Learning Outcomes
- Discuss the role of transcription factors in gene regulation
Like prokaryotic cells, the transcription of genes in eukaryotes requires the actions of an RNA polymerase to bind to a sequence upstream of a gene to initiate transcription. However, unlike prokaryotic cells, the eukaryotic RNA polymerase requires other proteins, or transcription factors, to facilitate transcription initiation. Transcription factors are proteins that bind to the promoter sequence and other regulatory sequences to control the transcription of the target gene. RNA polymerase by itself cannot initiate transcription in eukaryotic cells. Transcription factors must bind to the promoter region first and recruit RNA polymerase to the site for transcription to be established.
View the process of transcription—the making of RNA from a DNA template:
The Promoter and the Transcription Machinery
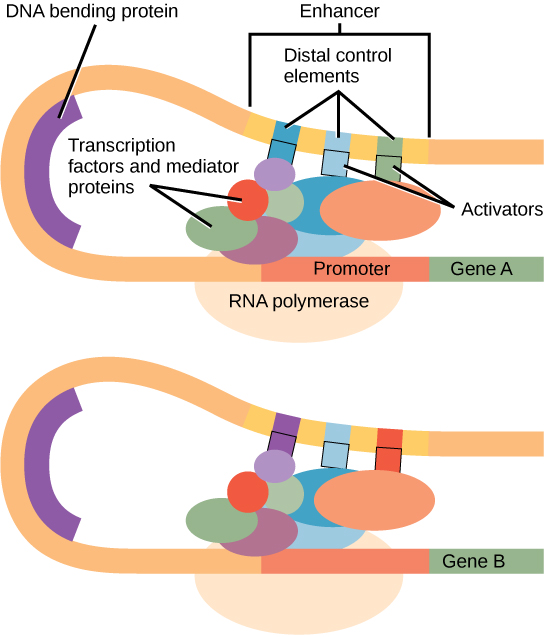
Figure 1. An enhancer is a DNA sequence that promotes transcription. Each enhancer is made up of short DNA sequences called distal control elements. Activators bound to the distal control elements interact with mediator proteins and transcription factors. Two different genes may have the same promoter but different distal control elements, enabling differential gene expression.
Genes are organized to make the control of gene expression easier. The promoter region is immediately upstream of the coding sequence. The purpose of the promoter is to bind transcription factors that control the initiation of transcription.
Enhancers and Transcription
In some eukaryotic genes, there are regions that help increase or enhance transcription. These regions, called enhancers, are not necessarily close to the genes they enhance. They can be located upstream of a gene, within the coding region of the gene, downstream of a gene, or may be thousands of nucleotides away. Enhancer regions are binding sequences, or sites, for transcription factors. When a DNA-bending protein binds, the shape of the DNA changes (Figure 1). This shape change allows for the interaction of the activators bound to the enhancers with the transcription factors bound to the promoter region and the RNA polymerase.
Turning Genes Off: Transcriptional Repressors
Like prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells also have mechanisms to prevent transcription. Transcriptional repressors can bind to promoter or enhancer regions and block transcription. Like the transcriptional activators, repressors respond to external stimuli to prevent the binding of activating transcription factors.
In Summary: Eukaryotic Transcription Gene Regulation
To start transcription, transcription factors, must first bind to the promoter and recruit RNA polymerase to that location. In addition to promoter sequences, enhancer regions help augment transcription. Enhancers can be upstream, downstream, within a gene itself, or on other chromosomes. Transcription factors bind to enhancer regions to increase or prevent transcription.
Practice Questions
The binding of ________ is required for transcription to start.
- a protein
- DNA polymerase
- RNA polymerase
- a transcription factor
What will result from the binding of a transcription factor to an enhancer region?
- decreased transcription of an adjacent gene
- increased transcription of a distant gene
- alteration of the translation of an adjacent gene
- initiation of the recruitment of RNA polymerase
A mutation within the promoter region can alter transcription of a gene. Describe how this can happen.
What could happen if a cell had too much of an activating transcription factor present?
Try It
Candela Citations
- Biology. Provided by: OpenStax CNX. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/185cbf87-c72e-48f5-b51e-f14f21b5eabd@10.8. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/185cbf87-c72e-48f5-b51e-f14f21b5eabd@10.8
