Learning Outcomes
- Define the different layers of protein structure
As discussed earlier, the shape of a protein is critical to its function. For example, an enzyme can bind to a specific substrate at a site known as the active site. If this active site is altered because of local changes or changes in overall protein structure, the enzyme may be unable to bind to the substrate. To understand how the protein gets its final shape or conformation, we need to understand the four levels of protein structure: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary.
Primary Structure
The unique sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide chain is its primary structure. For example, the pancreatic hormone insulin has two polypeptide chains, A and B, and they are linked together by disulfide bonds. The N terminal amino acid of the A chain is glycine, whereas the C terminal amino acid is asparagine (Figure 1). The sequences of amino acids in the A and B chains are unique to insulin.
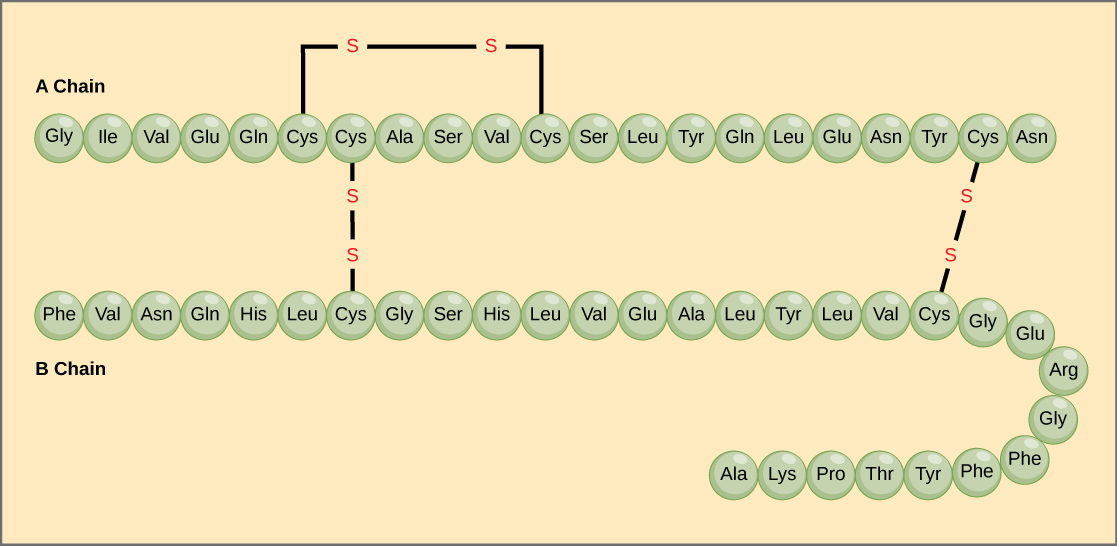
Figure 1. Bovine serum insulin is a protein hormone made of two peptide chains, A (21 amino acids long) and B (30 amino acids long). In each chain, primary structure is indicated by three-letter abbreviations that represent the names of the amino acids in the order they are present. The amino acid cysteine (cys) has a sulfhydryl (SH) group as a side chain. Two sulfhydryl groups can react in the presence of oxygen to form a disulfide (S-S) bond. Two disulfide bonds connect the A and B chains together, and a third helps the A chain fold into the correct shape. Note that all disulfide bonds are the same length, but are drawn different sizes for clarity.
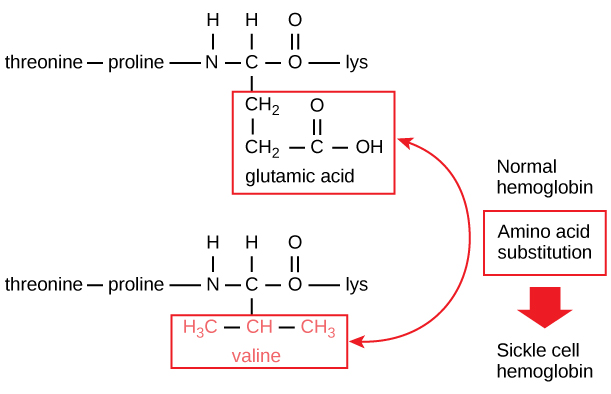
Figure 2. The beta chain of hemoglobin is 147 residues in length, yet a single amino acid substitution leads to sickle cell anemia. In normal hemoglobin, the amino acid at position seven is glutamate. In sickle cell hemoglobin, this glutamate is replaced by a valine.
The unique sequence for every protein is ultimately determined by the gene encoding the protein. A change in nucleotide sequence of the gene’s coding region may lead to a different amino acid being added to the growing polypeptide chain, causing a change in protein structure and function. In sickle cell anemia, the hemoglobin β chain (a small portion of which is shown in Figure 2) has a single amino acid substitution, causing a change in protein structure and function.
Specifically, the amino acid glutamic acid is substituted by valine in the β chain. What is most remarkable to consider is that a hemoglobin molecule is made up of two alpha chains and two beta chains that each consist of about 150 amino acids. The molecule, therefore, has about 600 amino acids. The structural difference between a normal hemoglobin molecule and a sickle cell molecule—which dramatically decreases life expectancy—is a single amino acid of the 600. What is even more remarkable is that those 600 amino acids are encoded by three nucleotides each, and the mutation is caused by a single base change (point mutation), 1 in 1800 bases.
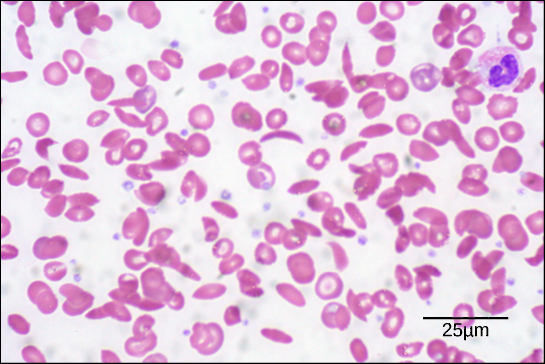
Figure 3. In this blood smear, visualized at 535x magnification using bright field microscopy, sickle cells are crescent shaped, while normal cells are disc-shaped. (credit: modification of work by Ed Uthman; scale-bar data from Matt Russell)
Because of this change of one amino acid in the chain, hemoglobin molecules form long fibers that distort the biconcave, or disc-shaped, red blood cells and assume a crescent or “sickle” shape, which clogs arteries (Figure 3). This can lead to myriad serious health problems such as breathlessness, dizziness, headaches, and abdominal pain for those affected by this disease.
Secondary Structure
The local folding of the polypeptide in some regions gives rise to the secondary structure of the protein. The most common are the α-helix and β-pleated sheet structures (Figure 4). Both structures are the α-helix structure—the helix held in shape by hydrogen bonds. The hydrogen bonds form between the oxygen atom in the carbonyl group in one amino acid and another amino acid that is four amino acids farther along the chain.
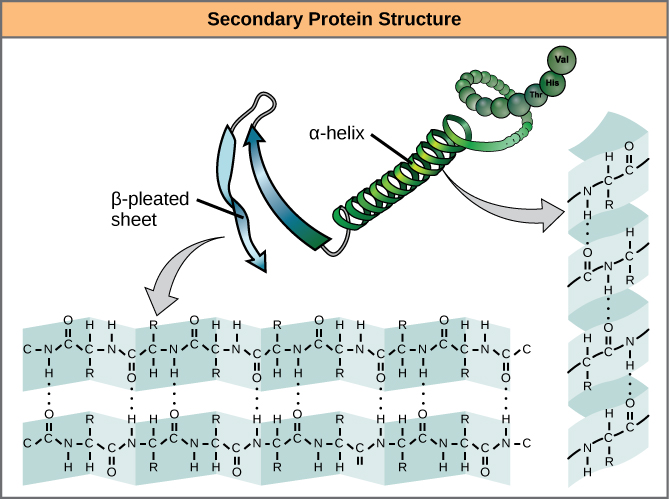
Figure 4. The α-helix and β-pleated sheet are secondary structures of proteins that form because of hydrogen bonding between carbonyl and amino groups in the peptide backbone. Certain amino acids have a propensity to form an α-helix, while others have a propensity to form a β-pleated sheet.
Every helical turn in an alpha helix has 3.6 amino acid residues. The R groups (the variant groups) of the polypeptide protrude out from the α-helix chain. In the β-pleated sheet, the “pleats” are formed by hydrogen bonding between atoms on the backbone of the polypeptide chain. The R groups are attached to the carbons and extend above and below the folds of the pleat. The pleated segments align parallel or antiparallel to each other, and hydrogen bonds form between the partially positive nitrogen atom in the amino group and the partially negative oxygen atom in the carbonyl group of the peptide backbone. The α-helix and β-pleated sheet structures are found in most globular and fibrous proteins and they play an important structural role.
Tertiary Structure
The unique three-dimensional structure of a polypeptide is its tertiary structure (Figure 5). This structure is in part due to chemical interactions at work on the polypeptide chain. Primarily, the interactions among R groups creates the complex three-dimensional tertiary structure of a protein. The nature of the R groups found in the amino acids involved can counteract the formation of the hydrogen bonds described for standard secondary structures. For example, R groups with like charges are repelled by each other and those with unlike charges are attracted to each other (ionic bonds). When protein folding takes place, the hydrophobic R groups of nonpolar amino acids lay in the interior of the protein, whereas the hydrophilic R groups lay on the outside. The former types of interactions are also known as hydrophobic interactions. Interaction between cysteine side chains forms disulfide linkages in the presence of oxygen, the only covalent bond forming during protein folding.
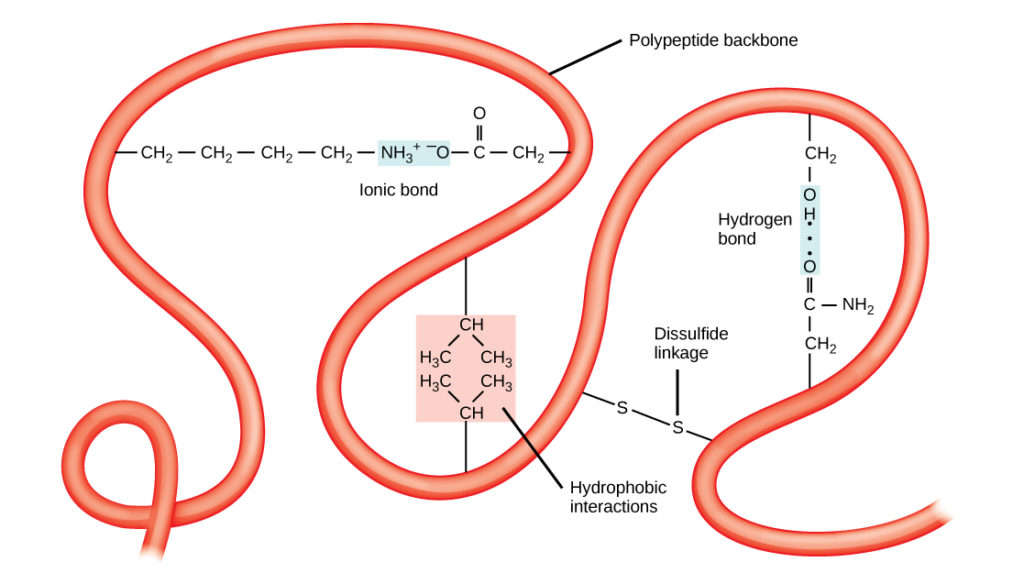
Figure 5. The tertiary structure of proteins is determined by a variety of chemical interactions. These include hydrophobic interactions, ionic bonding, hydrogen bonding and disulfide linkages.
All of these interactions, weak and strong, determine the final three-dimensional shape of the protein. When a protein loses its three-dimensional shape, it may no longer be functional.
Quaternary Structure
In nature, some proteins are formed from several polypeptides, also known as subunits, and the interaction of these subunits forms the quaternary structure. Weak interactions between the subunits help to stabilize the overall structure. For example, insulin (a globular protein) has a combination of hydrogen bonds and disulfide bonds that cause it to be mostly clumped into a ball shape. Insulin starts out as a single polypeptide and loses some internal sequences in the presence of post-translational modification after the formation of the disulfide linkages that hold the remaining chains together. Silk (a fibrous protein), however, has a β-pleated sheet structure that is the result of hydrogen bonding between different chains.
The four levels of protein structure (primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary) are illustrated in Figure 6.
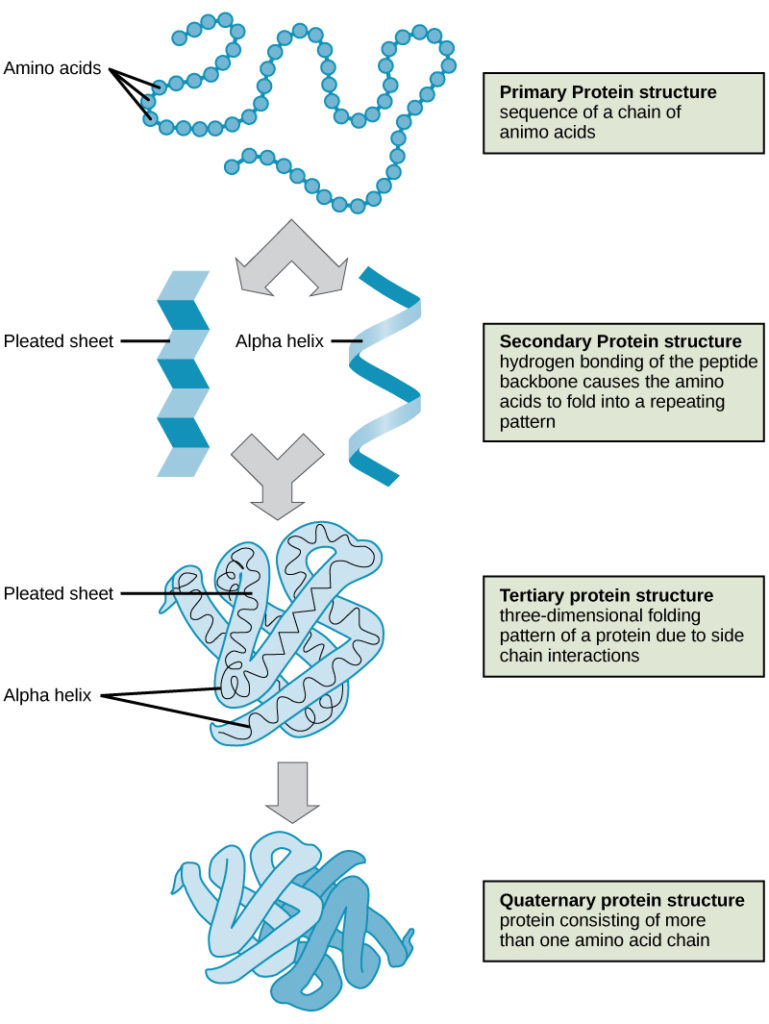
Figure 6. The four levels of protein structure can be observed in these illustrations. (credit: modification of work by National Human Genome Research Institute)
Denaturation and Protein Folding
Each protein has its own unique sequence and shape that are held together by chemical interactions. If the protein is subject to changes in temperature, pH, or exposure to chemicals, the protein structure may change, losing its shape without losing its primary sequence in what is known as denaturation. Denaturation is often reversible because the primary structure of the polypeptide is conserved in the process if the denaturing agent is removed, allowing the protein to resume its function. Sometimes denaturation is irreversible, leading to loss of function. One example of irreversible protein denaturation is when an egg is fried. The albumin protein in the liquid egg white is denatured when placed in a hot pan. Not all proteins are denatured at high temperatures; for instance, bacteria that survive in hot springs have proteins that function at temperatures close to boiling. The stomach is also very acidic, has a low pH, and denatures proteins as part of the digestion process; however, the digestive enzymes of the stomach retain their activity under these conditions.
Protein folding is critical to its function. It was originally thought that the proteins themselves were responsible for the folding process. Only recently was it found that often they receive assistance in the folding process from protein helpers known as chaperones (or chaperonins) that associate with the target protein during the folding process. They act by preventing aggregation of polypeptides that make up the complete protein structure, and they disassociate from the protein once the target protein is folded.
Try It
Candela Citations
- Biology 2e. Provided by: OpenStax. Located at: http://cnx.org/contents/185cbf87-c72e-48f5-b51e-f14f21b5eabd@10.8. License: CC BY: Attribution. License Terms: Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/biology-2e/pages/1-introduction
