Identify membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells
Have you ever heard the phrase “form follows function?” It’s a philosophy practiced in many industries. In architecture, this means that buildings should be constructed to support the activities that will be carried out inside them. For example, a skyscraper should be built with several elevator banks; a hospital should be built so that its emergency room is easily accessible.
Our natural world originated the principle of form following function, especially in cell biology, and this will become clear as we explore eukaryotic cells. Unlike prokaryotic cells, eukaryotic cells have: (1) a membrane-bound nucleus; (2) numerous membrane-bound organelles—such as the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, chloroplasts, mitochondria, and others; and (3) several, rod-shaped chromosomes. Because a eukaryotic cell’s nucleus is surrounded by a membrane, it is often said to have a “true nucleus.” The word “organelle” means “little organ,” and, as already mentioned, organelles have specialized cellular functions, just as the organs of your body have specialized functions.
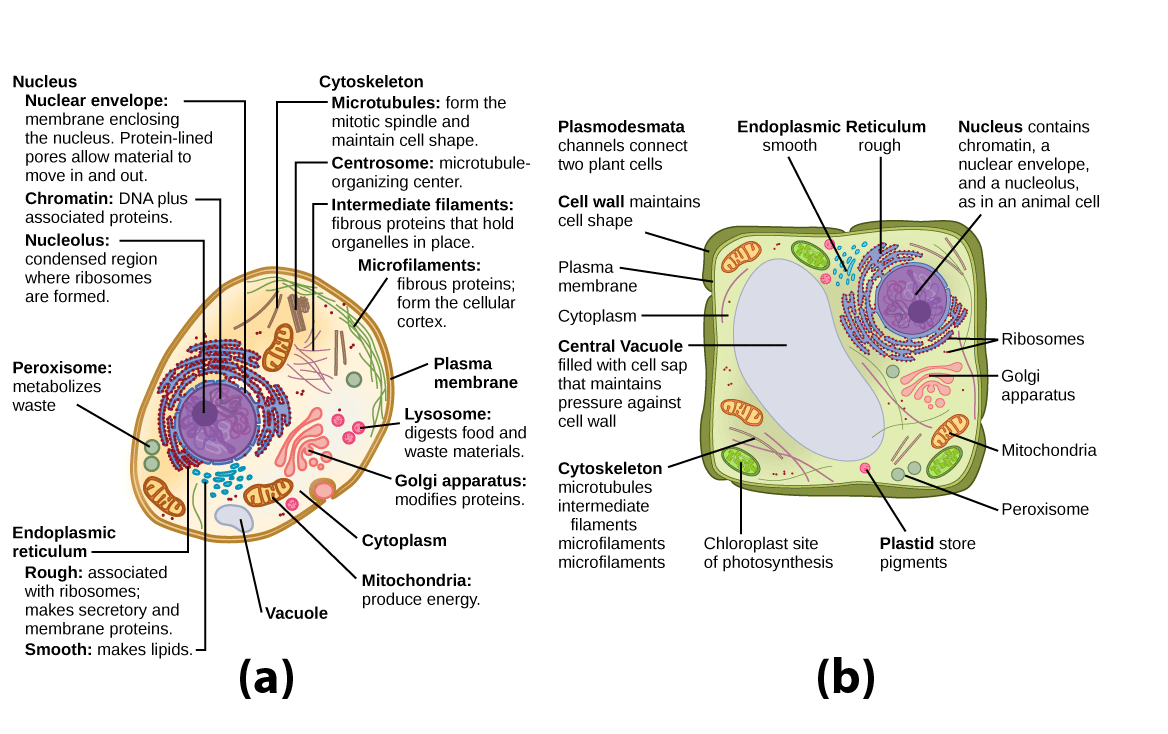
Figure 1. These figures show the major organelles and other cell components of (a) a typical animal cell and (b) a typical eukaryotic plant cell. The plant cell has a cell wall, chloroplasts, plastids, and a central vacuole—structures not found in animal cells. Plant cells do not have lysosomes or centrosomes.
What You’ll Learn to Do
- Describe the basic composition of cytoplasm
- Describe the structure and function of the nucleus and nuclear membrane
- Describe the structure and function of ribosomes
- Describe the structure and function of mitochondria
- Describe the structure and function of peroxisomes
- Describe the structure, function, and components of the endomembrane system
- Describe the structure and functions of vesicles
- Identify key organelles present only in animal cells, including centrosomes and lysosomes
- Identify key organelles present only in plant cells, including chloroplasts and vaculoles
Learning Activities
The learning activities for this section include the following:
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus
- Ribosomes, Mitochondria, and Peroxisomes
- Endomembrane System
- Vesicles
- Unique Features of Animal and Plant Cells
- Self Check: Organelles
Candela Citations
- Revision, adaptation, and original content. Authored by: Shelli Carter and Lumen Learning. Provided by: Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution
- Biology 2e. Provided by: OpenStax. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/185cbf87-c72e-48f5-b51e-f14f21b5eabd@10.8. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/biology-2e/pages/1-introduction
