by: Carnegie Mellon University. Located at: https://oli.cmu.edu/jcourse/workbook/activity/page?context=4348983980020ca6017b4e762b701630. Project: Anatomy & Physiology. License: CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike