Developmental Research Designs
Sometimes, especially in developmental research, the researcher is interested in examining changes over time and will need to consider a research design that will capture these changes. Remember, research methods are tools that are used to collect information, while research design is the strategy or blueprint for deciding how to collect and analyze information. Research design dictates which methods are used and how. There are three types of developmental research designs: cross-sectional, longitudinal, and sequential.
Video 2.9.1. Developmental Research Design summarizes the benefits of challenges of the three developmental design models.
Cross-Sectional Designs
The majority of developmental studies use cross-sectional designs because they are less time-consuming and less expensive than other developmental designs. Cross-sectional research designs are used to examine behavior in participants of different ages who are tested at the same point in time. Let’s suppose that researchers are interested in the relationship between intelligence and aging. They might have a hypothesis that intelligence declines as people get older. The researchers might choose to give a particular intelligence test to individuals who are 20 years old, individuals who are 50 years old, and individuals who are 80 years old at the same time and compare the data from each age group. This research is cross-sectional in design because the researchers plan to examine the intelligence scores of individuals of different ages within the same study at the same time; they are taking a “cross-section” of people at one point in time. Let’s say that the comparisons find that the 80-year-old adults score lower on the intelligence test than the 50-year-old adults, and the 50-year-old adults score lower on the intelligence test than the 20-year-old adults. Based on these data, the researchers might conclude that individuals become less intelligent as they get older. Would that be a valid (accurate) interpretation of the results?

Figure 2.9.1. Example of cross-sectional research design
No, that would not be a valid conclusion because the researchers did not follow individuals as they aged from 20 to 50 to 80 years old. One of the primary limitations of cross-sectional research is that the results yield information about age differences not necessarily changes over time. That is, although the study described above can show that the 80-year-olds scored lower on the intelligence test than the 50-year-olds, and the 50-year-olds scored lower than the 20-year-olds, the data used for this conclusion were collected from different individuals (or groups). It could be, for instance, that when these 20-year-olds get older, they will still score just as high on the intelligence test as they did at age 20. Similarly, maybe the 80-year-olds would have scored relatively low on the intelligence test when they were young; the researchers don’t know for certain because they did not follow the same individuals as they got older.
With each cohort being members of a different generation, it is also possible that the differences found between the groups are not due to age, per se, but due to cohort effects. Differences between these cohorts’ IQ results could be due to differences in life experiences specific to their generation, such as differences in education, economic conditions, advances in technology, or changes in health and nutrition standards, and not due to age-related changes.
Another disadvantage of cross-sectional research is that it is limited to one time of measurement. Data are collected at one point in time, and it’s possible that something could have happened in that year in history that affected all of the participants, although possibly each cohort may have been affected differently.
Longitudinal Research Designs
 Longitudinal research involves beginning with a group of people who may be of the same age and background (cohort) and measuring them repeatedly over a long period of time. One of the benefits of this type of research is that people can be followed through time and be compared with themselves when they were younger; therefore, changes with age over time are measured. What would be the advantages and disadvantages of longitudinal research? Problems with this type of research include being expensive, taking a long time, and subjects dropping out over time.
Longitudinal research involves beginning with a group of people who may be of the same age and background (cohort) and measuring them repeatedly over a long period of time. One of the benefits of this type of research is that people can be followed through time and be compared with themselves when they were younger; therefore, changes with age over time are measured. What would be the advantages and disadvantages of longitudinal research? Problems with this type of research include being expensive, taking a long time, and subjects dropping out over time.
Longitudinal research designs are used to examine behavior in the same individuals over time. For instance, with our example of studying intelligence and aging, a researcher might conduct a longitudinal study to examine whether 20-year-olds become less intelligent with age over time. To this end, a researcher might give an intelligence test to individuals when they are 20 years old, again when they are 50 years old, and then again when they are 80 years old. This study is longitudinal in nature because the researcher plans to study the same individuals as they age. Based on these data, the pattern of intelligence and age might look different than from the cross-sectional research; it might be found that participants’ intelligence scores are higher at age 50 than at age 20 and then remain stable or decline a little by age 80. How can that be when cross-sectional research revealed declines in intelligence with age?
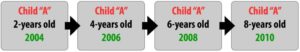
Figure 2.9.2. Example of a longitudinal research design
Since longitudinal research happens over a period of time (which could be short term, as in months, but is often longer, as in years), there is a risk of attrition. Attrition occurs when participants fail to complete all portions of a study. Participants may move, change their phone numbers, die, or simply become disinterested in participating over time. Researchers should account for the possibility of attrition by enrolling a larger sample into their study initially, as some participants will likely drop out over time. There is also something known as selective attrition—this means that certain groups of individuals may tend to drop out. It is often the least healthy, least educated, and lower socioeconomic participants who tend to drop out over time. That means that the remaining participants may no longer be representative of the whole population, as they are, in general, healthier, better educated, and have more money. This could be a factor in why our hypothetical research found a more optimistic picture of intelligence and aging as the years went by. What can researchers do about selective attrition? At each time of testing, they could randomly recruit more participants from the same cohort as the original members to replace those who have dropped out.
The results from longitudinal studies may also be impacted by repeated assessments. Consider how well you would do on a math test if you were given the exact same exam every day for a week. Your performance would likely improve over time, not necessarily because you developed better math abilities, but because you were continuously practicing the same math problems. This phenomenon is known as a practice effect. Practice effects occur when participants become better at a task over time because they have done it again and again (not due to natural psychological development). So our participants may have become familiar with the intelligence test each time (and with the computerized testing administration).
Another limitation of longitudinal research is that the data are limited to only one cohort. As an example, think about how comfortable the participants in the 2010 cohort of 20-year-olds are with computers. Since only one cohort is being studied, there is no way to know if findings would be different from other cohorts. In addition, changes that are found as individuals age over time could be due to age or to time of measurement effects. That is, the participants are tested at different periods in history, so the variables of age and time of measurement could be confounded (mixed up). For example, what if there is a major shift in workplace training and education between 2020 and 2040, and many of the participants experience a lot more formal education in adulthood, which positively impacts their intelligence scores in 2040? Researchers wouldn’t know if the intelligence scores increased due to growing older or due to a more educated workforce over time between measurements.
Sequential Research Designs
Sequential research designs include elements of both longitudinal and cross-sectional research designs. Similar to longitudinal designs, sequential research features participants who are followed over time; similar to cross-sectional designs, sequential research includes participants of different ages. This research design is also distinct from those that have been discussed previously in that individuals of different ages are enrolled into a study at various points in time to examine age-related changes, development within the same individuals as they age, and to account for the possibility of cohort and/or time of measurement effects
Consider, once again, our example of intelligence and aging. In a study with a sequential design, a researcher might recruit three separate groups of participants (Groups A, B, and C). Group A would be recruited when they are 20 years old in 2010 and would be tested again when they are 50 and 80 years old in 2040 and 2070, respectively (similar in design to the longitudinal study described previously). Group B would be recruited when they are 20 years old in 2040 and would be tested again when they are 50 years old in 2070. Group C would be recruited when they are 20 years old in 2070, and so on.
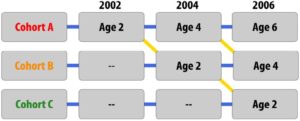
Figure 2.9.3. Example of sequential research design
Studies with sequential designs are powerful because they allow for both longitudinal and cross-sectional comparisons—changes and/or stability with age over time can be measured and compared with differences between age and cohort groups. This research design also allows for the examination of cohort and time of measurement effects. For example, the researcher could examine the intelligence scores of 20-year-olds at different times in history and different cohorts (follow the yellow diagonal lines in figure 3). This might be examined by researchers who are interested in sociocultural and historical changes (because we know that lifespan development is multidisciplinary). One way of looking at the usefulness of the various developmental research designs was described by Schaie and Baltes (1975): cross-sectional and longitudinal designs might reveal change patterns while sequential designs might identify developmental origins for the observed change patterns.
Since they include elements of longitudinal and cross-sectional designs, sequential research has many of the same strengths and limitations as these other approaches. For example, sequential work may require less time and effort than longitudinal research (if data are collected more frequently than over the 30-year spans in our example) but more time and effort than cross-sectional research. Although practice effects may be an issue if participants are asked to complete the same tasks or assessments over time, attrition may be less problematic than what is commonly experienced in longitudinal research since participants may not have to remain involved in the study for such a long period of time.
Comparing Developmental Research Designs
When considering the best research design to use in their research, scientists think about their main research question and the best way to come up with an answer. A table of advantages and disadvantages for each of the described research designs is provided here to help you as you consider what sorts of studies would be best conducted using each of these different approaches.
Table 2.9.1. Advantages and disadvantages of different research designs
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
| Cross-Sectional |
|
|
| Longitudinal |
|
|
| Sequential |
|
|
Candela Citations
- Developmental Research Design. Authored by: Nicole Arduini-Van Hoose. Provided by: Hudson Valley Community College. Located at: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/adolescent/chapter/developmental-research-design/. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike
- Developmental Research Design. Authored by: Margaret Clark-Plaskie . Provided by: Lumen Learning. Located at: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/wm-lifespandevelopment/chapter/developmental-research-designs/. License: CC BY-NC-SA: Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike
